EPAC and PKA-Inactivation
Binding Reaction
EPAC:
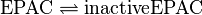
PKA:
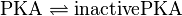
Kinetic Equation
EPAC:
![v_{\text{EPAC-Inactivation}} = \frac{v_{max} \cdot [\text{EPAC}] \cdot (1-\frac{[\text{inactiveEPAC}]}{[\text{EPAC}] \cdot K_{eq}})}{Km_{\text{EPAC}} \cdot (1 + \frac{[\text{EPAC}]}{Km_{\text{EPAC}}} + \frac{[\text{inactiveEPAC}]}{Km_{\text{inactiveEPAC}}})}](/wiki/images/math/c/4/4/c44d65f7533acfc5342fb103483ae3de.png)
PKA:
![v_{\text{PKA-Inactivation}} = \frac{v_{max} \cdot [\text{PKA}] \cdot (1-\frac{[\text{inactivePKA}]}{[\text{PKA}] \cdot K_{eq}})}{Km_{\text{PKA}} \cdot (1 + \frac{[\text{PKA}]}{Km_{\text{PKA}}} + \frac{[\text{inactivePKA}]}{Km_{\text{inactivePKA}}})}](/wiki/images/math/3/9/1/391621f1cdbb5a3807a7632b772bc3c5.png)
Final Parameter
EPAC:
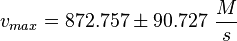
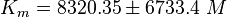
PKA:
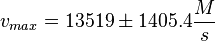
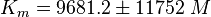
Notes
The equilibrium constant of the binding of cAMP to EPAC is used. As kcat the value calculated by the model by Xu et al (2010)[1] and the averaged relative standard error is used. As Km-values the same values as the one of the activation process by an argonist are used and as uncertainty the same relative error is assumed.
KmP value and equilibrium constant
The Km value for the product is assumed to be similar to but slightly smaller than the the Km value of the substrate because of the similarity of the both species. Therefore the Km value of the substrate is multiplied by 0.95 to gain the one of the product and the uncertainty is increased by increasing the error on Kmsubstrate by 50%.
For information about the equilibrium constant please see here.
References
- ↑ Tian-Rui Xu et al. (2010) "Inferring signaling pathway topologies from multiple perturbation measurements of specific biochemical species." Sci Signal. 3(134):ra20. (pmid:20234003)