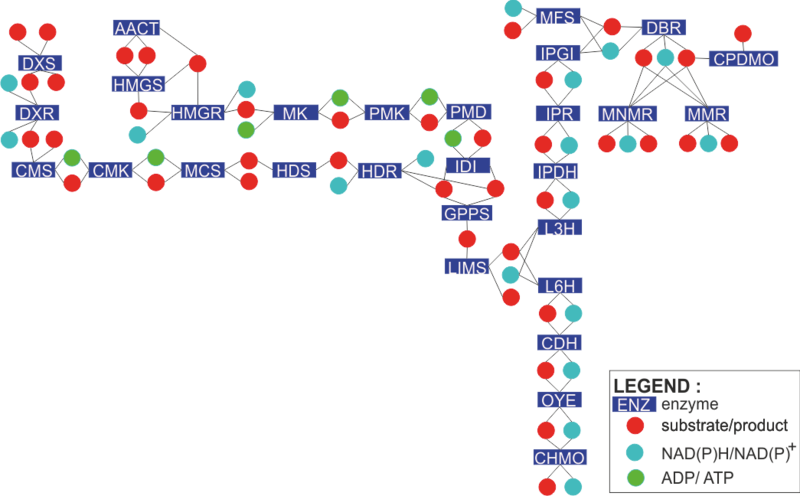
Engineered monoterpene synthesis network
This network is designed to engineer the production of monoterpenoids such as limonene, mint, spearmints and peppermints in E. coli. The network has 6 major pathways:-
- the methylerythritolphosphate (MEP) and mevalonate (MVA) pathways that produces terpene precursors isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP);
- the limonene synthesis pathway that uses these precursors to produce its main backbone geranyl diphosphate (GPP);
- the spearmint and peppermint pathways that would lead to the synthesis of important intermediates for the mint pathway.
Enzymatic reactions in this network
To find out how each enzyme in the network is modelled, click on the rectangles in the figure on the left. Alternatively, you can click the enzyme names from the list below.
| IPP and DMAPP Biosynthesis
Limonene Biosynthesis Peppermint Biosynthesis |
Mint Biosynthesis Spearmint Biosynthesis Methanofuran Biosynthesis |