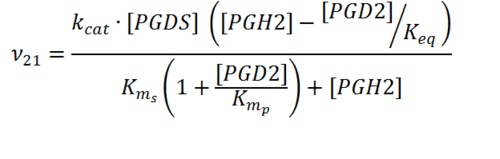Difference between revisions of "Transformation of PGH2 to PGD2"
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Welcome to the In-Silico Model of Cutaneous Lipids Wiki | Return to overview]] | [[Welcome to the In-Silico Model of Cutaneous Lipids Wiki | Return to overview]] | ||
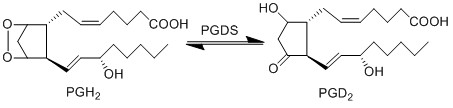
| − | The isomerisation of PGH2 to PGD2 | + | The isomerisation of PGH2 to PGD2 can be performed by prostaglandin D synthase (PGDS) and prostaglandin F synthase (PGFS). PGDS yields a hydroxyl group at C9 and a ketone group at C11. Two isoforms of PGDS have been found in humans, the lipocalin isoform, L-PGDS, does not require glutathione for catalysis whereas the hemopoietic type, H-PGDS, does require glutathione. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Reaction == | == Reaction == | ||
| Line 25: | Line 23: | ||
! Species | ! Species | ||
! Notes | ! Notes | ||
| + | ! Weight | ||
! Reference | ! Reference | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 34: | Line 33: | ||
pH: 8 | pH: 8 | ||
Temperature: 25 | Temperature: 25 | ||
| − | |<ref | + | |512 |
| − | ]</ref> | + | |<ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20667974 Zhou Y. , "Structure-function analysis of human l-prostaglandin D synthase bound with fatty acid molecules." FASEB J. 2010 Dec;24(12):4668-77. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-164863. Epub 2010 Jul 28.]</ref> |
|- | |- | ||
|4.00E-03 | |4.00E-03 | ||
| Line 44: | Line 43: | ||
pH:10 | pH:10 | ||
Temperature: Unspecified | Temperature: Unspecified | ||
| − | + | |256 | |
| − | |<ref | + | |<ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8093029 Watanabe K. , "Identification of beta-trace as prostaglandin D synthase."Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Sep 15;203(2):1110-6. ]</ref> |
| − | Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Sep 15;203(2):1110-6. ]</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|0.50 | |0.50 | ||
| Line 55: | Line 53: | ||
pH:6.5 | pH:6.5 | ||
Temperature: Unspecified | Temperature: Unspecified | ||
| − | |<ref | + | |128 |
| − | J Biol Chem. 2000 Oct 6;275(40):31239-44. ]</ref> | + | |<ref>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10871602 Pinzar E , "Structural basis of hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase activity elucidated by site-directed mutagenesis." J Biol Chem. 2000 Oct 6;275(40):31239-44. ]</ref> |
|- | |- | ||
|1.40E-02 | |1.40E-02 | ||
| Line 65: | Line 63: | ||
pH:7 | pH:7 | ||
Temperature: 25 | Temperature: 25 | ||
| − | |<ref | + | |256 |
| − | J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12410-5.]</ref> | + | |<ref>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3930495 Urade Y. , "Purification and characterization of rat brain prostaglandin D synthetase." J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12410-5.]</ref> |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 99: | Line 97: | ||
! Species | ! Species | ||
! Notes | ! Notes | ||
| + | ! Weight | ||
! Reference | ! Reference | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 108: | Line 107: | ||
pH: 8 | pH: 8 | ||
Temperature: 25 | Temperature: 25 | ||
| + | |256 | ||
| <ref name="Zhou2010"> [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20667974 Zhou Y. , "Structure-function analysis of human l-prostaglandin D synthase bound with fatty acid molecules.'' FASEB J. 2010 Dec;24(12):4668-77.]</ref> | | <ref name="Zhou2010"> [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20667974 Zhou Y. , "Structure-function analysis of human l-prostaglandin D synthase bound with fatty acid molecules.'' FASEB J. 2010 Dec;24(12):4668-77.]</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 117: | Line 117: | ||
pH:6.5 | pH:6.5 | ||
Temperature: Unspecified | Temperature: Unspecified | ||
| + | |128 | ||
|<ref name="Pinzar2000"> [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10871602 Pinzar E , "Structural basis of hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase activity elucidated by site-directed mutagenesis.'' | |<ref name="Pinzar2000"> [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10871602 Pinzar E , "Structural basis of hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase activity elucidated by site-directed mutagenesis.'' | ||
J Biol Chem. 2000 Oct 6;275(40):31239-44. ]</ref> | J Biol Chem. 2000 Oct 6;275(40):31239-44. ]</ref> | ||
| Line 133: | Line 134: | ||
=== Enzyme concentrations === | === Enzyme concentrations === | ||
| + | |||
| + | To convert the enzyme concentration from ppm to mM, the following [[Common equations#Enzyme concentration (mM)|equation]] was used. | ||
| + | |||
{|class="wikitable sortable" | {|class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|+ style="text-align: left;" | Literature values | |+ style="text-align: left;" | Literature values | ||
| Line 140: | Line 144: | ||
! Species | ! Species | ||
! Notes | ! Notes | ||
| + | ! Weight | ||
! Reference | ! Reference | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 149: | Line 154: | ||
pH: 7.5 | pH: 7.5 | ||
Temperature: 37 °C | Temperature: 37 °C | ||
| + | |1024 | ||
|<ref name="Kim2014"> [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v509/n7502/pdf/nature13302.pdf M. Kim ''A draft map of the human proteome'' Nature, 2014 509, 575–581]</ref> | |<ref name="Kim2014"> [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v509/n7502/pdf/nature13302.pdf M. Kim ''A draft map of the human proteome'' Nature, 2014 509, 575–581]</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 158: | Line 164: | ||
pH: 7.5 | pH: 7.5 | ||
Temperature: 37 °C | Temperature: 37 °C | ||
| + | |1024 | ||
|<ref name="Wilhelm2014"> [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v509/n7502/pdf/nature13319.pdf M. Wilhelm ''Mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome'' Nature, 2014 509, 582–587]</ref> | |<ref name="Wilhelm2014"> [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v509/n7502/pdf/nature13319.pdf M. Wilhelm ''Mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome'' Nature, 2014 509, 582–587]</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 167: | Line 174: | ||
pH: 7.5 | pH: 7.5 | ||
Temperature: 37 °C | Temperature: 37 °C | ||
| + | |1024 | ||
|<ref name="Kim2014"> [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v509/n7502/pdf/nature13302.pdf M. Kim ''A draft map of the human proteome'' Nature, 2014 509, 575–581]</ref> | |<ref name="Kim2014"> [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v509/n7502/pdf/nature13302.pdf M. Kim ''A draft map of the human proteome'' Nature, 2014 509, 575–581]</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 176: | Line 184: | ||
pH: 7.5 | pH: 7.5 | ||
Temperature: 37 °C | Temperature: 37 °C | ||
| + | |2048 | ||
|<ref name="Wilhelm2014"> [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v509/n7502/pdf/nature13319.pdf M. Wilhelm ''Mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome'' Nature, 2014 509, 582–587]</ref> | |<ref name="Wilhelm2014"> [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v509/n7502/pdf/nature13319.pdf M. Wilhelm ''Mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome'' Nature, 2014 509, 582–587]</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 182: | Line 191: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ style="text-align: left;" | Description of the PGDS concentration distribution | |+ style="text-align: left;" | Description of the PGDS concentration distribution | ||
| − | ! Mode (mM) !! Confidence Interval !! Location parameter (µ) !! Scale parameter (σ) | + | ! Mode (ppm) !! Mode (mM) !! Confidence Interval !! Location parameter (µ) !! Scale parameter (σ) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 6.76E+01 || 1.64E+00 || 4.41E+00 || 4.49E-01 | + | | 6.76E+01 ||3.74E-04|| 1.64E+00 || 4.41E+00 || 4.49E-01 |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 197: | Line 206: | ||
! Species | ! Species | ||
! Notes | ! Notes | ||
| + | ! Weight | ||
! Reference | ! Reference | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 206: | Line 216: | ||
pH: 8 | pH: 8 | ||
Temperature: 25 | Temperature: 25 | ||
| + | |64 | ||
|<ref name="Kume2014"> [http://ac.els-cdn.com/S0014579314000982/1-s2.0-S0014579314000982-main.pdf?_tid=7f323a24-6543-11e6-82ac-00000aab0f01&acdnat=1471525305_289e200c1e492c5fa693179a5396fd82 Kume S., "Fine-tuned broad binding capability of human lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase for various small lipophilic ligands'' FEBS Letters | |<ref name="Kume2014"> [http://ac.els-cdn.com/S0014579314000982/1-s2.0-S0014579314000982-main.pdf?_tid=7f323a24-6543-11e6-82ac-00000aab0f01&acdnat=1471525305_289e200c1e492c5fa693179a5396fd82 Kume S., "Fine-tuned broad binding capability of human lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase for various small lipophilic ligands'' FEBS Letters | ||
Volume 588, Issue 6, 18 March 2014, Pages 962–969]</ref> | Volume 588, Issue 6, 18 March 2014, Pages 962–969]</ref> | ||
| Line 218: | Line 229: | ||
pH: 7.3 | pH: 7.3 | ||
ionic strength: 0.25 | ionic strength: 0.25 | ||
| + | |64 | ||
|<ref name="MetaCyc”>[http://metacyc.org/META/NEW-IMAGE?type=REACTION&object=PROSTAGLANDIN-D-SYNTHASE-RXN Caspi et al 2014, "The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of Pathway/Genome Databases," Nucleic Acids Research 42:D459-D471]</ref> | |<ref name="MetaCyc”>[http://metacyc.org/META/NEW-IMAGE?type=REACTION&object=PROSTAGLANDIN-D-SYNTHASE-RXN Caspi et al 2014, "The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of Pathway/Genome Databases," Nucleic Acids Research 42:D459-D471]</ref> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 229: | Line 241: | ||
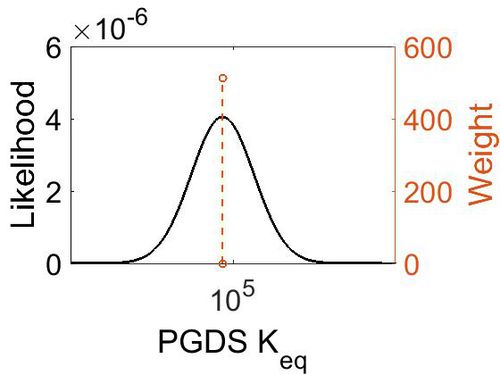
[[Image:68.jpg|none|thumb|500px|The estimated probability distribution for PGDS Keq. The value and weight of the literature values used to define the distribution are indicated by an orange dashed line. The x axis is plotted on a log-scale. ]] | [[Image:68.jpg|none|thumb|500px|The estimated probability distribution for PGDS Keq. The value and weight of the literature values used to define the distribution are indicated by an orange dashed line. The x axis is plotted on a log-scale. ]] | ||
| − | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 07:51, 21 August 2019
The isomerisation of PGH2 to PGD2 can be performed by prostaglandin D synthase (PGDS) and prostaglandin F synthase (PGFS). PGDS yields a hydroxyl group at C9 and a ketone group at C11. Two isoforms of PGDS have been found in humans, the lipocalin isoform, L-PGDS, does not require glutathione for catalysis whereas the hemopoietic type, H-PGDS, does require glutathione.
Contents
Reaction
Chemical equation
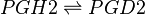
Rate equation
Enzyme Parameters
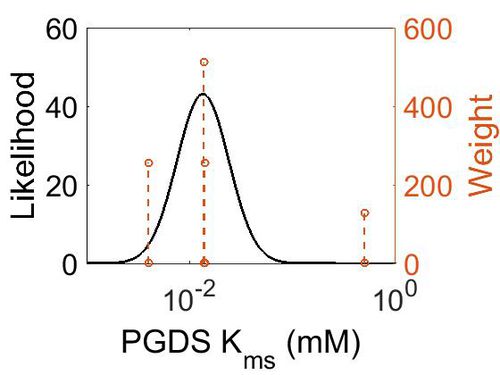
Kms
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Weight | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0138 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Human Cell
Enzyme: PGDS pH: 8 Temperature: 25 |
512 | [1] |
| 4.00E-03 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Cerebrospinal Fluid
Enzyme: PGDS pH:10 Temperature: Unspecified |
256 | [2] |
| 0.50 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: E. Coli.
Enzyme: PGDS pH:6.5 Temperature: Unspecified |
128 | [3] |
| 1.40E-02 | 
|
Rat | Expression Vector: Cerebrospinal Fluid
Enzyme: PGDS pH:7 Temperature: 25 |
256 | [4] |
| Mode (mM) | Confidence Interval | Location parameter (µ) | Scale parameter (σ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.35E-02 | 3.78E+00 | -3.44E+00 | 9.29E-01 |
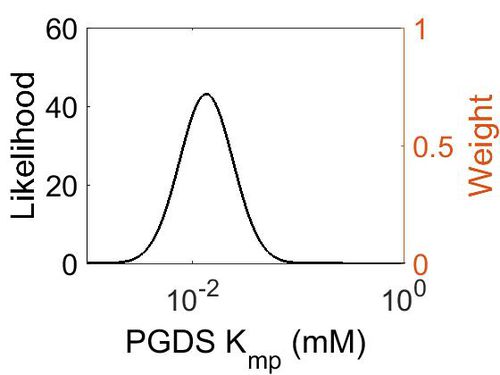
Kmp
| Mode (mM) | Location parameter (µ) | Scale parameter (σ) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.30E-02 | -4.02E+00 | 5.69E-01 |
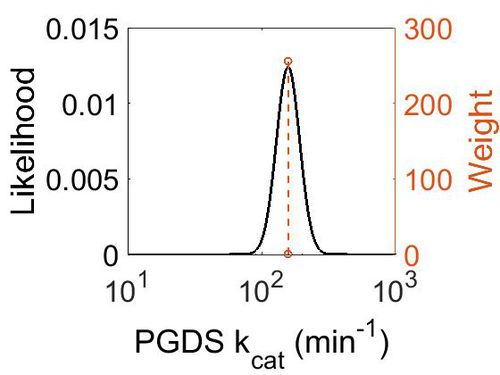
kcat
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Weight | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 158.4 | per minute | Human | Expression Vector: Human Cell
Enzyme: PGDS pH: 8 Temperature: 25 |
256 | [5] |
| 1302 | per minute | Human | Expression Vector: E. Coli.
Enzyme: PGDS pH:6.5 Temperature: Unspecified |
128 | [6] |
| Mode (min-1) | Confidence Interval | Location parameter (µ) | Scale parameter (σ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.58E+02 | 1.50E+00 | 5.10E+00 | 2.00E-01 |
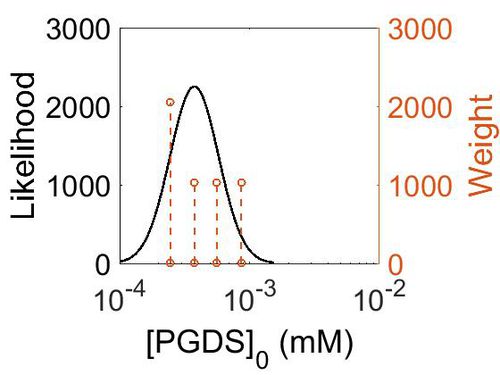
Enzyme concentrations
To convert the enzyme concentration from ppm to mM, the following equation was used.
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Weight | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 156 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Pancreas
Enzyme: PGDS pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
1024 | [7] |
| 101 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Oral Cavity
Enzyme: PGDS pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
1024 | [8] |
| 67.9 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Esophagus
Enzyme: PGDS pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
1024 | [7] |
| 44.5 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector:Skin
Enzyme: PGDS pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
2048 | [8] |
| Mode (ppm) | Mode (mM) | Confidence Interval | Location parameter (µ) | Scale parameter (σ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.76E+01 | 3.74E-04 | 1.64E+00 | 4.41E+00 | 4.49E-01 |
Keq
| Gibbs Free Energy Change | Units | Species | Notes | Weight | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
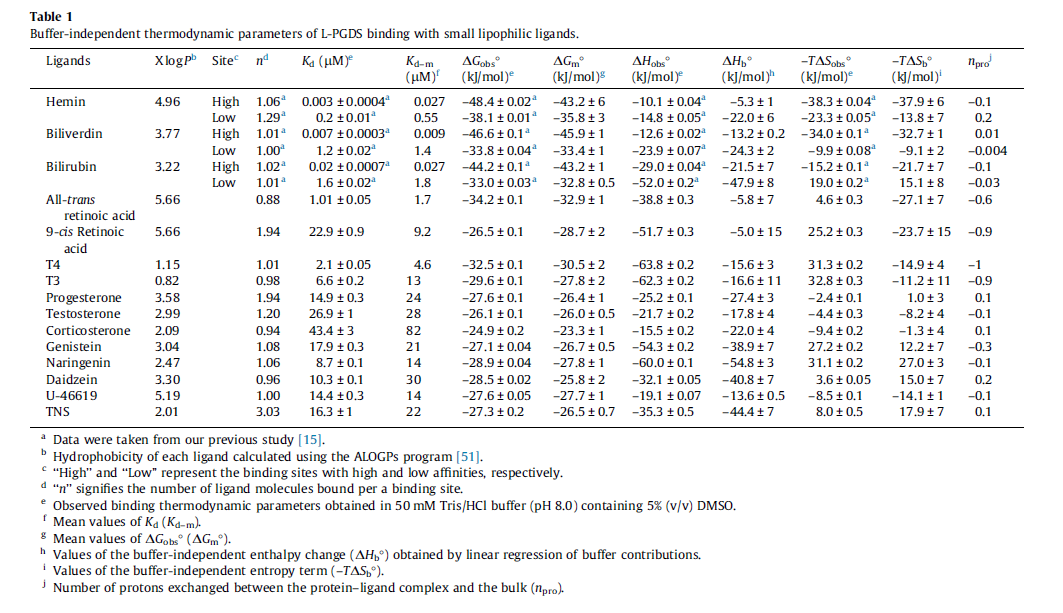
|
|
Human | Expression Vector: E. Coli
Enzyme: L-PGDS pH: 8 Temperature: 25 |
64 | [9] |
| 5.72 | kcal/mol | Not stated | Estimated
Enzyme: PGDS Substrate: Arachidonate Product: PGD2 pH: 7.3 ionic strength: 0.25 |
64 | [10] |
| Mode | Confidence Interval | Location parameter (µ) | Scale parameter (σ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7.46E+04 | 1.00E+01 | 1.20E+01 | 8.90E-01 |
References
- ↑ Zhou Y. , "Structure-function analysis of human l-prostaglandin D synthase bound with fatty acid molecules." FASEB J. 2010 Dec;24(12):4668-77. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-164863. Epub 2010 Jul 28.
- ↑ Watanabe K. , "Identification of beta-trace as prostaglandin D synthase."Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Sep 15;203(2):1110-6.
- ↑ Pinzar E , "Structural basis of hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase activity elucidated by site-directed mutagenesis." J Biol Chem. 2000 Oct 6;275(40):31239-44.
- ↑ Urade Y. , "Purification and characterization of rat brain prostaglandin D synthetase." J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12410-5.
- ↑ Zhou Y. , "Structure-function analysis of human l-prostaglandin D synthase bound with fatty acid molecules. FASEB J. 2010 Dec;24(12):4668-77.
- ↑ [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10871602 Pinzar E , "Structural basis of hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase activity elucidated by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 2000 Oct 6;275(40):31239-44. ]
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 M. Kim A draft map of the human proteome Nature, 2014 509, 575–581
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 M. Wilhelm Mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome Nature, 2014 509, 582–587
- ↑ [http://ac.els-cdn.com/S0014579314000982/1-s2.0-S0014579314000982-main.pdf?_tid=7f323a24-6543-11e6-82ac-00000aab0f01&acdnat=1471525305_289e200c1e492c5fa693179a5396fd82 Kume S., "Fine-tuned broad binding capability of human lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase for various small lipophilic ligands FEBS Letters Volume 588, Issue 6, 18 March 2014, Pages 962–969]
- ↑ Caspi et al 2014, "The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of Pathway/Genome Databases," Nucleic Acids Research 42:D459-D471