Cytochrome P450
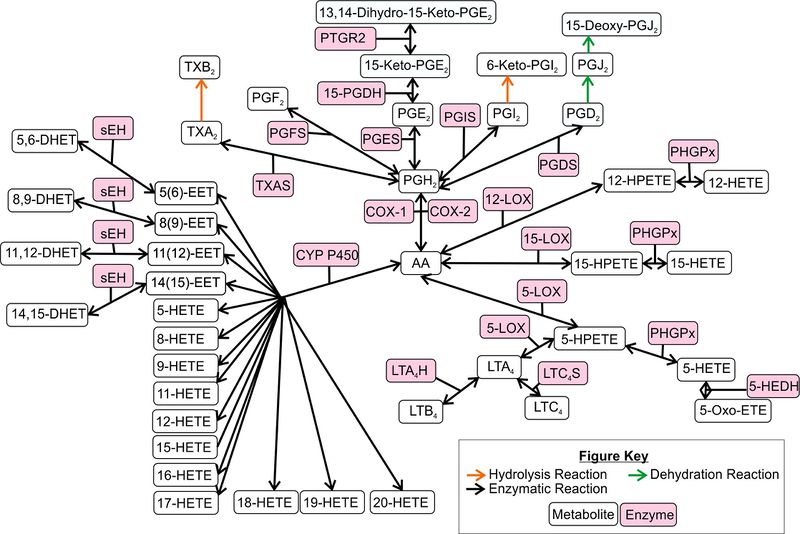
The superfamily of CYP P450 enzymes is encoded by a minimum of 57 genes in humans (Nelson et al., 2004, Nebert et al., 2002). This varied class possess epoxygenase and hydrolase activity and can convert PUFAs such as AA into cis-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid (EET), dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (DHET) and HETEs (Morisseau et al., 2013, Oliw, 1994). These reactions are redox coupled, include the activation of molecular oxygen and depending on the isoform the reactions, are NADPH independent or dependant. The reactions are typically performed by the microsomal CYP P450 isoforms.

Contents
Epoxygenation pathway
The genes CYP2C and CYP2J encode subfamilies of proteins which perform Olefin epoxidation reactions on AA, to generate epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) (Wu et al., 1996, Zeldin, 2001). This reaction is NADPH dependant and involves the electrophilic addition of oxygen to an alkene, and due to the four double bonds of AA, four regioisomeric EETs are formed (5,6-, 8,9-, 11,12-, and 14,15-EET). Due to the epoxide group EETs are unstable and are hydrolysed by the protein soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) (Morisseau et al., 2013, Capdevila et al., 2002, Spector, 2009, Zeldin, 2001). This reaction generates dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids (DHETs) by the addition of two hydrogens and one oxygen molecule across the epoxide ring. This protein is located at the microsomal and ER membranes.
Hydroxylation pathway
In addition, the CYP4A and CYP4F genes encode subfamilies of CYP P450 which convert PUFA into mono-hydroxy fatty acids by (Lasker et al., 2000, Powell et al., 1998). This is performed by a bis-allylic oxidation followed by an acid-catalysed rearrangement to the corresponding cis-trans dienols. This results in the generation of six regioisomeric HETEs (5-, 8-, 9-, 11-, 12- and 15-HETE) which contain cis, trans-conjugated dienol functionality. Furthermore, monohydroxy fatty acids can be generated via an omega oxidation, which involves oxidation at the terminal or the penultimate carbon (Harder et al., 1995). This reaction results in the formation of 16-, 17-, 18-, 19- and 20-HETE.
Cytochrome P450 pathway in biology
Products of the CYP P450 pathway are implicated in diseases such as cancer, metabolic disorders and cardiovascular disease (Smith et al., 2000, Capdevila et al., 2002, McGiff et al., 1999, McGiff et al., 2001, Roman, 2002). EETs have been demonstrated to mediate inflammatory processes such as clotting, angiogenesis, cell proliferation, pain, cell survival and remodelling of the extracellular matrix (Webler et al., 2008, Zhang et al., 2011, Inceoglu et al., 2007, Wang et al., 2012). More information is available on products of the CYP P450 pathway than others, for example 5,6-EET, 11,12-EET and 20-HETE have demonstrated vasoactive properties (McGiff and Quilley, 1999, McGiff and Quilley, 2001, Imig, 2000, Campbell et al., 1999, Roman, 2002). 5,6-EET and 11,12-EET are associated with vasodilation and activation of vascular smooth muscle potassium channels (McGiff and Quilley, 1999, McGiff and Quilley, 2001, Imig, 2000, Campbell and Harder, 1999, Roman, 2002, Campbell et al., 1996), whereas 20-HETE is associated with vasoconstriction and inactivation of vascular smooth muscle potassium channels (Zou et al., 1996, McGiff and Quilley, 1999, McGiff and Quilley, 2001). Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that 20-HETE is implicated in blood pressure control and hypertension (McGiff and Quilley, 2001).
Reactions
- Transformation of AA to 20-HETE
- Transformation of AA to 9-HETE
- Transformation of AA to 5,6-EET
- Transformation of AA to 8,9-EET
- Transformation of AA to 11,12-EET
- Transformation of AA to 14,15-EET
- Transformation of 5,6-EET to 5,6-DHET
- Transformation of 8,9-EET to 8,9-DHET
- Transformation of 1,12-EET to 11,12-DHET
- Transformation of 14,15-EET to 14,15-DHET
Model Structure