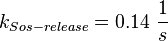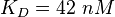Sos-Binding
Reaction
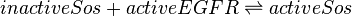
Rate Equation
![v_{Sos-binding} = k_{Sos-binding} \cdot [activeEGFR][inactiveSos] - k_{Sos-release} \cdot [activeSos]](/wiki/images/math/3/7/6/376a7ee474cbb144dd1b42a7cf4f2e6b.png)
final Parameter
The errors of the final parameter are increased by 50% because only a similar reaction is modelled.


Parameter
| Parameter | Notes | References |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The binding of the p85αSH2-N domain to 17-mer phosphopeptide similar to a PDGFR region. M. Hensmann et al. "Phosphopeptide binding to the N-terminal SH2 domain of the p85 alpha subunit of PI3'-kinase: a heteronuclear NMR study." eng. In: Protein Sci 3.7 (1994), pp. 1020-1030. DOI: 10.1002/pro.5560030704. URL: http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/pro.5560030704 |
|
|
The binding of the two different SH2 domains to phosphotyrosine containing peptides derived from and insuline receptor substrate. |
S. Felder et al. "SH2 domains exhibit high-affinity binding to tyrosine-phosphorylated peptides yet also exhibit rapid dissociation and exchange." eng. In Mol Cell Biol 13.3 (1993), pp. 1449-1455 |
|