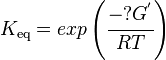Limonene-6-Hydroxylase (L6H)
You can go back to main page of the kinetic model here.
Contents
What we know
This enzyme is also known as (S)-limonene 6-monooxygenase, (-)-limonene 6-hydroxylase, (-)-limonene 6-monooxygenase, (-)-limonene,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (6-hydroxylating)
Reaction catalysed
Metabolite and Enzyme Background Information
Long metabolite and enzyme names are abbreviated in the model for clarity and standard identification purposes.
| Metabolite | Abbreviation | Chemical Formula | Molar mass (g/mol) | ChEBI | ChEMBL | PubChem | MetaCyc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (-)-4S-limonene | Limonene | C10H16 | 136.24 | 15384 | 449062 | 22311 or 439250 | |
| (-)-trans-carveol | carveol | Chemical Formula | Molar mass (g/mol) | ChEBI | ChEMBL | PubChem | MetaCyc |
| NADPH | NADPH | Chemical Formula | Molar mass (g/mol) | ChEBI | ChEMBL | PubChem | MetaCyc |
| NADP | NADP | Chemical Formula | Molar mass (g/mol) | ChEBI | ChEMBL | PubChem | MetaCyc |
| Limonene-6-hydroxylase | L6H | Chemical Formula | Molar mass (g/mol) | ChEBI | ChEMBL | PubChem | LIMONENE-6-MONOOXYGENASE-RXN |
| Metabolite | Abbreviation | Chemical Formula | Molar mass (g/mol) | ChEBI | ChEMBL | PubChem | MetaCyc |
Equation Rate
This reaction is modelled using the reversible Michaelis-Menten equation, with two substrates; Limonene and NADPH, and two products; Carveol and NADP.
| Parameter | Description | Units |
|---|---|---|
| VL6H | Net reaction rate for Limonene-6-Hydroxylase | Unit |
| Vmaxforward | Maximum reaction rate towards the production of trans-carveol | Unit |
| Kmlimonene | Michaelis-Menten constant for Limonene | Unit |
| Kmcarveol | Michaelis-Menten constant for trans-carveol | Unit |
| KmNADPH | Michaelis-Menten constant for NADPH | Unit |
| KmNADP | Michaelis-Menten constant for NADP | Unit |
| Keq | Equilibrium constant | Unit |
| [Limonene] | Limonene concentration | Unit |
| [Carveol] | trans-carveol concentration | Unit |
| [NADPH] | NADPH concentration | Unit |
| [NADP] | NADP concentration | Unit |
Strategies for estimating the kinetic parameter values
Calculating the Equilibrium Constant
The equilibrium constant can be calculated using the Van't Hoff Isotherm equation:
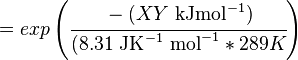
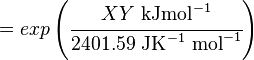
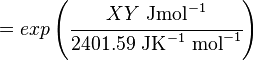
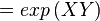
where;
| Keq | Equilibrium constant |
| -?G° | Gibbs free energy change. For (INSERT ENZYME) it is (INSERT VALUE) kJmol-1 |
| R | Gas constant with a value of 8.31 JK-1mol-1 |
| T | Temperature which is always expressed in kelvin |
Standard Gibbs Free energy
Standard Gibbs free energy is -92.52051 kcal·mol-1 [1] according to MetaCyc [[1]].
Published Kinetic Parameter Values
Km Values
| Km (mM) | Unit | Substrate / Product | Directionality | Organism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | unit | substrate | directionality | organism | Ref |
Vmax values
| Vmax | Unit | Directionality | Organism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | µmol/min/mg (unit) | directionality | Organism | References |
Kcat values
| Kcat | Unit | Organism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| value | s-1 | Organism | ref e.g. Alonso 1992 [2] |
Extracting Information from (INSERT SUBSTRATE/PRODUCT) Production Rates
| Amount produced (mg/L) | Time (H) | Organism | Description | Reaction Flux (µM/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
Published Kinetic Parameter Values
| Km (mM) | Vmax | Kcat (s-1) | Kcat/Km | Organism | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00125 | - | - | Z | A -> B | |
| 0.0018 | - | - | - | Z | A -> B |
| Y | Y | Y | Y | Z | A -> B |
| Y | Y | Y | Y | Z | A -> B |
| Y | Y | - | - | Z | A -> B |
| Y | - | Y | - | Z | GPP -> B |
| Y | - | Y | - | Z | GPP -> B |
| x | - | y | - | Z. | A -> B |
Detailed descriptions of kinetic values used in this model
A more detailed description of the kinetic values listed above can be found here.
Simulations
References
- ↑ Latendresse, M. 2013. http://www.biocyc.org/PGDBConceptsGuide.shtml#gibbs. "Computing Gibbs Free Energy of Compounds and Reactions in MetaCyc."
- ↑ Alonso et. al. 1992. "Purification of 4S-Limonene Synthase, a Monoterpene Cyclase from the Glandular Trichomes of Peppermint (Mentha x piperita) and Spearmint (Mentha spicata)", The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267(11):7582-7587
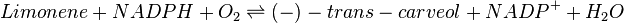
![V_\mathrm{L6H} = Vmax_\mathrm{forward} * \cfrac {\cfrac{[Limonene]}{Km_\mathrm{Limonene}} * \left ( 1 - \cfrac {[Limonene]*[PP]}{[GPP]*K_\mathrm{eq}} \right )}{1 + \cfrac {[GPP]}{Km_\mathrm{GPP}} + \cfrac {[Limonene]}{Km_\mathrm{Limonene}} + \cfrac {[PP]}{Km_\mathrm{PP}} + \cfrac {[Limonene]*[PP]}{Km_\mathrm{Limonene}*Km_\mathrm{PP}}}](/wiki/images/math/6/e/6/6e68d78babd5acdaa586f13c500e95dd.png)