Difference between revisions of "ATP-Binding Cassette Transporters"
(Created page with " Return to overview == Reaction == ==Chemical equation== <center><math> Intracellular \rightleftharpoons Extrac...") |
|||
| (22 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Welcome to the In-Silico Model of Cutaneous Lipids Wiki | Return to overview]] | [[Welcome to the In-Silico Model of Cutaneous Lipids Wiki | Return to overview]] | ||
| − | |||
| + | At physiological pH, eicosanoids exist primarily as charged species and therefore exhibit poor membrane permeability <ref>Svensson, C. I., Yaksh, T. L., ''The spinal phospholipase-cyclooxygenase-prostanoid cascade in nociceptive processing'', Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol (2002), 42, 553-83.</ref>. Several studies have reported that eicosanoids are transported into the extracellular compartment via energy-dependant, active transport <ref>Kochel, T. J. Fulton, A. M., ''Multiple drug resistance-associated protein 4 (MRP4), prostaglandin transporter (PGT), and 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) as determinants of PGE2 levels in cancer'', Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat (2015), 116-117, 99-103.</ref><ref>Lin, Z. P. Zhu, Y. L. Johnson, D. R. Rice, K. P. Nottoli, T. Hains, B. C. McGrath, J. Waxman, S. G. Sartorelli, A. C. , ''Disruption of cAMP and prostaglandin E2 transport by multidrug resistance protein 4 deficiency alters cAMP-mediated signaling and nociceptive response'', Mol Pharmacol (2008), 73, 243-51.</ref><ref>Chan, B. S. Satriano, J. A. Pucci, M. Schuster, V. L. , ''Mechanism of prostaglandin E2 transport across the plasma membrane of HeLa Cells and Xenopus Oocytes expressing the prostaglandin transporter “PGT”'', J Biol Chem (1998), 273, 6689-6697.</ref> | ||
| + | <ref>Schuster, V. L., ''Molecular mechanisms of prostaglandin transport'', Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat (2002), 68-69, 633-47.</ref><ref>Baroody, R. A. Bito, L. Z. , ''The impermeability of the basic cell membrane to thromboxane-B2' prostacyclin and 6-keto-PGF 1 alpha'', Prostaglandins (1981), 21, 133-42.</ref>.Responsible for this transport is an ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter, also known as a α-ketoglutarate organic anion exchanger and a prostaglandin specific organic anion transporter protein, OATP2A1 (PGT) <ref>Schuster, V. L., ''Molecular mechanisms of prostaglandin transport'', Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat (2002), 68-69, 633-47.</ref>. Both transporters are a channel/pump located in the phospholipid bilayer of a cell, which binds and hydrolyses ATP to drive translocation of eicosanoids against a concentration gradient <ref>Higgins, C. F., ''ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man'', Annu Rev Cell Biol (1992), 8, 67-113.</ref><ref>Dean, M. Allikmets, R., ''Evolution of ATP-binding cassette transporter genes'', Curr Opin Genet Dev (1995), 5, 779-85.</ref> <ref>Kanai, N. Lu, R. Satriano, J. A. Bao, Y. Wolkoff, A. W. Schuster, V. L. , ''Identification and characterization of a prostaglandin transporter | ||
| + | '', Science (1995), 268, 866-869.</ref>. | ||
| − | + | The member of the ABC transporter family which is reported to transport eicosanoids is the multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4/ABCC4) <ref>Higgins, C. F., ''ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man'', Annu Rev Cell Biol (1992), 8, 67-113.</ref><ref>Dean, M. Allikmets, R., ''Evolution of ATP-binding cassette transporter genes'', Curr Opin Genet Dev (1995), 5, 779-85.</ref>. The eicosanoid specificity of the ABC transporter has not been well explored beyond PGE2, but seems to be non-specific <ref>Schuster, V. L., ''Molecular mechanisms of prostaglandin transport'', Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat (2002), 68-69, 633-47.</ref>. | |
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == Reaction == |
| − | + | {|width ="80%" | |
| − | + | | | |
| − | {| | + | * [[Transformation of PGF2a to exPGF2a |Transformation of PGF<sub>2a</sub> to exPGF<sub>2a</sub> (R22)]] |
| − | | | + | * [[Transformation of TXB2 to exTXB2 |Transformation of TXB<sub>2</sub> to exTXB<sub>2</sub> (R23)]] |
| − | |- | + | * [[Transformation of K6PGF2a to exK6PGF2a |Transformation of 6-keto-PGF<sub>1a</sub> to ex6-keto-PGF<sub>1a</sub> (R24)]] |
| − | + | * [[Transformation of PGE2 to exPGE2 |Transformation of PGE<sub>2</sub> to exPGE<sub>2</sub> (R25)]] | |
| − | + | * [[Transformation of D15PGJ2 to exD15PGJ2 |Transformation of 15-deoxy-PGJ<sub>2</sub> to ex15-deoxy-PGJ<sub>2</sub> (R26) ]] | |
| − | + | * [[Transformation of 5-Oxo-ETE to ex5-Oxo-ETE |Transformation of 5-Oxo-ETE to ex5-Oxo-ETE (R27)]] | |
| − | + | * [[Transformation of 15-HETE to ex15-HETE |Transformation of 15-HETE to ex15-HETE (R28)]] | |
| − | + | * [[Transformation of LTB4 to exLTB4 |Transformation of LTB<sub>4</sub> to exLTB<sub>4</sub> (R29)]] | |
| − | |- | + | * [[Transformation of LTC4 to exLTC4 |Transformation of LTC<sub>4</sub> to exLTC<sub>4</sub> (R30)]] |
| − | + | * [[Transformation of 12-HETE to ex12-HETE |Transformation of 12-HETE to ex12-HETE (R31)]] | |
| − | |- | + | * [[Transformation of TXA2 to exTXA2 |Transformation of TXA<sub>2</sub> to exTXA<sub>2</sub> (R32)]] |
| + | * [[Transformation of PGI2 to exPGI2 |Transformation of PGI<sub>2</sub> to exPGI<sub>2</sub> (R33)]] | ||
| + | * [[Transformation of PGH2 to exPGH2 |Transformation of PGH<sub>2</sub> to exPGH<sub>2</sub> (R34) ]] | ||
| + | * [[Transformation of PGD2 to exPGD2 |Transformation of PGD<sub>2</sub> to exPGD<sub>2</sub> (R35)]] | ||
| + | * [[Transformation of PGJ2 to exPGJ2 |Transformation of PGJ<sub>2</sub> to exPGJ<sub>2</sub> (R36)]] | ||
| + | * [[Transformation of 12-HPETE to ex12-HPETE |Transformation of 12-HPETE to ex12-HPETE (R37) ]] | ||
| + | * [[Transformation of 15-HPETE to ex15-HPETE |Transformation of 15-HPETE to ex15-HPETE (R38)]] | ||
| + | * [[Transformation of 5-HPETE to ex5-HPETE |Transformation of 5-HPETE to ex5-HPETE (R39)]] | ||
| + | * [[Transformation of 5-HETE to ex5-HETE |Transformation of 5-HETE to ex5-HETE (R40) ]] | ||
| + | * [[Transformation of LTA4 to exLTA4 |Transformation of LTA<sub>4</sub> to exLTA<sub>4</sub> (R41)]] | ||
| + | * [[Transformation of AA to exAA|Transformation of AA to exAA (R42)]] | ||
| + | * [[Transformation of 15-Keto-PGE2 to ex15-Keto-PGE2 |Transformation of 15-Keto-PGE<sub>2</sub> to ex15-Keto-PGE<sub>2</sub> (R67)]] | ||
| + | * [[Transformation of 3,4-Dihydro-15-Keto-PGE2 to ex3,4-Dihydro-15-Keto-PGE2 |Transformation of 13,14-Dihydro-15-Keto-PGE2 to ex13,14-Dihydro-15-Keto-PGE<sub>2</sub> (R70) ]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
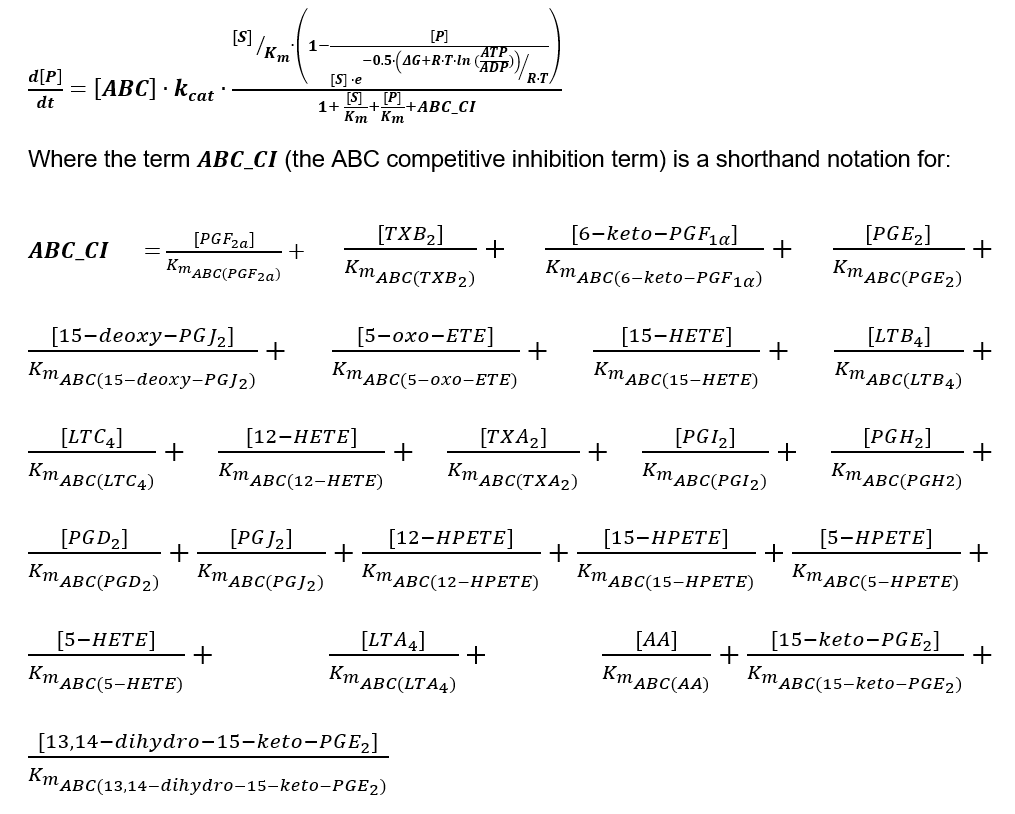
| − | + | == Rate Law == | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:ABC_CI.PNG]] | |
| − | |||
== Related Reactions == | == Related Reactions == | ||
* [[Transformation of AA to PGH2 |Transformation of AA to PGH2]] | * [[Transformation of AA to PGH2 |Transformation of AA to PGH2]] | ||
* [[Transformation of PGD2 to PGJ2 |Transformation of PGD2 to PGJ2]] | * [[Transformation of PGD2 to PGJ2 |Transformation of PGD2 to PGJ2]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:53, 26 August 2019
At physiological pH, eicosanoids exist primarily as charged species and therefore exhibit poor membrane permeability [1]. Several studies have reported that eicosanoids are transported into the extracellular compartment via energy-dependant, active transport [2][3][4] [5][6].Responsible for this transport is an ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter, also known as a α-ketoglutarate organic anion exchanger and a prostaglandin specific organic anion transporter protein, OATP2A1 (PGT) [7]. Both transporters are a channel/pump located in the phospholipid bilayer of a cell, which binds and hydrolyses ATP to drive translocation of eicosanoids against a concentration gradient [8][9] [10].
The member of the ABC transporter family which is reported to transport eicosanoids is the multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4/ABCC4) [11][12]. The eicosanoid specificity of the ABC transporter has not been well explored beyond PGE2, but seems to be non-specific [13].
Reaction
Rate Law
Related Reactions
- Transformation of AA to PGH2
- Transformation of PGD2 to PGJ2
- ↑ Svensson, C. I., Yaksh, T. L., The spinal phospholipase-cyclooxygenase-prostanoid cascade in nociceptive processing, Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol (2002), 42, 553-83.
- ↑ Kochel, T. J. Fulton, A. M., Multiple drug resistance-associated protein 4 (MRP4), prostaglandin transporter (PGT), and 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) as determinants of PGE2 levels in cancer, Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat (2015), 116-117, 99-103.
- ↑ Lin, Z. P. Zhu, Y. L. Johnson, D. R. Rice, K. P. Nottoli, T. Hains, B. C. McGrath, J. Waxman, S. G. Sartorelli, A. C. , Disruption of cAMP and prostaglandin E2 transport by multidrug resistance protein 4 deficiency alters cAMP-mediated signaling and nociceptive response, Mol Pharmacol (2008), 73, 243-51.
- ↑ Chan, B. S. Satriano, J. A. Pucci, M. Schuster, V. L. , Mechanism of prostaglandin E2 transport across the plasma membrane of HeLa Cells and Xenopus Oocytes expressing the prostaglandin transporter “PGT”, J Biol Chem (1998), 273, 6689-6697.
- ↑ Schuster, V. L., Molecular mechanisms of prostaglandin transport, Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat (2002), 68-69, 633-47.
- ↑ Baroody, R. A. Bito, L. Z. , The impermeability of the basic cell membrane to thromboxane-B2' prostacyclin and 6-keto-PGF 1 alpha, Prostaglandins (1981), 21, 133-42.
- ↑ Schuster, V. L., Molecular mechanisms of prostaglandin transport, Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat (2002), 68-69, 633-47.
- ↑ Higgins, C. F., ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man, Annu Rev Cell Biol (1992), 8, 67-113.
- ↑ Dean, M. Allikmets, R., Evolution of ATP-binding cassette transporter genes, Curr Opin Genet Dev (1995), 5, 779-85.
- ↑ Kanai, N. Lu, R. Satriano, J. A. Bao, Y. Wolkoff, A. W. Schuster, V. L. , Identification and characterization of a prostaglandin transporter , Science (1995), 268, 866-869.
- ↑ Higgins, C. F., ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man, Annu Rev Cell Biol (1992), 8, 67-113.
- ↑ Dean, M. Allikmets, R., Evolution of ATP-binding cassette transporter genes, Curr Opin Genet Dev (1995), 5, 779-85.
- ↑ Schuster, V. L., Molecular mechanisms of prostaglandin transport, Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat (2002), 68-69, 633-47.