Difference between revisions of "Nucleosid diphosphate kinase"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Random order Bi-Bi rate law is used | Random order Bi-Bi rate law is used | ||
| − | <center><math>\frac{ \frac{V_{max}}{K_m^{ATP}K_m^{UDP}}\left( [ATP][UDP] - \frac{[ADP][UTP]}{K_{eq}} \right) } {1}</math></center> | + | <center><math>\frac{ \frac{V_{max}}{K_m^{ATP}K_m^{UDP}}\left( [ATP][UDP] - \frac{[ADP][UTP]}{K_{eq}} \right) } { \left( 1 + \frac{[ATP]}{K_{m}^{ATP}} \right)\left( 1 + \frac{[UDP]}{K_{m}^{UDP}} \right) + \left( 1 + \frac{[ADP]}{K_{m}^{ADP}} \right)\left( 1 + \frac{[UTP]}{K_{m}^{UTP}} \right) -1 }</math></center> |
Revision as of 10:43, 13 May 2014
Nucleoside-diphosphate kinases are enzymes that catalyze the exchange of phosphate groups between different nucleotides. The overall effect of NDKs is to transfer a phosphate group from a nucleoside triphosphate to a nucleoside diphosphate. Starting with ATP and UDP, the activity of NDK produces ADP and UTP.
Chemical equation
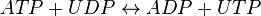
Rate equation
Random order Bi-Bi rate law is used
![\frac{ \frac{V_{max}}{K_m^{ATP}K_m^{UDP}}\left( [ATP][UDP] - \frac{[ADP][UTP]}{K_{eq}} \right) } { \left( 1 + \frac{[ATP]}{K_{m}^{ATP}} \right)\left( 1 + \frac{[UDP]}{K_{m}^{UDP}} \right) + \left( 1 + \frac{[ADP]}{K_{m}^{ADP}} \right)\left( 1 + \frac{[UTP]}{K_{m}^{UTP}} \right) -1 }](/wiki/images/math/9/e/6/9e6a0b14129bad329a3c09d3c7a69f43.png)