Difference between revisions of "Mevalonate pathway with limonene synthesis"
Aliah.hawari (talk | contribs) (→Mevalonate pathway models) |
Aliah.hawari (talk | contribs) (→Mevalonate pathway models) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Mevalonate pathway models == | == Mevalonate pathway models == | ||
| − | + | We have two MVA pathway models. Both models describe the synthesis of limonene, but one is more detailed than the other. In the basic MVA model, the enzyme concentrations are set as fixed concentrations whereas in the improved MVA model, the enzyme concentrations are not fixed and its degradation is taken into account. A detailed description of these models along with the simulations and analysis that were carried out can be accessed by clicking on the buttons below. | |
Revision as of 16:06, 29 January 2018
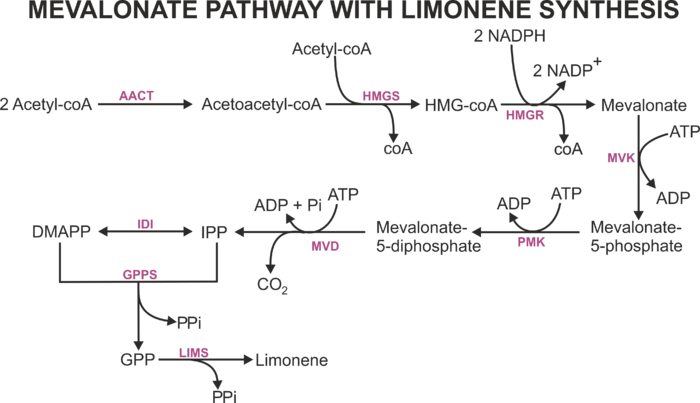
The mevalonate (MVA) pathway is one of two independent pathways that is responsible to produce isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) -- the two main precursors to synthesise terpenes. This pathway has seven enzymes to produce IPP and DMAPP, and these compounds are consumed to form geranyl diphosphate (GPP) -- the precursor for the synthesis of monoterpenes such as limonene.
Mevalonate pathway models
We have two MVA pathway models. Both models describe the synthesis of limonene, but one is more detailed than the other. In the basic MVA model, the enzyme concentrations are set as fixed concentrations whereas in the improved MVA model, the enzyme concentrations are not fixed and its degradation is taken into account. A detailed description of these models along with the simulations and analysis that were carried out can be accessed by clicking on the buttons below.
|
|

