Difference between revisions of "Kinetic model of Central Metabolism"
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
rect 357 156 382 179 [[Phosphoglucomutase|PGLM]] | rect 357 156 382 179 [[Phosphoglucomutase|PGLM]] | ||
rect 773 751 799 777 [[Glycine hydroxymethyltransferase|SHMT]] | rect 773 751 799 777 [[Glycine hydroxymethyltransferase|SHMT]] | ||
| − | rect 834 690 854 717 [[ | + | rect 834 690 854 717 [[Serine out|SERout]] |
| − | rect 842 826 862 846 [[ | + | rect 842 826 862 846 [[Glycine out|GlYCout]] |
rect 680 690 706 713 [[Phosphohydroxypyruvate|PSP]] | rect 680 690 706 713 [[Phosphohydroxypyruvate|PSP]] | ||
rect 507 686 526 715 [[Phosphoserine amino-transferase|PSA]] | rect 507 686 526 715 [[Phosphoserine amino-transferase|PSA]] | ||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
*[[Mitocondrial pyruvate metabolism]] | *[[Mitocondrial pyruvate metabolism]] | ||
*[[Glycine hydroxymethyltransferase]] | *[[Glycine hydroxymethyltransferase]] | ||
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Serine out]] |
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Glycine out]] |
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 13:54, 21 March 2014
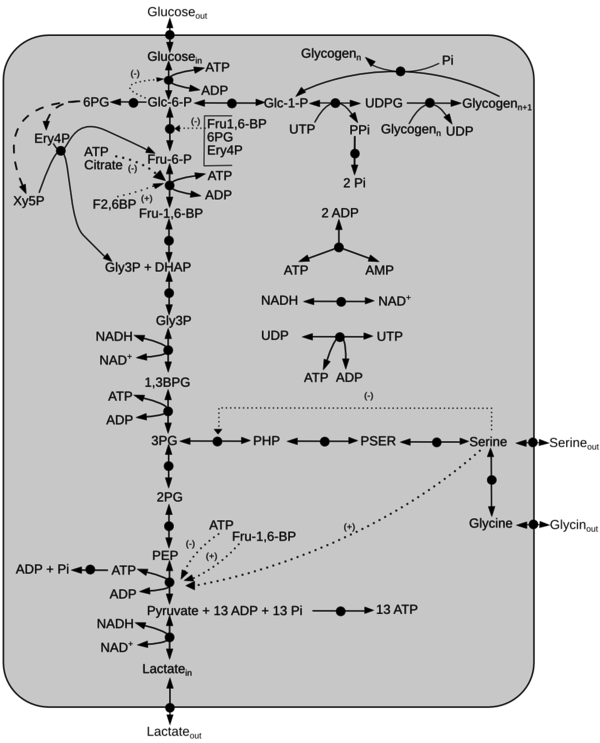
A kinetic model of glycolysis with serine activation is constructed from the literature data [1][2][3][4].
Description of the model
Click on a reaction to have more information
Reactions
Details of the abbreviations for this model is listed here
Initial concentration of the metabolites can be found here
Model File
Global parameters
The Vmax value in the paper "Modeling cancer glycolysis" is given in 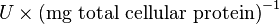 unit [1]. To homogenize the units it is then converted back to
unit [1]. To homogenize the units it is then converted back to 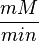 by multiplying
by multiplying 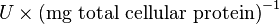 with 65 as the HeLa cell was incubated in
with 65 as the HeLa cell was incubated in 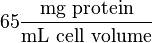 .
.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Marín-Hernández A, Gallardo-Pérez JC, Rodríguez-Enríquez S et al (2011). Modeling cancer glycolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1807:755–767 (doi)
- ↑ Turnaev II, Ibragimova SS, Usuda Y et al (2006). Mathematical modeling of serine and glycine synthesis regulation in Escherichia coli. Proceedings of the fifth international conference on bioinformatics of genome regulation and structure 2:78–83
- ↑ Smallbone K, Stanford NJ (2013). Kinetic modeling of metabolic pathways: Application to serine biosynthesis. In: Systems Metabolic Engineering, Humana Press. pp. 113–121
- ↑ Palm, D.C. (2013). The regulatory design of glycogen metabolism in mammalian skeletal muscle (Ph.D.). University of Stellenbosch