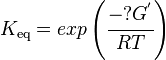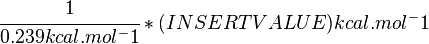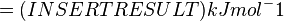Difference between revisions of "Limonene-6-Hydroxylase (L6H)"
Aliah.hawari (talk | contribs) (Created page with "You can go back to main page of the kinetic model [http://www.systemsbiology.ls.manchester.ac.uk/wiki/index.php/Kinetic_Model_of_Monoterpenoid_Biosynthesis_Wiki here]. == Wha...") |
Aliah.hawari (talk | contribs) (→Detailed descriptions of kinetic data used in this model) |
||
| Line 213: | Line 213: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ==== Detailed descriptions of kinetic | + | ==== Detailed descriptions of kinetic values used in this model ==== |
| − | A more detailed description of the kinetic values | + | A more detailed description of the kinetic values listed above can be found [[Limonene-6-Hydroxylase: Detailed description of the kinetics | here]]. |
== Simulations == | == Simulations == | ||
Revision as of 14:41, 16 March 2016
You can go back to main page of the kinetic model here.
Contents
What we know
Issues
Strategies
Reaction catalysed
Metabolite Background Information
Long metabolite names are abbreviated in the model for clarity and standard identification purposes.
| Metabolite | Abbreviation | Chemical Formula | Molar mass (g/mol) | ChEBI | ChEMBL | PubChem |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| geranyl diphosphate | GPP | C10H20O7P2 | 314.209 | 17211 | 41432 | 445995 |
| (-)-4S-limonene | Limonene | C10H16 | 136.24 | 15384 | 449062 | 22311 or 439250 |
| diphosphate | PP | O7P2 | 173.94 | 644102 |
Equation Rate
| Parameter | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| VLimSynth | Reaction rate for Limonene Synthase | ref |
| Vmaxforward | Maximum reaction rate towards the production of limonene | ref |
| KmGPP | Michaelis-Menten constant for GPP | ref |
| KmLimonene | Michaelis-Menten constant for Limonene | ref |
| KmPP | Michaelis-Menten constant for PP | ref |
| Keq | Equilibrium constant | ref |
| [GPP] | GPP concentration | ref |
| [Limonene] | Limonene concentration | ref |
| [PP] | PP concentration | ref |
Strategies for estimating the kinetic parameter values
Calculating the Equilibrium Constant
The equilibrium constant can be calculated using the Van't Hoff Isotherm equation:
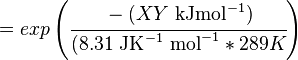
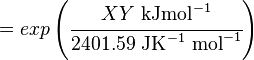
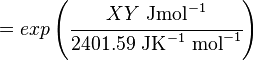
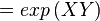
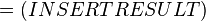
where;
| Keq | Equilibrium constant |
| -?G° | Gibbs free energy change. For (INSERT ENZYME) it is (INSERT VALUE) kJmol-1 |
| R | Gas constant with a value of 8.31 JK-1mol-1 |
| T | Temperature which is always expressed in kelvin |
Standard Gibbs Free energy
Standard Gibbs Free energy for (INSERT ENZYME) from MetaCyc (EC 4.2.3.16) is (INSERT VALUE) kcal/mol [1].
SI derived unit for Gibbs free energy is Joules per mol (J mol-1). 1 kJ·mol-1 is equal to 0.239 kcal·mol-1.
Therefore, the Gibbs free energy for (INSERT ENZYME) in kJ mol-1 is:
Extracting Information from (INSERT SUBSTRATE/PRODUCT) Production Rates
| Amount produced (mg/L) | Time (H) | Organism | Description | Reaction Flux (µM/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
Published Kinetic Parameter Values
| Km (mM) | Vmax | Kcat (s-1) | Kcat/Km | Organism | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00125 | - | - | Z | A -> B | |
| 0.0018 | - | - | - | Z | A -> B |
| Y | Y | Y | Y | Z | A -> B |
| Y | Y | Y | Y | Z | A -> B |
| Y | Y | - | - | Z | A -> B |
| Y | - | Y | - | Z | GPP -> B |
| Y | - | Y | - | Z | GPP -> B |
| x | - | y | - | Z. | A -> B |
Detailed descriptions of kinetic values used in this model
A more detailed description of the kinetic values listed above can be found here.
Simulations
References
- ↑ Latendresse M. (2013). "Computing Gibbs Free Energy of Compounds and Reactions in MetaCyc."
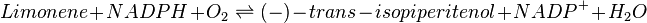
![V_\mathrm{LimSynth} = Vmax_\mathrm{forward} * \cfrac {\cfrac{[GPP]}{Km_\mathrm{GPP}} * \left ( 1 - \cfrac {[Limonene]*[PP]}{[GPP]*K_\mathrm{eq}} \right )}{1 + \cfrac {[GPP]}{Km_\mathrm{GPP}} + \cfrac {[Limonene]}{Km_\mathrm{Limonene}} + \cfrac {[PP]}{Km_\mathrm{PP}} + \cfrac {[Limonene]*[PP]}{Km_\mathrm{Limonene}*Km_\mathrm{PP}}}](/wiki/images/math/6/9/8/698f16353b522504a844aae5c37bdac9.png)