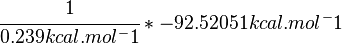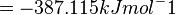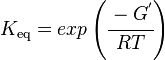Difference between revisions of "Limonene-6-Hydroxylase (L6H)"
Aliah.hawari (talk | contribs) (→Reaction catalysed) |
Aliah.hawari (talk | contribs) (→Published Kinetic Parameter Values) |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
This enzyme is also known as (S)-limonene 6-monooxygenase, (-)-limonene 6-hydroxylase, (-)-limonene 6-monooxygenase, (-)-limonene,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (6-hydroxylating) | This enzyme is also known as (S)-limonene 6-monooxygenase, (-)-limonene 6-hydroxylase, (-)-limonene 6-monooxygenase, (-)-limonene,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (6-hydroxylating) | ||
| − | = | + | === Reaction catalysed === |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == Reaction catalysed == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
| Line 20: | Line 13: | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| − | == Metabolite and Enzyme Background Information == | + | === Metabolite and Enzyme Background Information === |
Long metabolite and enzyme names are abbreviated in the model for clarity and standard identification purposes. | Long metabolite and enzyme names are abbreviated in the model for clarity and standard identification purposes. | ||
| Line 78: | Line 71: | ||
| ChEMBL | | ChEMBL | ||
| PubChem | | PubChem | ||
| − | | LIMONENE-6-MONOOXYGENASE-RXN | + | | [http://biocyc.org/META/NEW-IMAGE?type=REACTION&object=--LIMONENE-6-MONOOXYGENASE-RXN&redirect=T LIMONENE-6-MONOOXYGENASE-RXN] |
|- | |- | ||
| Metabolite | | Metabolite | ||
| Line 93: | Line 86: | ||
== Equation Rate == | == Equation Rate == | ||
| + | This reaction is modelled using the reversible Michaelis-Menten equation, with two substrates; Limonene and NADPH, and two products; Carveol and NADP. | ||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
| − | V_\mathrm{ | + | V_\mathrm{L6H} = Vmax_\mathrm{forward} * \cfrac {\cfrac{[Limonene]}{Km_\mathrm{Limonene}} * \left ( 1 - \cfrac {[Limonene]*[PP]}{[GPP]*K_\mathrm{eq}} \right )}{1 + \cfrac {[GPP]}{Km_\mathrm{GPP}} + \cfrac {[Limonene]}{Km_\mathrm{Limonene}} + \cfrac {[PP]}{Km_\mathrm{PP}} + \cfrac {[Limonene]*[PP]}{Km_\mathrm{Limonene}*Km_\mathrm{PP}}} |
</math> | </math> | ||
| Line 103: | Line 97: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| − | ! scope="col" style="width: 50px;" | Parameter | + | ! scope="col" style="width: 50px;" | Parameter |
! scope="col" style="width: 225px;" | Description | ! scope="col" style="width: 225px;" | Description | ||
| − | ! | + | ! Units |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | V<sub>L6H</sub> || Net reaction rate for Limonene-6-Hydroxylase || Unit | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | V<sub> | + | | V<sub>max<sub>forward</sub></sub> || Maximum reaction rate towards the production of trans-carveol || Unit |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Km<sub>limonene</sub> || Michaelis-Menten constant for Limonene || Unit |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Km<sub> | + | | Km<sub>carveol</sub> || Michaelis-Menten constant for trans-carveol || Unit |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Km<sub> | + | | Km<sub>NADPH</sub> || Michaelis-Menten constant for NADPH || Unit |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Km<sub> | + | | Km<sub>NADP</sub> || Michaelis-Menten constant for NADP || Unit |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | K<sub>eq</sub> || Equilibrium constant || | + | | K<sub>eq</sub> || Equilibrium constant || Unit |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | [ | + | | [Limonene] || Limonene concentration || Unit |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | [ | + | | [Carveol] || trans-carveol concentration || Unit |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [NADPH]|| NADPH concentration || Unit | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [NADP]|| NADP concentration || Unit | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 130: | Line 129: | ||
=== Calculating the Equilibrium Constant === | === Calculating the Equilibrium Constant === | ||
| − | The equilibrium constant can be calculated using the Van't Hoff Isotherm equation: | + | The equilibrium constant can be calculated using the Van't Hoff Isotherm equation, which requires the information on the enzyme's standard Gibbs free energy <ref name="Liebermeister2005"> Liebermeister, W. & Klipp, E. 2005. http://pubman.mpdl.mpg.de/pubman/item/escidoc:1585440/component/escidoc:1585439/Liebermeister+et+al.+-+IEE+Proc.-Syst.+Biol.pdf."Biochemical networks with uncertain parameters." IEE Proc-Syst. Biol. 152(3): 97-105 </ref>. |
| + | |||
| + | ==== Standard Gibbs Free energy ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Standard Gibbs free energy is '''-92.52051 kcal·mol<sup>-1</sup> ''' <ref name= "Latendresse2013"> Latendresse, M. 2013. http://www.biocyc.org/PGDBConceptsGuide.shtml#gibbs. "Computing Gibbs Free Energy of Compounds and Reactions in MetaCyc." </ref> according to MetaCyc [[http://biocyc.org/META/NEW-IMAGE?type=REACTION&object=--LIMONENE-6-MONOOXYGENASE-RXN&redirect=T]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | SI derived unit for Gibbs free energy is Joules per mol (J mol<sup>-1</sup>). 1 kJ·mol<sup>−1</sup> is equal to 0.239 kcal·mol<sup>−1</sup>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore, the Gibbs free energy for L6H in kJ mol<sup>-1</sup> is: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | \cfrac {1}{0.239 kcal.mol^-1} * -92.52051 kcal.mol^-1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = -387.115 kJmol^-1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== The equilibrium constant ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using the Van't Hoff Isotherm equation: | ||
| + | |||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
| − | K_\mathrm{eq} = exp \left ( \cfrac {- | + | K_\mathrm{eq} = exp \left ( \cfrac {-∆G^{°'}}{RT} \right ) |
</math> | </math> | ||
| Line 140: | Line 164: | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| − | = exp \left ( \cfrac {-( | + | = exp \left ( \cfrac {-(-387.1151 \text { kJmol}^{-1})}{ (8.31 \text{ JK}^{-1} \text { mol}^{-1} * 289 K} \right ) |
</math> | </math> | ||
| Line 146: | Line 170: | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| − | = exp \left ( \cfrac { | + | = exp \left ( \cfrac { 387.1151\text { kJmol}^{-1} }{ 2401.59 \text{ JK}^{-1}\text { mol}^{-1} }\right) |
</math> | </math> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| − | = exp \left ( \cfrac{ | + | = exp \left ( \cfrac{ 387115.1 \text { Jmol}^{-1}}{2401.59 \text{ JK}^{-1}\text { mol}^{-1}} \right) |
</math> | </math> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| − | =exp \left ( | + | =exp \left ( 161.19117 \right ) |
</math> | </math> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| − | = | + | = 1.0103 \mathsf{x} 10^\mathsf{70} |
| + | |||
| + | |||
</math> | </math> | ||
| Line 168: | Line 194: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="width: 50pt;" | K<sub>eq</sub> | | style="width: 50pt;" | K<sub>eq</sub> | ||
| − | + | | Equilibrium constant | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | - | + | | -∆G<sup>°</sup> || Gibbs free energy change. For L6H it is 387.1151 kJmol<sup>-1</sup> |
|- | |- | ||
| R || Gas constant with a value of 8.31 JK<sup>-1</sup>mol<sup>-1</sup> | | R || Gas constant with a value of 8.31 JK<sup>-1</sup>mol<sup>-1</sup> | ||
| Line 177: | Line 203: | ||
| T || Temperature which is always expressed in kelvin | | T || Temperature which is always expressed in kelvin | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Published Kinetic Parameter Values === | === Published Kinetic Parameter Values === | ||
| Line 194: | Line 216: | ||
! style="border: 1px solid black; padding: 5px; background: #ffdead; width: 50px;" | References | ! style="border: 1px solid black; padding: 5px; background: #ffdead; width: 50px;" | References | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 20 |
| − | | | + | | µM |
| − | | | + | | Carveol |
| + | | forward | ||
| + | | Mentha sp. | ||
| + | | <ref name="Karp1990">Karp, F. et. al. 1990. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2297225 "Monoterpene biosynthesis: Specificity of the hydroxylations of (-)-Limonene by enzyme preparations from Peppermint (Mentha piperita), Spearmint (Mentha spicata), and Perilla (Perilla frutescens) leaves", Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 276(1):219-226]</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | value | ||
| + | | µM | ||
| + | | susbstrate | ||
| directionality | | directionality | ||
| − | | organism | + | | organism |
| − | | | + | | ref |
| − | |- | + | |- |
| + | | value | ||
| + | | µM | ||
| + | | susbstrate | ||
| + | | directionality | ||
| + | | organism | ||
| + | | ref | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | value | ||
| + | | µM | ||
| + | | susbstrate | ||
| + | | directionality | ||
| + | | organism | ||
| + | | ref | ||
| + | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | [[File:LimSynth_01_Km.png|center|frame|μ :-5.05354 , σ : 0.49474]] | + | [[File:LimSynth_01_Km.png|center|frame|'''MOCK DISTRIBUTION''' μ :-5.05354 , σ : 0.49474]] |
==== Vmax values ==== | ==== Vmax values ==== | ||
| Line 215: | Line 258: | ||
! style="border: 1px solid black; padding: 5px; background: #ffdead; width: 50px;" | References | ! style="border: 1px solid black; padding: 5px; background: #ffdead; width: 50px;" | References | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 64 |
| + | | nmol/mg.h | ||
| + | | forward | ||
| + | | Mentha sp. | ||
| + | | <ref name="Karp1990"></ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | val | ||
| µmol/min/mg (unit) | | µmol/min/mg (unit) | ||
| directionality | | directionality | ||
Latest revision as of 17:49, 17 March 2016
You can go back to main page of the kinetic model here.
Contents
What we know
This enzyme is also known as (S)-limonene 6-monooxygenase, (-)-limonene 6-hydroxylase, (-)-limonene 6-monooxygenase, (-)-limonene,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (6-hydroxylating)
Reaction catalysed
Metabolite and Enzyme Background Information
Long metabolite and enzyme names are abbreviated in the model for clarity and standard identification purposes.
| Metabolite | Abbreviation | Chemical Formula | Molar mass (g/mol) | ChEBI | ChEMBL | PubChem | MetaCyc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (-)-4S-limonene | Limonene | C10H16 | 136.24 | 15384 | 449062 | 22311 or 439250 | |
| (-)-trans-carveol | carveol | Chemical Formula | Molar mass (g/mol) | ChEBI | ChEMBL | PubChem | MetaCyc |
| NADPH | NADPH | Chemical Formula | Molar mass (g/mol) | ChEBI | ChEMBL | PubChem | MetaCyc |
| NADP | NADP | Chemical Formula | Molar mass (g/mol) | ChEBI | ChEMBL | PubChem | MetaCyc |
| Limonene-6-hydroxylase | L6H | Chemical Formula | Molar mass (g/mol) | ChEBI | ChEMBL | PubChem | LIMONENE-6-MONOOXYGENASE-RXN |
| Metabolite | Abbreviation | Chemical Formula | Molar mass (g/mol) | ChEBI | ChEMBL | PubChem | MetaCyc |
Equation Rate
This reaction is modelled using the reversible Michaelis-Menten equation, with two substrates; Limonene and NADPH, and two products; Carveol and NADP.
| Parameter | Description | Units |
|---|---|---|
| VL6H | Net reaction rate for Limonene-6-Hydroxylase | Unit |
| Vmaxforward | Maximum reaction rate towards the production of trans-carveol | Unit |
| Kmlimonene | Michaelis-Menten constant for Limonene | Unit |
| Kmcarveol | Michaelis-Menten constant for trans-carveol | Unit |
| KmNADPH | Michaelis-Menten constant for NADPH | Unit |
| KmNADP | Michaelis-Menten constant for NADP | Unit |
| Keq | Equilibrium constant | Unit |
| [Limonene] | Limonene concentration | Unit |
| [Carveol] | trans-carveol concentration | Unit |
| [NADPH] | NADPH concentration | Unit |
| [NADP] | NADP concentration | Unit |
Strategies for estimating the kinetic parameter values
Calculating the Equilibrium Constant
The equilibrium constant can be calculated using the Van't Hoff Isotherm equation, which requires the information on the enzyme's standard Gibbs free energy [1].
Standard Gibbs Free energy
Standard Gibbs free energy is -92.52051 kcal·mol-1 [2] according to MetaCyc [[1]].
SI derived unit for Gibbs free energy is Joules per mol (J mol-1). 1 kJ·mol−1 is equal to 0.239 kcal·mol−1.
Therefore, the Gibbs free energy for L6H in kJ mol-1 is:
The equilibrium constant
Using the Van't Hoff Isotherm equation:
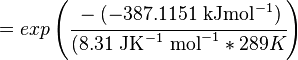
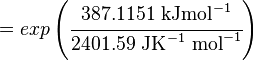

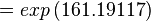
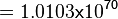
where;
| Keq | Equilibrium constant |
| -∆G° | Gibbs free energy change. For L6H it is 387.1151 kJmol-1 |
| R | Gas constant with a value of 8.31 JK-1mol-1 |
| T | Temperature which is always expressed in kelvin |
Published Kinetic Parameter Values
Km Values
| Km (mM) | Unit | Substrate / Product | Directionality | Organism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | µM | Carveol | forward | Mentha sp. | [3] |
| value | µM | susbstrate | directionality | organism | ref |
| value | µM | susbstrate | directionality | organism | ref |
| value | µM | susbstrate | directionality | organism | ref |
Vmax values
| Vmax | Unit | Directionality | Organism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64 | nmol/mg.h | forward | Mentha sp. | [3] |
| val | µmol/min/mg (unit) | directionality | Organism | References |
Kcat values
| Kcat | Unit | Organism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| value | s-1 | Organism | ref e.g. Alonso 1992 [4] |
Extracting Information from (INSERT SUBSTRATE/PRODUCT) Production Rates
| Amount produced (mg/L) | Time (H) | Organism | Description | Reaction Flux (µM/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
| X | X | Y | Z | Z |
Published Kinetic Parameter Values
| Km (mM) | Vmax | Kcat (s-1) | Kcat/Km | Organism | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00125 | - | - | Z | A -> B | |
| 0.0018 | - | - | - | Z | A -> B |
| Y | Y | Y | Y | Z | A -> B |
| Y | Y | Y | Y | Z | A -> B |
| Y | Y | - | - | Z | A -> B |
| Y | - | Y | - | Z | GPP -> B |
| Y | - | Y | - | Z | GPP -> B |
| x | - | y | - | Z. | A -> B |
Detailed descriptions of kinetic values used in this model
A more detailed description of the kinetic values listed above can be found here.
Simulations
References
- ↑ Liebermeister, W. & Klipp, E. 2005. http://pubman.mpdl.mpg.de/pubman/item/escidoc:1585440/component/escidoc:1585439/Liebermeister+et+al.+-+IEE+Proc.-Syst.+Biol.pdf."Biochemical networks with uncertain parameters." IEE Proc-Syst. Biol. 152(3): 97-105
- ↑ Latendresse, M. 2013. http://www.biocyc.org/PGDBConceptsGuide.shtml#gibbs. "Computing Gibbs Free Energy of Compounds and Reactions in MetaCyc."
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Karp, F. et. al. 1990. "Monoterpene biosynthesis: Specificity of the hydroxylations of (-)-Limonene by enzyme preparations from Peppermint (Mentha piperita), Spearmint (Mentha spicata), and Perilla (Perilla frutescens) leaves", Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 276(1):219-226
- ↑ Alonso et. al. 1992. "Purification of 4S-Limonene Synthase, a Monoterpene Cyclase from the Glandular Trichomes of Peppermint (Mentha x piperita) and Spearmint (Mentha spicata)", The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267(11):7582-7587
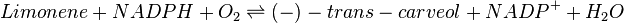
![V_\mathrm{L6H} = Vmax_\mathrm{forward} * \cfrac {\cfrac{[Limonene]}{Km_\mathrm{Limonene}} * \left ( 1 - \cfrac {[Limonene]*[PP]}{[GPP]*K_\mathrm{eq}} \right )}{1 + \cfrac {[GPP]}{Km_\mathrm{GPP}} + \cfrac {[Limonene]}{Km_\mathrm{Limonene}} + \cfrac {[PP]}{Km_\mathrm{PP}} + \cfrac {[Limonene]*[PP]}{Km_\mathrm{Limonene}*Km_\mathrm{PP}}}](/wiki/images/math/6/e/6/6e68d78babd5acdaa586f13c500e95dd.png)