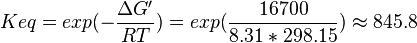Difference between revisions of "Hexokinase"
(→Parameters with uncertainty) |
(→Parameters with uncertainty) |
||
| Line 130: | Line 130: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Calculating average from these equlibrium constant gives the value of <math>2214.66 \pm 2332.60</math> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 12:58, 24 June 2014
The enzyme hexokinase phosphorylates (adds a phosphate group to) glucose in the cell's cytoplasm. In the process, a phosphate group from Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is transferred to glucose producing glucose 6-phosphate (Glc6P).
Contents
Chemical equation
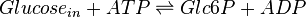
Rate equation
Without inhibition
Random Bi-Bi Michaelis Menten is used.[1]
![v = \frac{\frac{V_{mf}}{Km_{Glucose_{in}}K_{ATP}}\Big( [Glucose_{in}][ATP] - \frac{[Glc6P][ADP]}{K_{eq}} \Big)}{1 + \frac{[Glucose_{in}]}{Km_{Glucose_{in}}} + \frac{[ATP]}{K_{ATP}} + \frac{[Glucose_{in}][ATP]}{Km_{Glucose_{in}}K_{ATP}} + \frac{[Glc6P]}{K_{Glc6P}} + \frac{[ADP]}{K_{ADP}} +\frac{[Glc6P][ADP]}{K_{Glc6P}K_{ADP}} + \frac{[Glucose_{in}][ADP]}{K_{Glucose_{in}}K_{ADP}} +\frac{[Glc6P][ATP]}{K_{Glc6P}K_{ATP}} }](/wiki/images/math/d/2/d/d2d1c3d1115eef8cdf23e7eb98f65b04.png)
With allosteric inhibition
Hexokinase is allosterically inhibited by Glc6P [2]. The rate law taking into account this inhibition is
![\frac{V_{mf}* \frac{[Glucose]*[ATP]}{Km_{Glucose}*Km_{ATP}} }{ \left(1 + \frac{[Glc6P]}{Ki_{Glc6P}} \right)* \left( 1 + \frac{[Glucose]}{Km_{Glucose}} \right) + \frac{[ATP]}{Km_{ATP}} + \frac{[Glucose]*[ATP]}{Km_{Glucose}*Km_{ATP}} }](/wiki/images/math/c/2/6/c26962b0cefb2c26a75d64c2de18328e.png)
Parameters
Without inhibition
| Parameter | Value | Units | Organism | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0.04 [3] | 
|
HeLa cell line | |
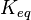
|
651[4] | |||
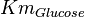
|
0.1[1] | mM | ||
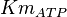
|
1.1[1] | mM | ||
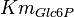
|
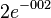 [1] [1]
|
mM | ||
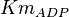
|
3.5[1] | mM |
With inhibition
| Parameter | Value | Units | Organism | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
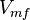
|
0.04 [3] | 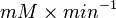
|
HeLa cell line | |
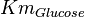
|
0.1[1] | mM | ||
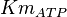
|
1.1[1] | mM | ||
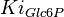
|
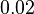 [2] [2]
|
mM |
Parameters with uncertainty
Hexokinase isoenzyme has been reported to vary in different developmental and metabolic status of the cell. In mammalian tissues four isoenzymes of Hexokinase is present [5]. Hexokinase-II has been found to be overexpressed in several first growith cancer cells [3]. Therefore in our model we have considered only the Hexokinase-II kinetic parameter values.
| Parameter | Value | Units | Organism | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
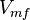
|
Failed to parse (Cannot store math image on filesystem.): 0.02 \pm 0.006 (n=4)[3] | 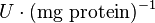
|
HeLA cell line | |
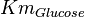
|
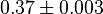 (n=5)[6] (n=5)[6]
|
mM | SNU449 cell (Human Liver Tissue) | |
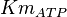
|
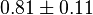 (n=5)[6] (n=5)[6]
|
mM | ||
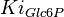
|
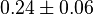 (n=5)[6] (n=5)[6]
|
mM |
Equilibrium constant
| Equilibrium constant | Conditions | Source |
|---|---|---|
| 4908 | pH=7, T=25°C | Voet et al.[7] from Newshole et al. (1973) [8]:
|
| 846 | pH=7, T=25°C | Lehninger, (1975)[9] p 553:
|
| 890 | pH=7, T=25°C | Lehninger, (1975)[10] p 396 |
Calculating average from these equlibrium constant gives the value of 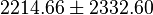
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Marín-Hernández A, Gallardo-Pérez JC, Rodríguez-Enríquez S et al (2011) Modeling cancer glycolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1807:755–767 (doi)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Wilson J E (2003). Isozymes of mammalian hexokinase: structure, subcellular localization and metabolic function. Journal of Experimental Biology, 206, pp. 2049–2057 (doi)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Marín-Hernández A , Rodríguez-Enríquez S, Vital-González P A, et al. (2006). Determining and understanding the control of glycolysis in fast-growth tumor cells. Flux control by an over-expressed but strongly product-inhibited hexokinase. FEBS J., 273 , pp. 1975–1988(doi) Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Hernandez_2006" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Arbitrary value
- ↑ Adams V, Kempf W, Hassam S, Briner J. (1995), Determination of hexokinase isoenzyme I and II by RT-PCR: increased hexokinase II isoenzyme in human renal cell carcinoma. J Biochem Mol Med 1995;54:53–58.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Ahn, K.J.; Kim, J.; Yun, M.; Park, J.H.; Lee, J.D.(2009), Enzymatic properties of the N- and C-terminal halves of human hexokinase II, BMB Rep. 42, 350-355.
- ↑ Voet, D., Voet., J.G. and Pratt, C. W. (1999) Fundamentals of biochemistry, Wiley
- ↑ Newshole, E.A. and Stuart, C. (1973) Regulation in Metabolism, Wiley
- ↑ David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox (2008), Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry (5th edn), W. H. Freeman and Company
- ↑ Lehninger, A.L. (1975) Biochemistry (2nd edn), Worth
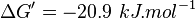 ,
, 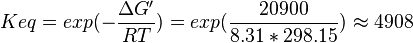
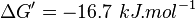 ,
,