Monocarboxylate (Lactate) transporter
Monocarboxylate transporters,[1] or MCTs, constitute a family of proton-linked plasma membrane transporters that carry molecules having one carboxylate group (monocarboxylates), such as lactate and pyruvate.
Chemical equation
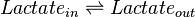
Rate equation
Reversible Michaelis-Menten rate law is used
![\frac{V_{f}\frac{[Lactate_{in}]}{Km_{Lactate_{in}}}- V_{r}\frac{[Lactate_{out}]}{Km_{Lactate_{out}}}}{1+ \frac{[Lactate_{in}]}{Km_{Lactate_{in}}} - \frac{[Lactate_{out}]}{Km_{Lactate_{out}}} }](/wiki/images/math/a/b/c/abc535a21e702a99833c028802c5fcf3.png)