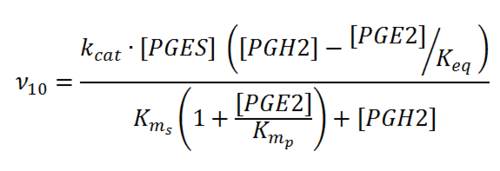Difference between revisions of "Transformation of PGH2 to PGE2"
(→Parameters) |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Welcome to the In-Silico Model of Cutaneous Lipids Wiki | Return to overview]] | [[Welcome to the In-Silico Model of Cutaneous Lipids Wiki | Return to overview]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | PGE2 is produced by the isomerisation of the PGH2 peroxide, into a ketone at C9 and an alcohol at C11 by PGES, yielding PGE2. This reaction is catalysed by isoforms of PGES, such as cPGES (also known as PGES-3), mPGES-1 and mPGES-2 <ref>Samuelsson, B. Morgenstern, R. Jakobsson, P. J. , ''Membrane prostaglandin E synthase-1: a novel therapeutic target'', Pharmacol Rev (2007), 59, 207-24.</ref>. cPGES is the cytosolic isoform of PGES which is constitutively expressed in the cytosol of various cells <ref>Tanioka, T. Nakatani, Y. Semmyo, N. Murakami, M. Kudo, I., ''Molecular identification of cytosolic prostaglandin E2 synthase that is functionally coupled with cyclooxygenase-1 in immediate prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis'', J Biol Chem (2000), 275, 32775-82.</ref>, whereas mPGES-1/-2 are Golgi membrane-associated proteins which only become cytosolic following spontaneous cleavage of a hydrophobic domain <ref>Murakami, M. Nakashima, K. Kamei, D. Masuda, S. Ishikawa, Y. Ishii, T. Ohmiya, Y. Watanabe, K. Kudo, I., ''Cellular prostaglandin E2 production by membrane-bound prostaglandin E synthase-2 via both cyclooxygenases-1 and -2'', J Biol Chem (2003), 278, 37937-47.</ref><ref>Tanioka, T. Nakatani, Y. Semmyo, N. Murakami, M. Kudo, I., ''Molecular identification of cytosolic prostaglandin E2 synthase that is functionally coupled with cyclooxygenase-1 in immediate prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis'', J Biol Chem (2000), 275, 32775-82.</ref>. It has been suggested that a functional coupling of cPGES and COX-1 may occur in vitro as cPGES appears to convert only COX-1 derived PGH2 and not COX-2 derived PGH2 <ref>Tanioka, T. Nakatani, Y. Semmyo, N. Murakami, M. Kudo, I., ''Molecular identification of cytosolic prostaglandin E2 synthase that is functionally coupled with cyclooxygenase-1 in immediate prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis'', J Biol Chem (2000), 275, 32775-82.</ref>. Interestingly, the opposite has been observed for mPGES and COX-2 <ref>Murakami, M. Nakashima, K. Kamei, D. Masuda, S. Ishikawa, Y. Ishii, T. Ohmiya, Y. Watanabe, K. Kudo, I., ''Cellular prostaglandin E2 production by membrane-bound prostaglandin E synthase-2 via both cyclooxygenases-1 and -2'', J Biol Chem (2003), 278, 37937-47.</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
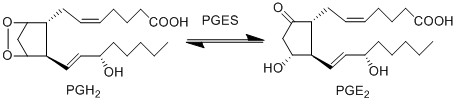
== Reaction == | == Reaction == | ||
[[File:R10_PGH2_-_PGE2.jpg|center|500px]] | [[File:R10_PGH2_-_PGE2.jpg|center|500px]] | ||
| Line 5: | Line 9: | ||
==Chemical equation== | ==Chemical equation== | ||
| − | <center><math> | + | <center><math> PGH2 \rightleftharpoons PGE2 </math></center> |
== Rate equation == | == Rate equation == | ||
| + | [[File:R10.PNG|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Parameters == | ||
| + | === K<sub>ms</sub> === | ||
| + | {|class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| + | |+ style="text-align: left;" | Literature values | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Value | ||
| + | ! Units | ||
| + | ! Species | ||
| + | ! Notes | ||
| + | ! Weight | ||
| + | ! Reference | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |1.6E-01 ± 4.00E-03 | ||
| + | |<math> mM </math> | ||
| + | |Human | ||
| + | |Expression Vector: E. Coli | ||
| + | Enzyme: PGES | ||
| + | pH: 8 | ||
| + | Temperature: 37 | ||
| + | |512 | ||
| + | |<ref name="Pettersson2005"> [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16399384 Pettersson P. , "Identification of beta-trace as prostaglandin D synthase.'' FASEB J. 2010 Dec;24(12):4668-77. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-164863. Epub 2010 Jul 28.]</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |2.15E-01 | ||
| + | |<math> mM </math> | ||
| + | |Human | ||
| + | |Wild Type Enzyme | ||
| + | |1024 | ||
| + | |<ref name="Hamza2010"> [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20369883 Hamza A. , "Understanding microscopic binding of human microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) trimer with substrate PGH2 and cofactor GSH: insights from computational alanine scanning and site-directed mutagenesis.'' J Phys Chem B. 2010 Apr 29;114(16):5605-16. doi: 10.1021/jp100668y.]</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |1.49E-02 | ||
| + | |<math> mM </math> | ||
| + | |Human | ||
| + | |Expression Vector: E. Coli | ||
| + | Enzyme: PGES | ||
| + | pH: Unknown | ||
| + | Temperature: Unknown | ||
| + | |||
| + | Other: cPGES, casein kinase II and Hsp90 | ||
| + | |64 | ||
| + | |<ref name="Kobayashi04"> [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15040786 Kobayashi T. , "Regulation of cytosolic prostaglandin E synthase by phosphorylation.'' Biochem J. 2004 Jul 1;381(Pt 1):59-69.]</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |6.66E-02 | ||
| + | |<math> mM </math> | ||
| + | |Human | ||
| + | |Expression Vector: E. Coli | ||
| + | Enzyme: PGES | ||
| + | pH: Unknown | ||
| + | Temperature: Unknown | ||
| + | |64 | ||
| + | |<ref name="Kobayashi04"></ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ style="text-align: left;" | Description of the PGES Kms distribution | ||
| + | ! Mode (mM) !! Confidence Interval !! Location parameter (µ) !! Scale parameter (σ) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1.97E-01 || 1.73E+00 || -1.39E+00 || 4.91E-01 | ||
| + | |} | ||
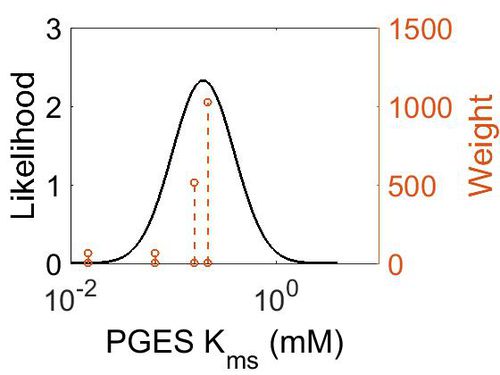
| + | [[Image:29.jpg|none|thumb|500px|The estimated probability distribution for PGES Kms. The value and weight of the literature values used to define the distribution are indicated by an orange dashed line. The x axis is plotted on a log-scale. ]] | ||
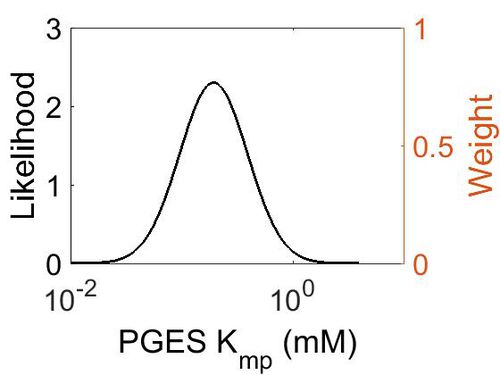
| − | == | + | === K<sub>mp</sub>=== |
| + | This is a “Dependent parameter”, meaning that the log-normal distribution for this parameter was calculated using multivariate distributions (this is discussed in detail[[Quantification of parameter uncertainty | here]]). As a result, no confidence interval factor or literature values were cited for this parameter. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ style="text-align: left;" | Description of the PGES Kmp distribution | ||
| + | ! Mode (mM) !! Location parameter (µ) !! Scale parameter (σ) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1.93E-01 || -1.15E+00 || 7.02E-01 (mM) | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:30.jpg|none|thumb|500px|The estimated probability distribution for PGES Kmp. The value and weight of the literature values used to define the distribution are indicated by an orange dashed line. The x axis is plotted on a log-scale. ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === k<sub>cat</sub>=== | ||
| + | {|class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| + | |+ style="text-align: left;" | Literature values | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Value | ||
| + | ! Units | ||
| + | ! Species | ||
| + | ! Notes | ||
| + | ! Weight | ||
| + | ! Reference | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 3000 ± 360 | ||
| + | | per minute | ||
| + | | Human | ||
| + | |Expression Vector: E. Coli. | ||
| + | Enzyme: Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthase | ||
| + | pH: 7.5 | ||
| + | Temperature: 37 | ||
| + | |1024 | ||
| + | | <ref name="Pettersson20005"> [www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16399384 Pettersson P., "Human microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 1: a member of the MAPEG protein superfamily.'' Methods Enzymol. 2005;401:147-61.]</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ style="text-align: left;" | Description of the PGES kcat distribution | ||
| + | ! Mode (min-1) !! Confidence Interval !! Location parameter (µ) !! Scale parameter (σ) | ||
| + | |- | ||
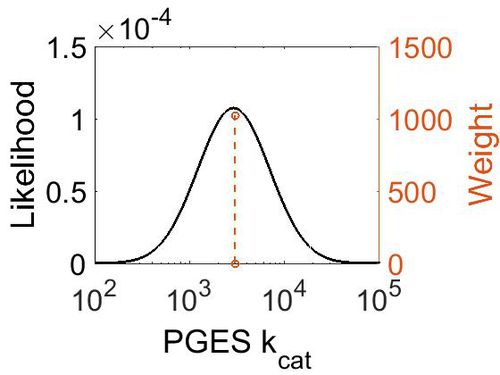
| + | | 2.98E+03 || 1.13E+00 || 8.01E+00 || 1.19E-01 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:31.jpg|none|thumb|500px|The estimated probability distribution for PGES kcat. The value and weight of the literature values used to define the distribution are indicated by an orange dashed line. The x axis is plotted on a log-scale. ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Enzyme concentration === | ||
| + | |||
| + | To convert the enzyme concentration from ppm to mM, the following [[Common equations#Enzyme concentration (mM)|equation]] was used. | ||
{|class="wikitable sortable" | {|class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| − | |+ style="text-align: left;" | | + | |+ style="text-align: left;" | Literature values |
|- | |- | ||
! Value | ! Value | ||
| Line 19: | Line 130: | ||
! Species | ! Species | ||
! Notes | ! Notes | ||
| + | ! Weight | ||
! Reference | ! Reference | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |220 |
| − | | | + | |<math> ppm </math> |
| − | | | + | |Human |
| − | | A | + | |Expression Vector: Placenta |
| − | | | + | Enzyme: PGES |
| + | pH: 7.5 | ||
| + | Temperature: 37 °C | ||
| + | |1024 | ||
| + | |<ref name="Wilhelm2014"> [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v509/n7502/pdf/nature13319.pdf M. Wilhelm ''Mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome'' Nature, 2014 509, 582–587]</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |75.3 | ||
| + | |<math> ppm </math> | ||
| + | |Human | ||
| + | |Expression Vector: Urinary Bladder | ||
| + | Enzyme: PGES | ||
| + | pH: 7.5 | ||
| + | Temperature: 37 °C | ||
| + | |1024 | ||
| + | |<ref name="Kim2014"> [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v509/n7502/pdf/nature13302.pdf M. Kim ''A draft map of the human proteome'' Nature, 2014 509, 575–581]</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |208 | ||
| + | |<math> ppm </math> | ||
| + | |Human | ||
| + | |Expression Vector: Stomach | ||
| + | Enzyme: PGES | ||
| + | pH: 7.5 | ||
| + | Temperature: 37 °C | ||
| + | |1024 | ||
| + | |<ref name="Wilhelm2014"> [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v509/n7502/pdf/nature13319.pdf M. Wilhelm ''Mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome'' Nature, 2014 509, 582–587]</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |28.1 | ||
| + | |<math> ppm </math> | ||
| + | |Human | ||
| + | |Expression Vector: Lung | ||
| + | Enzyme: PGES | ||
| + | pH: 7.5 | ||
| + | Temperature: 37 °C | ||
| + | |1024 | ||
| + | |<ref name="Kim2014"> [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v509/n7502/pdf/nature13302.pdf M. Kim ''A draft map of the human proteome'' Nature, 2014 509, 575–581]</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |11.6 | ||
| + | |<math> ppm </math> | ||
| + | |Human | ||
| + | |Expression Vector: Colon | ||
| + | Enzyme: PGES | ||
| + | pH: 7.5 | ||
| + | Temperature: 37 °C | ||
| + | |1024 | ||
| + | |<ref name="Kim2014"> [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v509/n7502/pdf/nature13302.pdf M. Kim ''A draft map of the human proteome'' Nature, 2014 509, 575–581]</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ style="text-align: left;" | Description of the PGES concentration distribution | ||
| + | ! Mode (ppm) !! Mode (mM) !! Confidence Interval !! Location parameter (µ) !! Scale parameter (σ) | ||
| + | |- | ||
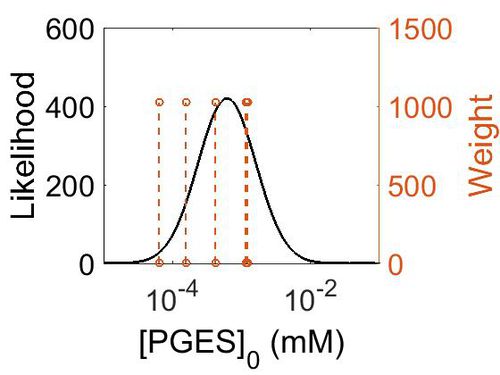
| + | | 7.49E+01 ||4.15E-04 || 3.15E+00 || 5.03E+00 || 8.44E-01 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:162.jpg|none|thumb|500px|The estimated probability distribution for PGES concentration. The value and weight of the literature values used to define the distribution are indicated by an orange dashed line. The x axis is plotted on a log-scale. ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === K<sub>eq </sub> === | ||
{|class="wikitable sortable" | {|class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| − | |+ style="text-align: left;" | | + | |+ style="text-align: left;" | Gibbs Free Energy Change |
|- | |- | ||
! Value | ! Value | ||
| Line 35: | Line 203: | ||
! Species | ! Species | ||
! Notes | ! Notes | ||
| + | ! Weight | ||
! Reference | ! Reference | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |5.72 |
| − | | | + | |kcal/mol |
| − | | | + | |Not stated |
| − | | | + | |Estimated |
| − | | | + | Enzyme: PGES |
| + | Substrate: Arachidonate | ||
| + | Product: PGE2 | ||
| + | pH: 7.3 | ||
| + | ionic strength: 0.25 | ||
| + | |64 | ||
| + | |<ref name="MetaCyc”>[http://metacyc.org/META/NEW-IMAGE?type=REACTION&object=PROSTAGLANDIN-E-SYNTHASE-RXN Caspi et al 2014, "The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of Pathway/Genome Databases," Nucleic Acids Research 42:D459-D471]</ref> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ style="text-align: left;" | Description of the PGES Keq distribution | ||
| + | ! Mode !! Confidence Interval !! Location parameter (µ) !! Scale parameter (σ) | ||
| + | |- | ||
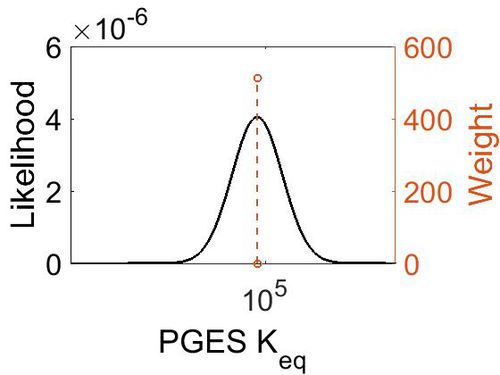
| + | | 7.46E+04 || 1.00E+01 || 1.20E+01 || 8.90E-01 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:32.jpg|none|thumb|500px|The estimated probability distribution for PGES Keq. The value and weight of the literature values used to define the distribution are indicated by an orange dashed line. The x axis is plotted on a log-scale. ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
== Related Reactions == | == Related Reactions == | ||
* [[Transformation of AA to PGH2 |Transformation of AA to PGH2]] | * [[Transformation of AA to PGH2 |Transformation of AA to PGH2]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:48, 21 August 2019
PGE2 is produced by the isomerisation of the PGH2 peroxide, into a ketone at C9 and an alcohol at C11 by PGES, yielding PGE2. This reaction is catalysed by isoforms of PGES, such as cPGES (also known as PGES-3), mPGES-1 and mPGES-2 [1]. cPGES is the cytosolic isoform of PGES which is constitutively expressed in the cytosol of various cells [2], whereas mPGES-1/-2 are Golgi membrane-associated proteins which only become cytosolic following spontaneous cleavage of a hydrophobic domain [3][4]. It has been suggested that a functional coupling of cPGES and COX-1 may occur in vitro as cPGES appears to convert only COX-1 derived PGH2 and not COX-2 derived PGH2 [5]. Interestingly, the opposite has been observed for mPGES and COX-2 [6].
Contents
Reaction
Chemical equation
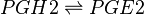
Rate equation
Parameters
Kms
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Weight | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.6E-01 ± 4.00E-03 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: E. Coli
Enzyme: PGES pH: 8 Temperature: 37 |
512 | [7] |
| 2.15E-01 | 
|
Human | Wild Type Enzyme | 1024 | [8] |
| 1.49E-02 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: E. Coli
Enzyme: PGES pH: Unknown Temperature: Unknown Other: cPGES, casein kinase II and Hsp90 |
64 | [9] |
| 6.66E-02 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: E. Coli
Enzyme: PGES pH: Unknown Temperature: Unknown |
64 | [9] |
| Mode (mM) | Confidence Interval | Location parameter (µ) | Scale parameter (σ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.97E-01 | 1.73E+00 | -1.39E+00 | 4.91E-01 |
Kmp
This is a “Dependent parameter”, meaning that the log-normal distribution for this parameter was calculated using multivariate distributions (this is discussed in detail here). As a result, no confidence interval factor or literature values were cited for this parameter.
| Mode (mM) | Location parameter (µ) | Scale parameter (σ) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.93E-01 | -1.15E+00 | 7.02E-01 (mM) |
kcat
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Weight | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3000 ± 360 | per minute | Human | Expression Vector: E. Coli.
Enzyme: Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthase pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 |
1024 | [10] |
| Mode (min-1) | Confidence Interval | Location parameter (µ) | Scale parameter (σ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.98E+03 | 1.13E+00 | 8.01E+00 | 1.19E-01 |
Enzyme concentration
To convert the enzyme concentration from ppm to mM, the following equation was used.
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Weight | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 220 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Placenta
Enzyme: PGES pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
1024 | [11] |
| 75.3 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Urinary Bladder
Enzyme: PGES pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
1024 | [12] |
| 208 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Stomach
Enzyme: PGES pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
1024 | [11] |
| 28.1 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Lung
Enzyme: PGES pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
1024 | [12] |
| 11.6 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Colon
Enzyme: PGES pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
1024 | [12] |
| Mode (ppm) | Mode (mM) | Confidence Interval | Location parameter (µ) | Scale parameter (σ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.49E+01 | 4.15E-04 | 3.15E+00 | 5.03E+00 | 8.44E-01 |
Keq
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Weight | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.72 | kcal/mol | Not stated | Estimated
Enzyme: PGES Substrate: Arachidonate Product: PGE2 pH: 7.3 ionic strength: 0.25 |
64 | [13] |
| Mode | Confidence Interval | Location parameter (µ) | Scale parameter (σ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7.46E+04 | 1.00E+01 | 1.20E+01 | 8.90E-01 |
References
- ↑ Samuelsson, B. Morgenstern, R. Jakobsson, P. J. , Membrane prostaglandin E synthase-1: a novel therapeutic target, Pharmacol Rev (2007), 59, 207-24.
- ↑ Tanioka, T. Nakatani, Y. Semmyo, N. Murakami, M. Kudo, I., Molecular identification of cytosolic prostaglandin E2 synthase that is functionally coupled with cyclooxygenase-1 in immediate prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis, J Biol Chem (2000), 275, 32775-82.
- ↑ Murakami, M. Nakashima, K. Kamei, D. Masuda, S. Ishikawa, Y. Ishii, T. Ohmiya, Y. Watanabe, K. Kudo, I., Cellular prostaglandin E2 production by membrane-bound prostaglandin E synthase-2 via both cyclooxygenases-1 and -2, J Biol Chem (2003), 278, 37937-47.
- ↑ Tanioka, T. Nakatani, Y. Semmyo, N. Murakami, M. Kudo, I., Molecular identification of cytosolic prostaglandin E2 synthase that is functionally coupled with cyclooxygenase-1 in immediate prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis, J Biol Chem (2000), 275, 32775-82.
- ↑ Tanioka, T. Nakatani, Y. Semmyo, N. Murakami, M. Kudo, I., Molecular identification of cytosolic prostaglandin E2 synthase that is functionally coupled with cyclooxygenase-1 in immediate prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis, J Biol Chem (2000), 275, 32775-82.
- ↑ Murakami, M. Nakashima, K. Kamei, D. Masuda, S. Ishikawa, Y. Ishii, T. Ohmiya, Y. Watanabe, K. Kudo, I., Cellular prostaglandin E2 production by membrane-bound prostaglandin E synthase-2 via both cyclooxygenases-1 and -2, J Biol Chem (2003), 278, 37937-47.
- ↑ Pettersson P. , "Identification of beta-trace as prostaglandin D synthase. FASEB J. 2010 Dec;24(12):4668-77. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-164863. Epub 2010 Jul 28.
- ↑ Hamza A. , "Understanding microscopic binding of human microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) trimer with substrate PGH2 and cofactor GSH: insights from computational alanine scanning and site-directed mutagenesis. J Phys Chem B. 2010 Apr 29;114(16):5605-16. doi: 10.1021/jp100668y.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Kobayashi T. , "Regulation of cytosolic prostaglandin E synthase by phosphorylation. Biochem J. 2004 Jul 1;381(Pt 1):59-69.
- ↑ [www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16399384 Pettersson P., "Human microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 1: a member of the MAPEG protein superfamily. Methods Enzymol. 2005;401:147-61.]
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 M. Wilhelm Mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome Nature, 2014 509, 582–587
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 M. Kim A draft map of the human proteome Nature, 2014 509, 575–581
- ↑ Caspi et al 2014, "The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of Pathway/Genome Databases," Nucleic Acids Research 42:D459-D471