Pyruvate kinase
Pyruvate kinase is a transferase enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to ADP, yielding one molecule of pyruvate and one molecule of ATP.
Contents
Chemical reaction
Rate equation
The rate equation is represented by the allosteric regualation model of Monod, Wyman and Changeux (MWS). Fru1,6BP and Serine are activators and ATP is inhibiting. Simple Micahelis-Menten kinetics (Briggs Haldane) is used for ADP and reverse reaction [1]
![v=V_m \left( \left(\frac{\frac{[ADP]}{K_{ADP}}}{1+\frac{[ADP]}{K_{ADP}}}\right) \left( \frac{\frac{[PEP]}{Km_{PEP}}\left( 1+\frac{[PEP]}{Km_{PEP}} \right)^3 }{ \frac{L \left( 1 + \frac{[ATP]}{Ki_{ATP}} \right)^4 }{ \left( 1 + \frac{[SER]}{Ka_{SER}} \right)^4 \left( 1 + \frac{F1,6BP}{Ka_{F1,6BP}} \right)^4 } + \left( 1 + \frac{[PEP]}{Km_{PEP}} \right)^4} \right) - \left( \frac{\frac{[ATP][PYR]}{K_{ATP} \times K_{PYR} \times K_{eq}}}{1 +\frac{[ATP]}{K_{ATP}} + \frac{[PYR]}{K_{PYR}} + \frac{[ATP][PYR]}{K_{ATP} \times K_{PYR} }} \right) \right)](/wiki/images/math/6/0/8/608585715d214881c663ba97b3810b40.png)
Parameter values
- The dissociation constant is commonly used to describe the affinity between a ligand (L) (such as a drug) and a protein (P) i.e. how tightly a ligand binds to a particular protein. In the specific case of antibodies (Ab) binding to antigen (Ag), usually the affinity constant is used. It is the inverted dissociation constant.
- Failed to parse (Cannot store math image on filesystem.): K_{a} = = \frac{1}{K_{d}}
| Parameter | Value | Units | Organism | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
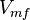
|
1.9[2] | 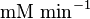
|
HeLa cell line | |
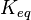 [2] [2]
|
195172 | Recalculated from the ΔGº´ = - 31.4 KJ mol-1. | ||
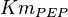 [2] [2]
|
0.014 | mM | ||
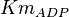 [2] [2]
|
0.4 | mM | ||
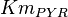 [3] [3]
|
10 | mM | ||
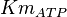 [3] [3]
|
0.86 | mM | ||
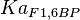 [4] [4]
|
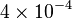
|
mM | ||
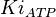 [4] [4]
|
2.5 | mM | ||
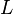 [5] [5]
|
1 | Dimensionless | ||
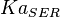
|
5 | mM | For allosteric regulation the affinity constant is used. It is the inverted dissociation constant. so 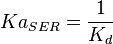 where where 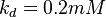 [6] [6]
|
Parameters with uncertainty
- Three values of
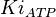 have been reported as 0.14, 0.12, 0.33 in Boyer et. al. (1969) [7]. The Mean and Std. Dev. is Failed to parse (Cannot store math image on filesystem.): 0.19 \pm 0.09
.
have been reported as 0.14, 0.12, 0.33 in Boyer et. al. (1969) [7]. The Mean and Std. Dev. is Failed to parse (Cannot store math image on filesystem.): 0.19 \pm 0.09
.
- Four isoforms of PYK exists. Among those four, three isoforms (R, L and M2) exhibits cooperative kinetics activated by Fru1,6BP (Ka = 0.00006 - 0.0004). For calculating the mean and standard deviation we consider max = 0.0004 and min = 0.00006. The range rule tells that the mean of a sample is the average of the maximum and the minimum value and standard deviation is approximately equal to one fourth of the range of the data ie. s = (Maximum – Minimum)/4. So the mean is (0.0004 + 0.00006)/2= 0.00023 and std. dev. = 0.000085[8].
| Parameter | Value | Units | Organism | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
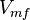
|
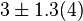 [9] [9]
|
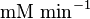
|
HeLa cell line | |
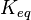 [2] [2]
|
195172 | Recalculated from the ΔGº´ = - 31.4 KJ mol-1. | ||
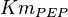
|
Failed to parse (Cannot store math image on filesystem.): 0.17 \pm 0.01 [10] | mM | ||
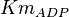
|
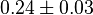 [10] [10]
|
mM | ||
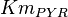 [3] [3]
|
10 | mM | ||
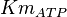 [3] [3]
|
0.86 | mM | ||
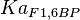 [4] [4]
|
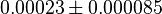
|
mM | ||
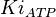
|
Failed to parse (Cannot store math image on filesystem.): 0.19 \pm 0.09 [7] | mM | ||
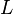
|
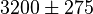 [11] [11]
|
Dimensionless | ||
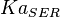
|
5 | mM | For allosteric regulation the affinity constant is used. It is the inverted dissociation constant. so 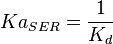 where where 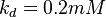 [6] [6]
|
References
- ↑ Monod J, Wyman J, Changeux J-P (1965). On the Nature of Allosteric Transitions: A Plausible Model . Journal of Molecular Biology 12:88–118 (doi)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Marín-Hernández A, Gallardo-Pérez JC, Rodríguez-Enríquez S et al (2011) Modeling cancer glycolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1807:755–767 (doi)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 H.U. Bergmeyer. Methods of Enzymatic Analysis. Verlag Chemie, Winheim
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Imamura K, Tanaka T (1982). Pyruvate kinase isoenzymes from rat, Methods Enzymol. 90 (1982) 150–165
- ↑ Arbitrary value
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Chaneton, B. et al.(2012) Serine is a natural ligand and allosteric activator of pyruvate kinase M2. Nature 491, 458–462
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 P.D. Boyer (1969, The inhibition of pyruvate kinase by ATP: A Mg++ buffer system for use in enzyme studies, Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, Volume 34, Issue 5, 10 March 1969, Pages 702–706
- ↑ A. Marín-Hernández, J.C. Gallardo-Pérez, S.J. Ralph, S. Rodríguez-Enríquez, R. Moreno-Sánchez (2009), HIF-1alpha modulates energy metabolism in cancer cells by inducing over-expression of specific glycolytic isoforms, Mini Rev. Med. Chem., 9, pp. 1084–1101
- ↑ Marín-Hernández A , Rodríguez-Enríquez S, Vital-González P A, et al. (2006). Determining and understanding the control of glycolysis in fast-growth tumor cells. Flux control by an over-expressed but strongly product-inhibited hexokinase. FEBS J., 273 , pp. 1975–1988(doi)
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Dombrauckas, J. D., Santarsiero, B. D. & Mesecar, A. D. (2005) Structural basis for tumor pyruvate kinase M2 allosteric regulation and catalysis. Biochemistry 44, 9417–9429
- ↑ del Valle,P.,de Arriaga, D., Busto, F. and Soler, J. (1986) A study of the allosteric kinetics of Phycomyces pyruvate kinase as judged by the effect of e-alanine and fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 874, 193-204