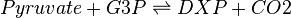Difference between revisions of "DXS"
Aliah.hawari (talk | contribs) (→Modelling DXS) |
Aliah.hawari (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Modelling DXS == | == Modelling DXS == | ||
| − | In the kinetic model, the DXS reaction is modelled with reversible Michaelis-Menten using the Hanekom <ref> Hanekom2016 </ref> bi-bi random order generic equation. In total, this reaction requires | + | In the kinetic model, the DXS reaction is modelled with reversible Michaelis-Menten using the Hanekom <ref> Hanekom2016 </ref> bi-bi random order generic equation. In total, this reaction requires five kinetic parameters (Kms for all substrates and products, and a forward Kcat) and one thermodynamic parameter (Equilibrium constant, Keq). |
<math> | <math> | ||
| − | V_\mathrm{DXS}= Kcat_\mathrm{forward} | + | V_\mathrm{DXS}= \cfrac{Kcat_\mathrm{forward} \bullet [DXS] \bullet \left( \cfrac{[Pyr]}{Km_\mathrm{DXS}} \right) \bullet \left( \cfrac{[G3P]}{Km_\mathrm{g3p}} \right) \bullet \left( 1 - \cfrac{\left( \cfrac{[DXP]\bullet[CO2]}{[Pyr]\bullet[G3P]} \right)}{K_\mathrm{eq}} \right)} {\left( 1 + \cfrac {[Pyr]}{Km_\mathrm{pyr}} + \cfrac{[CO2]}{Km_\mathrm{co2}}\right) \bullet \left( 1 + \cfrac{[G3P]}{Km_\mathrm{g3p}} + \cfrac{[DXP]}{KM_\mathrm{dxp}} \right)} |
</math> | </math> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==References == | ==References == | ||
| − | </ | + | <references/> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 13:16, 23 March 2017
You can go back to main page of the kinetic model here.
The DXS reaction (EC 2.2.1.7)
Deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate synthase (DXS) catalyses the production of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP) from pyruvate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). This reaction is the first step in the MEP pathway.
Modelling DXS
In the kinetic model, the DXS reaction is modelled with reversible Michaelis-Menten using the Hanekom [1] bi-bi random order generic equation. In total, this reaction requires five kinetic parameters (Kms for all substrates and products, and a forward Kcat) and one thermodynamic parameter (Equilibrium constant, Keq).
![V_\mathrm{DXS}= \cfrac{Kcat_\mathrm{forward} \bullet [DXS] \bullet \left( \cfrac{[Pyr]}{Km_\mathrm{DXS}} \right) \bullet \left( \cfrac{[G3P]}{Km_\mathrm{g3p}} \right) \bullet \left( 1 - \cfrac{\left( \cfrac{[DXP]\bullet[CO2]}{[Pyr]\bullet[G3P]} \right)}{K_\mathrm{eq}} \right)} {\left( 1 + \cfrac {[Pyr]}{Km_\mathrm{pyr}} + \cfrac{[CO2]}{Km_\mathrm{co2}}\right) \bullet \left( 1 + \cfrac{[G3P]}{Km_\mathrm{g3p}} + \cfrac{[DXP]}{KM_\mathrm{dxp}} \right)}](/wiki/images/math/4/a/8/4a8faa589ce739bde2b441190759da1b.png)
References
- ↑ Hanekom2016