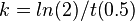|
|
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | [[Welcome to the In-Silico Model of Cutaneous Lipids Wiki | Return to overview]] | | [[Welcome to the In-Silico Model of Cutaneous Lipids Wiki | Return to overview]] |
| | | | |
| − | Upon being transported out of the cell, the eicosanoids accumulate in the interstitial fluid, which for simplicity is referred to as the extracellular compartment in the model. A decay constant was included for each extracellular metabolite to represent degradation. To describe the breaking down of metabolites an irreversible mass action rate law was used for reactions 43-64. The half life of each eicosanoid was initially assumed as 24 hours, but will be made metabolite specific when all of the values have been collected.
| + | To account for the decay in metabolite concentration over time, there are 46 decay reactions in this network. In these reactions, the product mass is pooled together under the term “Miscellaneous metabolites”. This is a collective term which refers to metabolites which are no longer of interest to this work, for example they are exported to the systemic circulation or undergo degradation. To account for the different rate of metabolite decay in the intracellular and extracellular compartments, each metabolite has two decay reactions which are governed by independent parameters. |
| | | | |
| − | Pseudo-first order reactions.
| + | To calculate the rate constant, the following equation was used: |
| | <math> k = ln(2)/t(0.5) </math> | | <math> k = ln(2)/t(0.5) </math> |
| | | | |
| | {|width ="80%" | | {|width ="80%" |
| | | | | | |
| − | * [[Decay of PGF2a/exPGF2a |Decay of PGF2a/exPGF2a ]] | + | * [[Decay of AA to exAA|Decay of AA/exAA (R64/72) ]] |
| − | * [[Decay of TXB2/exTXB2 |Decay of TXB2/exTXB2]] | + | * [[Decay of PGI2 to exPGI2 |Decay of PGI<sub>2</sub>/exPGI<sub>2</sub> (R48/77) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of K6PGF2a to exK6PGF2a |Transformation of K6PGF2a to exK6PGF2a ]] | + | * [[Decay of PGE2 to exPGE2 |Decay of PGE<sub>2</sub>/exPGE<sub>2</sub> (R49/76) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of PGE2 to exPGE2 |Transformation of PGE2 to exPGE2]] | + | * [[Decay of PGF2a/exPGF2a |Decay of PGF<sub>2a</sub>/exPGF<sub>2a</sub> (R44/74) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of D15PGJ2 to exD15PGJ2 |Transformation of D15PGJ2 to exD15PGJ2 ]] | + | * [[Decay of PGH2 to exPGH2 |Decay of PGH<sub>2</sub>/exPGH<sub>2</sub> (R53/73) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of 5-Oxo-ETE to ex5-Oxo-ETE |Transformation of 5-Oxo-ETE to ex5-Oxo-ETE]] | + | * [[Decay of PGD2 to exPGD2 |Decay of PGD<sub>2</sub>/exPGD<sub>2</sub> (R52/78) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of 15-HETE to ex15-HETE |Transformation of 15-HETE to ex15-HETE]] | + | * [[Decay of PGJ2 to exPGJ2 |Decay of PGJ<sub>2</sub>/exPGJ<sub>2</sub> (R51/83) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of LTB4 to exLTB4 |Transformation of LTB4 to exLTB4]] | + | * [[Decay of TXB2/exTXB2 |Decay of TXB<sub>2</sub>/exTXB<sub>2</sub> (R45/81) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of LTC4 to exLTC4 |Transformation of LTC4 to exLTC4]] | + | * [[Decay of TXA2 to exTXA2 |Decay of TXA<sub>2</sub>/exTXA<sub>2</sub> (R46/75) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of 12-HETE to ex12-HETE |Transformation of 12-HETE to ex12-HETE]] | + | * [[Decay of K6PGF2a to exK6PGF2a |Decay of 6-keto-PGF<sub>1a</sub>/ex6-keto-PGF<sub>1a</sub> (R47/82)]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of TXA2 to exTXA2 |Transformation of TXA2 to exTXA2]] | + | * [[Decay of D15PGJ2 to exD15PGJ2 |Decay of 15-deoxy-PGJ<sub>2</sub>/ex15-deoxy-PGJ<sub>2</sub> (R50/84) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of PGI2 to exPGI2 |Transformation of PGI2 to exPGI2]] | + | * [[Decay of 15-Keto-PGE2 to ex15-Keto-PGE2 |Decay of 15-keto-PGE<sub>2</sub>/ex15-keto-PGE<sub>2</sub> (R68/79)]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of PGH2 to exPGH2 |Transformation of PGH2 to exPGH2 ]] | + | * [[Decay of 3,4-Dihydro-15-Keto-PGE2 to ex3,4-Dihydro-15-Keto-PGE2 |Decay of 13,14-dihydro-15-keto-PGE<sub>2</sub>/ex13,14-dihydro-15-keto-PGE<sub>2</sub> (R71/80)]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of PGD2 to exPGD2 |Transformation of PGD2 to exPGD2]] | + | * [[Decay of 5-Oxo-ETE to ex5-Oxo-ETE |Decay of 5-oxo-ETE/ex5-oxo-ETE (R54/91) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of PGJ2 to exPGJ2 |Transformation of PGJ2 to exPGJ2]] | + | * [[Decay of LTB4 to exLTB4 |Decay of LTB<sub>4</sub>/exLTB<sub>4</sub> (R56/93) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of 12-HPETE to ex12-HPETE |Transformation of 12-HPETE to ex12-HPETE ]] | + | * [[Decay of LTC4 to exLTC4 |Decay of LTC<sub>4</sub>/exLTC<sub>4</sub> (R57/94) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of 15-HPETE to ex15-HPETE |Transformation of 15-HPETE to ex15-HPETE ]] | + | * [[Decay of LTA4 to exLTA4 |Decay of LTA<sub>4</sub>/exLTA<sub>4</sub> (R58/92) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of 5-HPETE to ex5-HPETE |Transformation of 5-HPETE to ex5-HPETE ]] | + | * [[Decay of 12-HPETE to ex12-HPETE |Decay of 12-HPETE/ex12-HPETE (R63/86) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of 5-HETE to ex5-HETE |Transformation of 5-HETE to ex5-HETE ]] | + | * [[Decay of 15-HPETE to ex15-HPETE |Decay of 15-HPETE/ex15-HPETE (R61/85)]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of LTA4 to exLTA4 |Transformation of LTA4 to exLTA4 ]] | + | * [[Decay of 5-HPETE to ex5-HPETE |Decay of 5-HPETE/ex5-HPETE (R59/87) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of AA to exAA|Transformation of AA to exAA ]]
| + | * [[Decay of 5-HETE to ex5-HETE |Decay of 5-HETE/ex5-HETE (R55/90) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of 15-Keto-PGE2 to ex15-Keto-PGE2 |Transformation of 15-Keto-PGE2 to ex15-Keto-PGE2 ]]
| + | * [[Decay of 15-HETE to ex15-HETE |Decay of 15-HETE/ex15-HETE (R60/88) ]] |
| − | * [[Transformation of 3,4-Dihydro-15-Keto-PGE2 to ex3,4-Dihydro-15-Keto-PGE2 |Transformation of 3,4-Dihydro-15-Keto-PGE2 to ex3,4-Dihydro-15-Keto-PGE2 ]] | + | * [[Decay of 12-HETE to ex12-HETE |Decay of 12-HETE/ex12-HETE (R62/89) ]] |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable"
| |
| − | ! style="text-align: center; font-weight: bold;" | Reaction #
| |
| − | ! style="text-align: center; font-weight: bold;" | Species
| |
| − | ! style="text-align: center; font-weight: bold;" | Half Life (min)
| |
| − | ! style="text-align: center; font-weight: bold;" | Rate constant(min -1)
| |
| − | ! style="text-align: center; font-weight: bold;" | Notes
| |
| − | ! style="text-align: center; font-weight: bold;" | Reference
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 44
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | exPGF2a
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 900 ± 492
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.001 ± 0.001
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |Study performed in decidual stromal cells and macrophages in culture.
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | <ref name="Ishihara1991”>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1789996 O. Ishihara, "Differences of metabolism of prostaglandin E2 and F2 alpha by decidual stromal cells and macrophages in culture." Eicosanoids. 1991;4(4):203-7.]</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 45
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | exTXB2
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 20 to 30
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.035 to 0.023
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |Quoted in a textbook(https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=_9kEeTjyJdMC&pg=PA864&lpg=PA864&dq=half+life+txa2&source=bl&ots=2OTF4Mh2Jk&sig=hu79GprliUcW4QE_Zm79islesOA&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwj0oo2sgfjOAhXLIcAKHcaPDHQQ6AEIRjAI#v=onepage&q=half%20life%20txa2&f=false) with no ref.
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 46
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | exTXA2
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.333
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 2.079
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |Quoted in a textbook(https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=_9kEeTjyJdMC&pg=PA864&lpg=PA864&dq=half+life+txa2&source=bl&ots=2OTF4Mh2Jk&sig=hu79GprliUcW4QE_Zm79islesOA&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwj0oo2sgfjOAhXLIcAKHcaPDHQQ6AEIRjAI#v=onepage&q=half%20life%20txa2&f=false) with no ref.
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 47
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | ex6-KETO-PGF1A
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 30
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.0231
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | Human Plasma
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | <ref name="Ylikorkala1981”>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7025068 Ylikorkala, "Measurement of 6-keto-prostaglandin E1 alpha in human plasma with radioimmunoassay: effect of prostacyclin infusion." Prostaglandins Med. 1981 Apr;6(4):427-36.]</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 48
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | exPGI2
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 3
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.231
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |<ref name="Cawello1994”>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8070511 Cawello W., "Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of prostaglandin E1 administered by intravenous infusion in human subjects." Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1994;46(3):275-7.]</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 49
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | exPGE2
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 528 ± 204
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.001 ± 0.003
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | Study performed in decidual stromal cells and macrophages in culture.
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | <ref name="Ishihara1991”>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1789996 O. Ishihara, "Differences of metabolism of prostaglandin E2 and F2 alpha by decidual stromal cells and macrophages in culture." Eicosanoids. 1991;4(4):203-7.]</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 50
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | ex15-DEOXY-PGJ2
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 720
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.001
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | Dehydration of PGD2 to ultimatley 15d-PGJ2 occurs with a half life of about 12 hours in the presense of albumin (protien found in blood).
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | <ref name="Fitzpatrick1983”>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6578214 F. Fitzpatrick, "Albumin-catalyzed metabolism of prostaglandin D2. Identification of products formed in vitro." J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11713-8.]</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 51
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | exPGJ2
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | rowspan="2" style="text-align: center;" | 52
| |
| − | | rowspan="2" style="text-align: center;" | exPGD2
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 1.5 - 1.6
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.462 to 0.433
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | Human brain
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | <ref name="Suzuki1986”>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3465420 Suzuki F. "Transport of prostaglandin D2 into brain." Brain Res. 1986 Oct 22;385(2):321-8.]</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 30
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.023
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | Human plasma
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | <ref name="Schuligoi2007”>[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006295207001918?via%3Dihub R. Schuligoi. "PGD2 metabolism in plasma: Kinetics and relationship with bioactivity on DP1 and CRTH2 receptors" Biochemical Pharmacology, Volume 74, Issue 1, 30 June 2007, Pages 107-117]</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 53
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | exPGH2
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 5
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.139
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | Quoted on supplier page (http://www.enzolifesciences.com/BML-PH002/prostaglandin-h2/)
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 54
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | ex5-OXO-ETE
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 11
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.064
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | Study half life of 15-OXO-ETE in in R15L Cells
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | <ref name="Cong2009”>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2730384/ Cong W., "15-oxo-Eicosatetraenoic Acid, a Metabolite of Macrophage 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin Dehydrogenase That Inhibits Endothelial Cell Proliferation" Mol Pharmacol. 2009 Sep; 76(3): 516–525.]</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 55
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | ex5-HETE
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 56
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | exLTB4
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.47 ± 0.02 to 0.63 ± 0.04
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 1.475 ± 34.657 to 1.100 ± 17.329
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | Rabbit, Immunoreactive LTB4
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | <ref name="Marleau1994”>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8075884 Marleau S., "Metabolic disposition of leukotriene B4 (LTB4) and oxidation-resistant analogues of LTB4 in conscious rabbits." Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jun;112(2):654-8.]</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 57
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | exLTC4
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 58
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | exLTA4
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.05
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 13.863
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 37 degrees C
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | <ref name="Zimmer2004”>[http://www.jlr.org/content/45/11/2138.long Zimmer J., "Fatty acid binding proteins stabilize leukotriene A4 competition with arachidonic acid but not other lipoxygenase products" November 2004 The Journal of Lipid Research, 45, 2138-2144.]</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 59
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | ex5-HPETE
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 60
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | ex15-HETE
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 21
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.0331
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | Study in R15L Cells
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | <ref name="Cong2009”>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2730384/ Cong W., "15-oxo-Eicosatetraenoic Acid, a Metabolite of Macrophage 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin Dehydrogenase That Inhibits Endothelial Cell Proliferation" Mol Pharmacol. 2009 Sep; 76(3): 516–525.]</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 61
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | ex15-HPETE
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 62
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | ex12-HETE
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 180
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.004
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | "During the first 2 min., the half-life of 12-HETE was 0.9 s, which implies
| |
| − | a fast clearance of the compound from the circulation. However, during
| |
| − | the subsequent half-hour the estimated half-life was 3 min. and increased
| |
| − | dramatically at the interval of time from 30 to 60 min. (t1/2 around 3 h)."
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |<ref name="Dadaian1998”>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9661215 Dadaian M., "12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid is a long-lived substance in the rabbit circulation." Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 1998 Jan;55(1):3-25.]</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 63
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | ex12-HPETE
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.5
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 1.386
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | <ref name="Maclouf1982”>[http://www.pnas.org/content/79/19/6042.abstract J. Maclouf, "Stimulation of leukotriene biosynthesis in human blood leukocytes by platelet-derived 12-hydroperoxy-icosatetraenoic acid" (1982) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 79, 6042-6046 ]</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 64
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | exAA
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 240 to 660
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | 0.003 to 0.001
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: center;" |<ref name="Vinge1985”>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3921386 Vinge E., "Arachidonic acid-induced platelet aggregation and prostanoid formation in whole blood in relation to plasma concentration of indomethacin." Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1985;28(2):163-9.]</ref>
| |
| − | |}
| |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | == References == | | == References == |
| | <references/> | | <references/> |