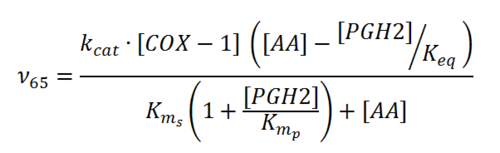Difference between revisions of "Transformation of AA to PGH2 (COX-1)"
(Created page with " Return to overview The COX enzyme possesses two isoforms, COX-1 and COX-2, of which both produce bioactive eicos...") |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Rate equation == | == Rate equation == | ||
** | ** | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:R65.PNG|center|500px]] |
== Enzyme Parameters == | == Enzyme Parameters == | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
|<ref name="Silva2003”>[http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00214-003-0476-9 P. Silva, "A theoretical study of radical-only and combined radical/carbocationic mechanisms of arachidonic acid cyclooxygenation by prostaglandin H synthase" Theor Chem Acc (2003) 110: 345]</ref> | |<ref name="Silva2003”>[http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00214-003-0476-9 P. Silva, "A theoretical study of radical-only and combined radical/carbocationic mechanisms of arachidonic acid cyclooxygenation by prostaglandin H synthase" Theor Chem Acc (2003) 110: 345]</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 50: | Line 49: | ||
|} | |} | ||
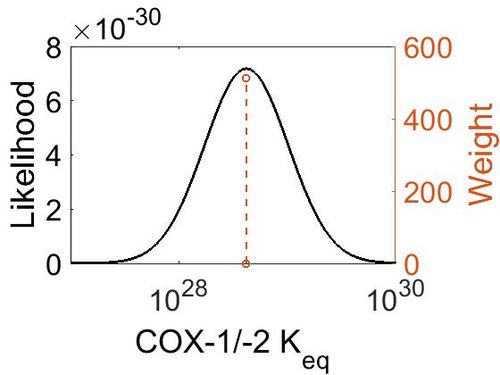
| − | + | [[Image:72.jpg|none|thumb|500px|The estimated probability distribution for COX-1 Keq. The value and weight of the literature values used to define the distribution are indicated by an orange dashed line. The x axis is plotted on a log-scale. ]] | |
| − | [[Image: | ||
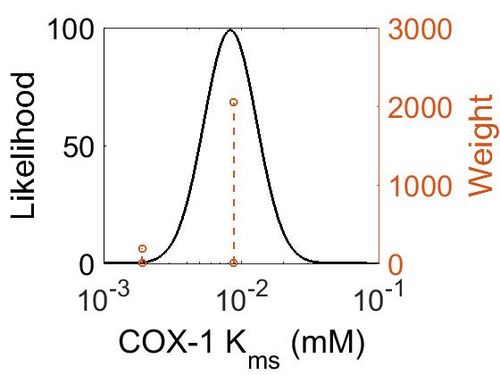
=== K<sub>ms<\sub> === | === K<sub>ms<\sub> === | ||
| Line 81: | Line 79: | ||
|<ref name="Mukherjee2007"> [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bi602502jA. Mukherjee ''Molecular Oxygen Dependent Steps in Fatty Acid Oxidation by Cyclooxygenase-1'' Biochemistry, 2007, 46 (13), pp 3975–3989]</ref> | |<ref name="Mukherjee2007"> [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bi602502jA. Mukherjee ''Molecular Oxygen Dependent Steps in Fatty Acid Oxidation by Cyclooxygenase-1'' Biochemistry, 2007, 46 (13), pp 3975–3989]</ref> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:69.jpg|none|thumb|500px|The estimated probability distribution for COX-2 Kms. The value and weight of the literature values used to define the distribution are indicated by an orange dashed line. The x axis is plotted on a log-scale. ]] | ||
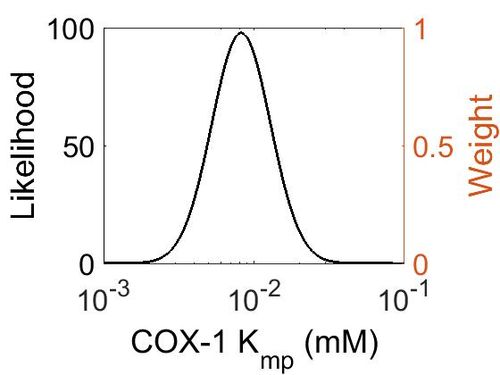
=== K<sub>mp<\sub> === | === K<sub>mp<\sub> === | ||
| + | [[Image:70.jpg|none|thumb|500px|The estimated probability distribution for COX-2 Kms. The value and weight of the literature values used to define the distribution are indicated by an orange dashed line. The x axis is plotted on a log-scale. ]] | ||
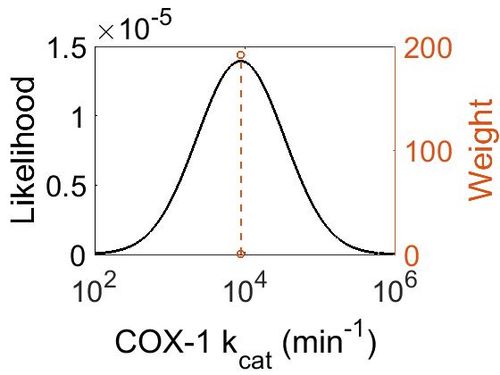
=== k<sub>cat<\sub> === | === k<sub>cat<\sub> === | ||
| Line 107: | Line 109: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:71.jpg|none|thumb|500px|The estimated probability distribution for COX-1 Kmp. The value and weight of the literature values used to define the distribution are indicated by an orange dashed line. The x axis is plotted on a log-scale. ]] | ||
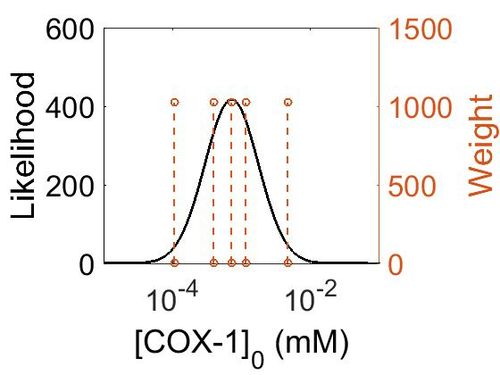
=== Enzyme concentration === | === Enzyme concentration === | ||
| Line 177: | Line 181: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:154.jpg|none|thumb|500px|The estimated probability distribution for COX-1 concentration. The value and weight of the literature values used to define the distribution are indicated by an orange dashed line. The x axis is plotted on a log-scale. ]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 15:16, 14 May 2019
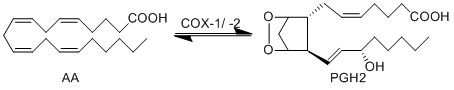
The COX enzyme possesses two isoforms, COX-1 and COX-2, of which both produce bioactive eicosanoids. The two isoforms have nearly identical active site residues (Simmons et al. 2004), but COX-1 is a constitutive enzyme, whereas COX-2 is an inducible enzyme. Both enzymes add molecular oxygen to arachidonic acid, generating an endoperoxide species, PGH2, by catalysing the two-step reaction of cycloooxygenation and oxygenation, followed by a hydroperoxide reduction.
PGH2 possesses a short life time due to the formation of a reactive functional group. The endoperoxide undergoes rapid isomerisation reactions, catalysed by a series of synthase enzymes (PGES, PGDS, PGIS, PGFS and TXAS). The resultant species of the isomerisation reactions are PGs (PGE2, PGD2, PGJ2, deoxy-PGJ2 and PGF2α), TXs (TXA2 and TXB2) and prostacyclin (PGI2), all of which have varying effects on the immune system.
Contents
Reaction
Chemical equation
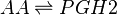
Rate equation
Enzyme Parameters
=== Keq<\sub>
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (-30) | kcal/mol | Unspecified | Calculations with a Gaussian98 suite of programs
Enzyme: COX (Unspecific) Substrate: Arachidonate Temperature: 298.15 K Pressure: 1 bar |
[1] |
| Mode | Confidence Interval | Location parameter (µ) | Scale parameter (σ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.18E+28 | 1.00E+01 | 6.67E+01 | 8.90E-01 |
Kms<\sub>
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0088 ± 0.0022 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Human
Enzyme: Cyclooxygenase-1 pH: 7.6 - 8.4 Temperature: 37 °C |
[2] |
| 0.0019 ± 0.0002 | 
|
Ram | Expression Vector: Ram
Enzyme: Cyclooxygenase-1 pH: 8 Temperature: 30 ± 0.2 °C |
[3] |
Kmp<\sub>
kcat<\sub>
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8820 ± 360 | 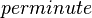
|
Ram | Expression Vector: Ram
Enzyme: Cyclooxygenase-1 pH: 8 Temperature: 30 ± 0.2 °C |
[3] |
Enzyme concentration
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1176 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Urinary Bladder
Enzyme: Cyclooxygenase-1 (PGTS1) pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
[4] |
| 849 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Platlet
Enzyme: Cyclooxygenase-1 (PGTS1) pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
[4] |
| 208 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Stomach
Enzyme: Cyclooxygenase-1 (PGTS1) pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
[5] |
| 130 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Esophagus
Enzyme: Cyclooxygenase-1 (PGTS1) pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
[5] |
| 70.8 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Oral Cavity
Enzyme: Cyclooxygenase-1 (PGTS1) pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
[5] |
| 19.1 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Lung
Enzyme: Cyclooxygenase-1 (PGTS1) pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
[4] |
References
- ↑ P. Silva, "A theoretical study of radical-only and combined radical/carbocationic mechanisms of arachidonic acid cyclooxygenation by prostaglandin H synthase" Theor Chem Acc (2003) 110: 345
- ↑ Y. Noreen Development of a Radiochemical Cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 in Vitro Assay for Identification of Natural Products as Inhibitors of Prostaglandin BiosynthesisJ. Nat. Prod., 1998, 61 (1), pp 2–7)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Mukherjee Molecular Oxygen Dependent Steps in Fatty Acid Oxidation by Cyclooxygenase-1 Biochemistry, 2007, 46 (13), pp 3975–3989
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 M. Kim A draft map of the human proteome Nature, 2014 509, 575–581
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v509/n7502/pdf/nature13319.pdf M. Wilhelm Mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome Nature, 2014 509, 582–587]
Related Reactions
- Transformation of PL to AA
- Transformation of PGH2 to PGF2α
- Transformation of PGH2 to TXA2
- Transformation of PGH2 to PGI2
- Transformation of PGH2 to PGD2
- Transformation of PGH2 to PGE2