Transformation of PL to AA
Contents
Reaction
Catalysed by cPLA2α (3.1.1.4).
Chemical equation
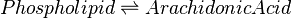
Rate equation
cPLA2a Parameters
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.50E-03 | 
|
Mouse | Fibroblasts Cytosolic PLA2 | [1] |
| 5.00E-02 | 
|
Human | Recombinant PLA2 (Phosphatidylcholine as the substrate) | [2] |
| 2.00E-02 | 
|
Human | Recombinant PLA2 (Phosphatidylethanolamine as the substrate) | [2] |
| 4.13E-01 ± 2.80E-02 | 
|
Rat | PMN Neutrophils | [3] |
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.6E+03± 0.1E+03 | 
|
Bos taurus | Organism: Bovine
Expression Vector: Bovine pancreatic PLA2 pH: 7.5 Temperature:25'C
|
[4] |
| 3000 | per minute | Porcine | Organism: Porcine
Expression Vector: Porcine Enzme: Pancreatic phospholipase A, Substrate: 1,2-dipalmitoyl-phosphatidylcholine, Enzyme concentration: 0.2 mg/ml, pH: 8.0. Temperature: 41 C |
[5] |
| 11220 | per minute | Stingray | Expression Vector: Stingray
Enzyme: Secreted pH:8.5 Temperature: 40 °C |
[6] |
| 8400 | per minute | Camel | Expression Vector: Camel
Enzyme: Pancreatic pH: 8.5 Temperature: 40 °C |
[6] |
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
|
Porcine | Pancreatic phospholipase A, Substrate: 1,2-dipalmitoyl-phosphatidylcholine, Enzyme concentration: 0.2 mg/ml, pH 8.0. | [5] |
| 3.7 | 
|
Camel | 18kDa protein, 20g of enzyme in 300ml solution.
Pancreatic, 4 mM NaTDC, 8 mM, CaCl2, pH 8,5 and 40 °C |
[6] |
| 0.004 | mM | Plant | sPLA2 with 1,2-diheptanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine as the substrate | [7] |
References
- ↑ Spaargaren M. “Characterization and identification of an epidermal-growth-factor-activated phospholipase A2.” Biochem J. 1992 Oct 1; 287(Pt 1): 37–43.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Kawauchi Y. “Preparation and characterization of human rheumatoid arthritic synovial fluid phospholipase A2 produced by recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells.” J Biochem. 1994 Jul;116(1):81-7.
- ↑ Kawauchi Y. “Changes in kinetic properties of cytosolic phospholipase A2 in activated rat neutrophils.” Adv Exp Med Biol. 1997;433:439-42.
- ↑ [www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8454568 Hada S. “Hydrolysis of Micellar Diheptanoylphosphatidylcholine Catalyzed byBovine Pancreatic Phospholipase A2: Kinetic Characterization of Group I and II Enzymes1” J Biochem (1993) 113 (1): 13-17.]
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 [http://www.jbc.org/content/261/12/5328.long Menashe M. “Hydrolysis of Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine Small Unilamellar
Vesicles by Porcine Pancreatic Phospholipase A2” J Biochem (1986) 261, 5328-5333.] Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Menashe1986" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Bacha B. “Purification and biochemical characterization of pancreatic phospholipase A2 from the common stingray Dasyatis pastinaca” Lipids Health Dis. 10, 32 (2011)
- ↑ Mansfield J. “Secretory phospholipase A2- from Arabidopsis thaliana:functional parameters and substrate preference” Chemistry and Physics of Lipids 150 (2007) 156–166