Sos-Removal
The binding affinity of phosphorylated Sos to Grb2 is less than of unphosphorylated Sos(Hu and Bowtell, 1996)[1]. So the inactivation is assumed to occure due to a phosphorylation. Experiments showed that this phosphorylation is catalyzed by Erk. However there are two different kinds of active Erk: the mono-(pT) and the biphosphorylated Erk (pTpY), which show different activities.(Kholodenko et al. 1999) [2]
Binding Reaction
active Sos-Removal:
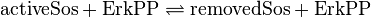
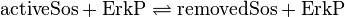
inactive Sos-Removal:
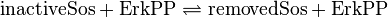
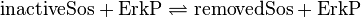
Kinetic Equation
active Sos-Removal:
![v_{\text{Sos-Removal}} = \frac{k_{cat} \cdot [\text{ErkPP}] \cdot [\text{activeSos}] \cdot (1-\frac{[\text{removedSos}]}{[\text{activeSos}] \cdot K_{eq}})}{Km_{\text{activeSos}} \cdot (1 + \frac{[\text{activeSos}]}{Km_{\text{activeSos}}} + \frac{[\text{removedSos}]}{Km_{\text{removedSos}}})}](/wiki/images/math/6/e/9/6e98e31ac2537f16925ee8679a71e801.png)
![v_{\text{Sos-Removal}} = \frac{k_{cat} \cdot [\text{ErkP}] \cdot [\text{activeSos}] \cdot (1-\frac{[\text{removedSos}]}{[\text{activeSos}] \cdot K_{eq}})}{Km_{\text{activeSos}} \cdot (1 + \frac{[\text{activeSos}]}{Km_{\text{activeSos}}} + \frac{[\text{removedSos}]}{Km_{\text{removedSos}}})}](/wiki/images/math/e/9/6/e9658b29c219b1dbb5fdaf4ccb540281.png)
inactive Sos-Removal:
![v_{\text{Sos-Removal}} = \frac{k_{cat} \cdot [\text{ErkPP}] \cdot [\text{inactiveSos}] \cdot (1-\frac{[\text{removedSos}]}{[\text{inactiveSos}] \cdot K_{eq}})}{Km_{\text{inactiveSos}} \cdot (1 + \frac{[\text{inactiveSos}]}{Km_{\text{inactiveSos}}} + \frac{[\text{removedSos}]}{Km_{\text{removedSos}}})}](/wiki/images/math/b/7/d/b7d0735f0d6987806a05948d5862b9ee.png)
![v_{\text{Sos-Removal}} = \frac{k_{cat} \cdot [\text{ErkP}] \cdot [\text{inactiveSos}] \cdot (1-\frac{[\text{removedSos}]}{[\text{inactiveSos}] \cdot K_{eq}})}{Km_{\text{inactiveSos}} \cdot (1 + \frac{[\text{inactiveSos}]}{Km_{\text{inactiveSos}}} + \frac{[\text{removedSos}]}{Km_{\text{removedSos}}})}](/wiki/images/math/6/2/c/62c18e435878f8c35ce14a79196bb339.png)
final Parameter
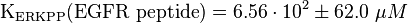
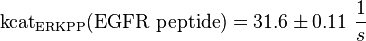
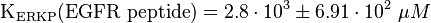
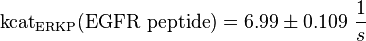
alternative values (Xu et al (2010)[3]):
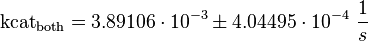
Parameter
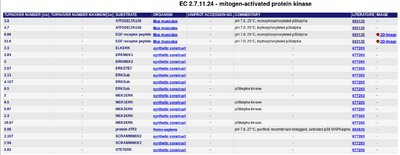
Data found in BRENDA for EGF receptor peptide as substrate (EC 2.7.11.24- mitogen-activated protein kinase), which is published by Zhang et al. (2008) [4] is used.
KEGFR peptide(residues 661-681)(ERKPP) = 656 ± 62 μM ; pH7, 25 °C, biphosphorylated p38α, mouse
kcatEGFR peptide(residues 661-681)(ERKPP) = 31.6 ± 1.1 s-1 pH7, 25 °C, biphosphorylated p38α, mouse
KEGFR peptide(residues 661-681)(ERKP) = 2800 ± 691 μM pH7, 25 °C, p38α pT, mouse
KcatEGFR peptide(residues 661-681)(ERKP) = 6.99 ± 1.09 s-1 ; pH7, 25 °C, p38α pT, mouse
KmP value and equilibrium constant
The Km value for the product is assumed to be similar to but slightly smaller than the the Km value of the substrate because of the similarity of the both species. Therefore the Km value of the substrate is multiplied by 0.95 to gain the one of the product and the uncertainty is increased by increasing the error on Kmsubstrate by 50%.
For information about the equilibrium constant please see here.
References
- ↑ Hu Y. and Bowtell D.D. (1996) "Sos 1 rapidly associates with Grb2 and is hypophosphorylated when complexed with the EGF receptor after EGF stimulation." Oncogene 12.9:1865-1872 (pmid:8649846)
- ↑ Kholodenko et al. (1999) "Quantification of short term signaling by the epidermal growth factor receptor." J Biol Chem 274.42:30169-30181 (pmid:10514507)
- ↑ Tian-Rui Xu et al. (2010) "Inferring signaling pathway topologies from multiple perturbation measurements of specific biochemical species." Sci Signal. 3(134):ra20. (pmid:20234003)
- ↑ Zhang et al. (2008) "Enzymatic activity and substrate specificity of mitogen-activated protein kinase p38alpha in different phosphorylation states" J. Biol. Chem. 283,26591-26601