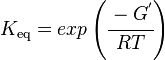Limonene Synthase
You can go back to main page of the kinetic model here.
Model construction progress :
| Enzyme | Pathway | Keq | Kcat | VmaxF | KmGPP | KmSub2 | [GPP] | [Sub2] | VmaxR | KmLim | KmPP | [Limonene] | [PP] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 02_LimSynth | Limonene Biosynthesis | 1 | 5 | 3 | >6 | no Sub2 | 4 | no Sub2 | estimated | estimated | estimated | estimated | estimated |
Legend:
| Have not started ·· | 1 -2 data found ·· | 3-4 data found ·· | sufficient data found/estimated ·· | data distribution generated ·· | data sampled |
| to do | DONE! |
Contents
What we know
Issues
Strategies
Reaction catalysed
Metabolite Background Information
Long metabolite names are abbreviated in the model for clarity and standard identification purposes.
| Metabolite | Abbreviation | Chemical Formula | Molar mass (g/mol) | ChEBI | ChEMBL | PubChem |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| geranyl diphosphate | GPP | C10H20O7P2 | 314.209 | 17211 | 41432 | 445995 |
| (-)-4S-limonene | Limonene | C10H16 | 136.24 | 15384 | 449062 | 22311 or 439250 |
| diphosphate | PP | O7P2 | 173.94 | 644102 | ||
| limonene synthase | LimSynth | 72.4 kDa [1] ; 60kDa [2] |
Equation Rate
The reversible Michaelis-Menten equation to model the dynamic changes of LimSynth is:
where :
| Parameter | Description | Units |
|---|---|---|
| VLimSynth | Reaction rate for Limonene Synthase | |
| Vmaxforward | Maximum reaction rate towards the production of limonene | ref |
| KmGPP | Michaelis-Menten constant for GPP | mM |
| KmLimonene | Michaelis-Menten constant for Limonene | mM |
| KmPP | Michaelis-Menten constant for PP | mM |
| Keq | Equilibrium constant | |
| [GPP] | GPP concentration | mM |
| [Limonene] | Limonene concentration | mM |
| [PP] | PP concentration | mM |
Strategies for estimating the kinetic parameter values
Calculating the Equilibrium Constant
Standard Gibbs Free energy
Standard Gibbs Free energy for Limonene Synthase from MetaCyc (EC 4.2.3.16) is -28.049988 kcal/mol [3].
SI derived unit for Gibbs free energy is Joules per mol (J mol-1). 1 kJ·mol−1 is equal to 0.239 kcal·mol−1.
Therefore, the Gibbs free energy for Limonene synthase in kJ mol-1 is:
- Failed to parse (Cannot store math image on filesystem.): \cfrac {1}{0.239 kcal.mol^-1} * -28.049988 kcal.mol^-1
- Failed to parse (Cannot store math image on filesystem.): = -117.36396 kJmol^-1
The Equilibrium Constant
The equilibrium constant can be calculated using the Van't Hoff Isotherm equation:
Failed to parse (Cannot store math image on filesystem.): = exp \left ( \cfrac {-(- 117.36396 \text { kJmol}^{-1})}{ (8.31 \text{ JK}^{-1} \text { mol}^{-1} * 289 K} \right )
Failed to parse (Cannot store math image on filesystem.): = exp \left ( \cfrac { + 117.36396 \text { kJmol}^{-1} }{ 2401.59 \text{ JK}^{-1}\text { mol}^{-1} }\right)
Failed to parse (Cannot store math image on filesystem.): = exp \left ( \cfrac{ 117.364 * 10^3 \text { Jmol}^{-1}}{2401.59 \text{ JK}^{-1}\text { mol}^{-1}} \right)
Failed to parse (Cannot store math image on filesystem.): =exp \left ( 48.8693 \right )
Failed to parse (Cannot store math image on filesystem.): = 1.6736 * 10^{21}
where;
| Keq | Equilibrium constant |
| -ΔG° | Gibbs free energy change. For Limonene Synthase it is -117.364 kJmol-1 |
| R | Gas constant with a value of 8.31 JK-1mol-1 |
| T | Temperature which is always expressed in Kelvin |
Kinetic Parameter Values
Values for the kinetic parameter required to simulate this model can be obtained from published and unpublished literature.
A more detailed descriptions of the values listed above can be found HERE , where I've linked and highlighted where these data came from.
Substrate, Product & Enzyme Concentration Values
| Concentration | Unit | Substrate / Product | Directionality | Organism | Method notes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | µM | GPP | forward | E. coli | [4] | |
| 10 | µM | GPP | forward | Cannabis sativa L. | [5] | |
| 10 | µM | GPP | forward | Mentha sp. | [6] | |
| 2 | µM | GPP | forward | Citrus limon | [7] | |
| 150 | µg | Limonene synthase | - | E. coli | [4] | |
| 0.07 | µM | Limonene synthase | - | Citrus sinensis | with 200µM GPP as substrate, at 20°C, pH7.5 | [8] |
| 0.26 | µM | Limonene synthase | - | Citrus sinensis | with 200µM GPP, at 37°C, pH7.5 | [8] |
| 200 | µM | GPP | forward | Citrus sinensis | used for Limonene synthase activity assay at 20°C and 37°C, pH 7.5 | [8] |
| 100 | µM | GPP | - | Citrus limon | [7] | |
| 0.1 | µM | GPP | - | Citrus limon | [7] |
Km Values
| Km (mM) | Unit | Substrate / Product | Directionality | Organism | Method notes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.13 | mM | GPP | forward | Citrus sinensis | Enzyme assay, pH 7.5, 20°C | [8] |
| 0.00125 | mM | GPP | forward | Ricciocarpos natans | [9] | |
| 0.0018 | mM | GPP | forward | Mentha piperita | Ref | |
| 0.01176 ± 0.00245 | mM | GPP | forward | Cannabis sativa L. | [10] | |
| 0.0031 | mM | GPP | forward | Citrus limon | ref | |
| 0.016 | mM | GPP | forward | Escherichia coli | [4] | |
| 0.0067 | mM | GPP | forward | Escherichia coli (wt) | [11] | |
| 0.0068 | mM | GPP | forward | Cannabis sativa L. | enzyme assay, pH7.5, 40°C | [5] |
| 0.0086 | mM | GPP | forward | Escherichia coli (Q53). | [4] | |
| 0.006 | mM | GPP | forward | Escherichia coli (E57). | [4] | |
| 0.0126 | mM | GPP | forward | Escherichia coli (R58). | [4] | |
| 0.0299 | mM | GPP | forward | Escherichia coli (R59). | [4] | |
| 0.0324 | mM | GPP | forward | Escherichia coli (R58P59) | [4] | |
| 0.0275 | mM | GPP | forward | Escherichia coli (R58A59) | [4] | |
| 0.0188 | mM | GPP | forward | Escherichia coli (S60) | [4] | |
| 0.0007 | mM | GPP | forward | Citrus limon | [7] | |
| 0.00625 ± 0.00041 | mM | GPP | forward | Cannabis sativa L | [10] |
Vmax values
| Vmax | Unit | Directionality | Organism | Organism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.08 | µmol/min/mg | forward | Cannabis sativa L. | [10] | |
| 0.12 ± 0.01 | µmol/min/mg | forward | Cannabis sativa | [10] | |
| 0.4748 | µmol/min/mg | forward | Citrus limon | References | |
| 0.53 | µM/min | forward | Citrus sinensis | 200µM GPP, 20°C, [E]: 0.07µM, pH7.5 | [8] |
| 0.64 | µM/min | forward | Citrus sinensis | 200µM GPP, 37°C, [E]: 0.26µM, pH7.5 | [8] |
| Vmax | Unit | Directionality | Organism | References |
Kcat values
| Kcat | Unit | Directionality | Organism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.13 | s-1 | forward | Citrus sinensis | [8] |
| 0.04 | s-1 | forward | Citrus sinensis | [8] |
| 0.3 | s-1 | forward | Mentha piperita & Mentha spicata | [6] |
| 0.09 | s-1 | forward | Cannabis sativa L. | [10] |
| 0.13 | s-1 | forward | Cannabis sativa L. | [10] |
| 0.02 | s-1 | forward | E. coli | [4] |
| 0.082 | s-1 | forward | Cannabis sativa L. | [5] |
| 0.0024 | s-1 | forward | E. coli (wt) | [11] |
| 0.0020 | s-1 | forward | E. coli (preprotein) | [4] |
| 0.0036 | s-1 | forward | E. coli (Q54) | [11] [4] |
| 0.0034 | s-1 | forward | E. coli (E57) | [11] [4] |
| 0.0037 | s-1 | forward | E. coli (R58) | [11] [4] |
| <0.0004 | s-1 | forward | E. coli (R59) | [11] [4] |
| <0.0004 | s-1 | forward | E. coli (R58P59) | [11] [4] |
| <0.0004 | s-1 | forward | E. coli (R58A59) | [11] [4] |
| <0.0004 | s-1 | forward | E. coli (S60) | [11] [4] |
Extracting Information from Limonene Production Rates
The production rates would reflect on the flux for this enzyme, and this would provide provide the insights on the Vmax of this enzyme.
| Amount produced (mg/L) | Time (H) | Organism | Description | Reaction Flux (µM/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 24 | Escherichia coli | Possible reason for the low limonene production might due to the insufficient supply of IPP and DMAPP [12]. | 0.0255 |
| 335 | 48 | Escherichia coli | Engineered E.coli in which heterologous MVA pathway was installed [13]. | 0.8537 |
| 35.8 | 48 | Escherichia coli | E.coli was engineered to express GPPS, LS, DXS, and IDI [14] . | 0.0912 |
| 4.87 | 48 | Escherichia coli | This was the initial titer. The study established a limonene biosynthesis pathway in E.coli using four different polycistronic operons based on 3 vectors with varied expression strength [14]. | 0.0124 |
| 17.4 | 48 | Escherichia coli | Using a plasmid with DXS and IDI over expressed [14]. | 0.0445 |
| 430 | 72 | Escherichia coli | [13] | 0.7306 |
Parameter estimation
This section can be found HERE
Simulations
Simulations performed can be found HERE.
References
- ↑ Turner,G. et. al.1999. "Limonene synthase, the enzyme responsible for monoterpene biosynthesis in peppermint, is localized to leucoplasts of oil gland secretory cells", Plant Physiology 120(3): 879-886
- ↑ Maruyama, T. et. al. 2002. "Molecular cloning, functional expression and characterization of d-Limonene synthase from Agastache rugosa" Biol. Pharm. Bull. 25(5): 661-665
- ↑ Latendresse M. (2013). "Computing Gibbs Free Energy of Compounds and Reactions in MetaCyc."
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 4.12 4.13 4.14 4.15 4.16 4.17 4.18 Williams, D.C. et. al. 1998. "Truncation of Limonene Synthase preprotein provides a fully active 'pseudomature' form of this monoterpene cyclase and reveals the function of the amino-terminal arginine pair ",Biochemistry, 37:12213-12220 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Williams1998" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Gunnewich, N., et al. 2006."Functional expression and characterization of trichome-specific (-)-limonene synthase and (+)-α-pinene synthase from Cannabis sativa", Natural Product Communications, 0(0): pp1-10 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Gunnewich2006" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 6.0 6.1 Alonso et. al. 1992. "Purification of 4S-Limonene Synthase, a Monoterpene Cyclase from the Glandular Trichomes of Peppermint (Mentha x piperita) and Spearmint (Mentha spicata)", The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267(11):7582-7587
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Lücker, J. et. al. 2002."Monoterpene biosynthesis in lemon (Citrus limon). cDNA isolation and functional analysis of four monoterpene synthases", Eur. J. Biochem. 269: pp3160-3171
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 8.6 8.7 Entova, S. 2013. "Kinetic characterization, crystallization, and photosynthetic expression of (+)-4R-limonene synthase from C. sinensis", Masters Thesis, Brandeis Univeristy Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Entova2013" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Adam, K. et. al. 1996. "Partial purification and characterization of a monoterpene cyclase, limonene synthase, from the liverwort Ricciocarpos natans. 332(2):pp 352-356.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 Gunnewich, N. 2008. "Expression and characterization of terpene synthases from Cannabis sativa L. and Salvia sclarea L. Doctoral thesis. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Gunnewich2008" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 11.6 11.7 11.8 Ogura, K. & Koyama, T. 1997, "Dynamic aspects of Natural Products Chemistry". pp 1-23.
- ↑ Carter, Ora A. et. al.2013. "Monoterpene biosynthesis pathway construction in Escherichia coli",Phytochemistry, 64:425–433, 2003.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Alonso-Gutierez et. al. 2013. "Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for limonene and perillyl alcohol production", Metabolic Engineering, 19:33-41 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "AlonsoGutierez2013" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 Du et. al. 2014. "Enhanced limonene production by optimizing the expression of limonene biosynthesis and MEP pathway genes in E.coli", Bioprocessing and Bioprocessing, 1:10
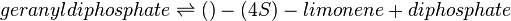
![V_\mathrm{LimSynth} = Vmax_\mathrm{forward} * \cfrac {\cfrac{[GPP]}{Km_\mathrm{GPP}} * \left ( 1 - \cfrac {[Limonene]*[PP]}{[GPP]*K_\mathrm{eq}} \right )}{1 + \cfrac {[GPP]}{Km_\mathrm{GPP}} + \cfrac {[Limonene]}{Km_\mathrm{Limonene}} + \cfrac {[PP]}{Km_\mathrm{PP}} + \cfrac {[Limonene]*[PP]}{Km_\mathrm{Limonene}*Km_\mathrm{PP}}}](/wiki/images/math/6/9/8/698f16353b522504a844aae5c37bdac9.png)