Difference between revisions of "Mevalonate pathway with limonene synthesis"
Aliah.hawari (talk | contribs) |
Aliah.hawari (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:MVA_v1.png|700px|link=]] | + | [[File:MVA_v1.png|left|700px|link=]] |
The mevalonate (MVA) pathway is one of two independent pathways that is responsible to produce isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) -- the two main precursors to synthesise terpenes. This pathway has seven enzymes to produce IPP and DMAPP, and these compounds are consumed to form geranyl diphosphate (GPP) -- the precursor for the synthesis of monoterpenes such as limonene. In this model, the MVA | The mevalonate (MVA) pathway is one of two independent pathways that is responsible to produce isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) -- the two main precursors to synthesise terpenes. This pathway has seven enzymes to produce IPP and DMAPP, and these compounds are consumed to form geranyl diphosphate (GPP) -- the precursor for the synthesis of monoterpenes such as limonene. In this model, the MVA | ||
Revision as of 16:35, 18 January 2018
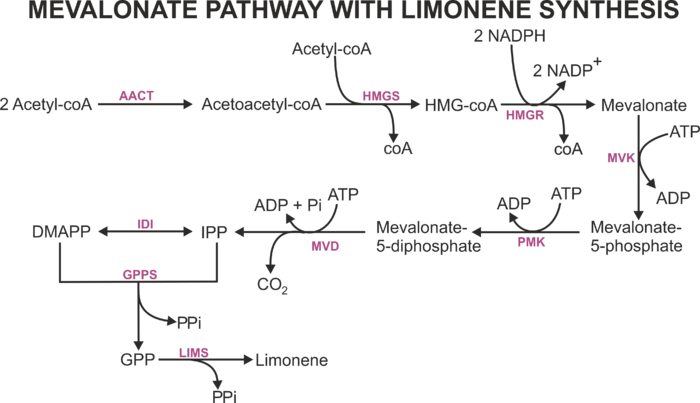
The mevalonate (MVA) pathway is one of two independent pathways that is responsible to produce isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) -- the two main precursors to synthesise terpenes. This pathway has seven enzymes to produce IPP and DMAPP, and these compounds are consumed to form geranyl diphosphate (GPP) -- the precursor for the synthesis of monoterpenes such as limonene. In this model, the MVA