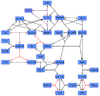
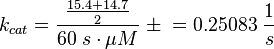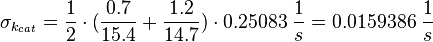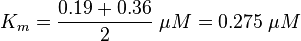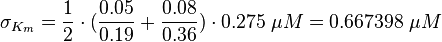MEK-Activation(BRaf)
Binding Reaction
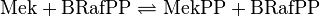
Kinetic Equation
![v_{\text{Mek-Activation}} = \frac{k_{\text{cat}} \cdot [\text{BRafPP}] \cdot [\text{Mek}] \cdot (1-\frac{[\text{MekPP}]}{[\text{Mek}] \cdot K_{\text{eq}}})}{Km_{\text{Mek}} \cdot (1 + \frac{[\text{Mek}]}{Km_{\text{Mek}}} + \frac{[\text{MekPP}]}{Km_{\text{MekPP}}})}](/wiki/images/math/6/c/2/6c26fab2a566ff111ba14f9660be878c.png)
final Parameter
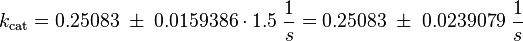
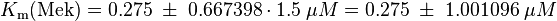
Parameter Reference
| Parameter Calculation | Reference |
|---|---|
|
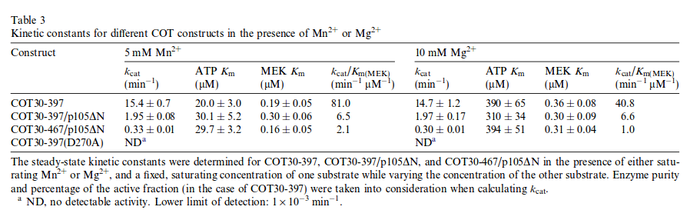
kcat:
The values are averaged and then divided by 60 s to change the unit.
Km: The two measured Km values are also averaged.
The so calculated error is increased by 1.5, because only a similar reaction is measured and so the uncertainty about the parameter is larger. |
Yong Jia et al. (2005) [1] table 3 |
KmP value and equilibrium constant
The Km value for the product is assumed to be similar to but slightly smaller than the the Km value of the substrate because of the similarity of the both species. Therefore the Km value of the substrate is multiplied by 0.95 to gain the one of the product and the uncertainty is increased by increasing the error on Kmsubstrate by 50%.
For information about the equilibrium constant please see here.
References
- ↑ Yong Jia et al. (2005) "Purification and kinetic characterization of recombinant human mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase COT and the complexes with its cellular partner NF-kappa B1 p105." Arch Biochem Biophys 441.1, pp. 64-74. DOI:10.1016/j.abb.2005.06.020. (pmid:16087150)