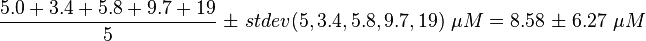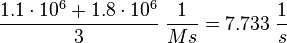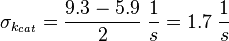RasRap1-Inactivation
Reaction
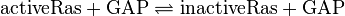
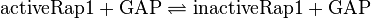
Kinetic Equation
![v_{\text{Ras-Inactivation}} = \frac{\text{k}_{\text{cat}} \cdot [\text{GAP}] \cdot [\text{activeRas}] \cdot (1-\frac{[\text{inactiveRas}]}{[\text{activeRas}] \cdot \text{K}_{\text{eq}}})}{\text{Km}_{\text{activeRas}} \cdot (1 + \frac{[\text{activeRas}]}{\text{Km}_{\text{activeRas}}} + \frac{[\text{inactiveRas}]}{\text{Km}_{\text{inactiveRas}}})}](/wiki/images/math/c/f/5/cf5b1b4ebcf47a1588515a1a4ae880ed.png)
![v_{\text{Rap1-Inactivation}} = \frac{\text{k}_{\text{cat}} \cdot [\text{GAP}] \cdot [\text{activeRap1}] \cdot (1-\frac{[\text{inactiveRap1}]}{[\text{activeRap1}] \cdot \text{K}_{\text{eq}}})}{\text{Km}_{\text{activeRap1}} \cdot (1 + \frac{[\text{activeRap1}]}{\text{Km}_{\text{activeRap1}}} + \frac{[\text{inactiveRap1}]}{\text{Km}_{\text{inactiveRap1}}})}](/wiki/images/math/6/f/2/6f2724133d99ed8ca18166c9b2604502.png)
General Information
The inactivation of Ras is du to its intrinsic hydrolase function. This process is accelerated by a further GTPase-activating protein (GAP). Because Ras and Rap1 are similiar enzymes [1], the same parameter for both inactivation reactions are used. And the standard deviation of Ras is assumed to be 1.5 times larger than the measured one, and the for Rap1 1.75 times larger, because it the measurement were done with Ras. As equilibrium constant the same constant as for the activation is used.
final Parameter
Inactivation of Ras:
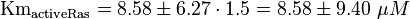
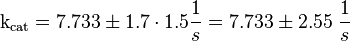
Inactivation of Rap1:
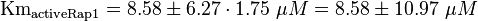
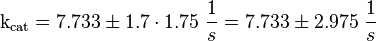
Parameter
| Notes | References |
|---|---|
| The five measured Km values are used to calculate the Km value and a first estimation for the standard deviation. This standard deviation is then for Ras increased by 1.5 and for Rap by 1.75.
Calculation of Km
Calculation of kcat
To estimate the error the difference between the largest and the smallest value is calculated and set to σ.
|
 Ahmadian et al. (1996)[2] |
|
KmactiveRas = 9.7 μM (GAP) Gideon P. et al. (1992)[3] |
KmP value and equilibrium constant
The Km value for the product is assumed to be similar to but slightly higher than the the Km value of the substrate because of the similarity of the both species. Therefore the Km value of the substrate is multiplied by 1.05 to gain the one of the product and the uncertainty is increased by increasing the error on Kmsubstrate by 50%.
For information about the equilibrium constant please see here.
References
- ↑ Raaijmakers J. and Bos1 J.(2009) "Specificity in Ras and Rap Signaling The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284,10995-10999.
- ↑ Ahmadian M. et al. (1996) "Individual rate constants for the interaction of Ras proteins with GTPase-activating proteins determined by fluorescence spectroscopy. Biochemistry 36.15,4535-4541 DOI:10.1021/bi962556y. (pmid:9109662)
- ↑ Gideon P. et al. (1992) "Mutational and kinetic analyses of the GTPase-activating protein(GAP)-p21 interaction; The C-terminal domain of GAP is not sufficient for full activity." Molecular and Cellular Biology 12(5),2050-2056 (pmid:1569940)