Phosphoserine phosphatase
This enzyme converts PSER to Serine.
Contents
Reaction equation
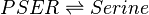
Rate equation
Special rate law is used. [1]
![\frac{serB*KcatB* \frac{[PSER]}{Kb_{PSER}} }{ 1 + \frac{[PSER]}{Kb_{PSER}} + \frac{[Serine]}{Kb_{Serine}} }](/wiki/images/math/0/b/8/0b8a657e93a37dcecdc000cbddc497ee.png)
Parameters
| Parameter | Value | Units | Organism | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
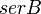
|
0.25 [2] | mM | Escherichia coli | |
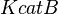
|
1.43 [2] | 1/s | ||
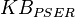
|
0.0015[2] | mM | ||
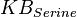
|
0.15[2] | mM |
Parameters with uncertainty
-
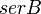 is the enzyme concentration and therefore considered to be constant.
is the enzyme concentration and therefore considered to be constant.
- The value of
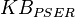 is reported as
is reported as  for human brain in [3].
for human brain in [3].
- Two values of
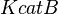 for Porphyromonas gingivalis (nonmotile, Gram-negative, rod-shaped, anaerobic, pathogenic bacterium) are reported in Tribble et. al.[4]; 1.508, 2.94. The value with uncertainty comes as
for Porphyromonas gingivalis (nonmotile, Gram-negative, rod-shaped, anaerobic, pathogenic bacterium) are reported in Tribble et. al.[4]; 1.508, 2.94. The value with uncertainty comes as  .
.
| Parameter | Value | Units | Organism | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
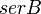
|
0.25 | mM | Escherichia coli | |
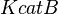
|

|
1/s | Porphyromonas gingivalis | |
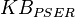
|
 [3] [3]
|
mM | Human brain | |
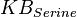
|
mM | Escherichia coli |
References
- ↑ Smallbone K, Stanford NJ (2013). Kinetic modeling of metabolic pathways: Application to serine biosynthesis. In: Systems Metabolic Engineering, Humana Press. pp. 113–121
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Turnaev II, Ibragimova SS, Usuda Y et al (2006). Mathematical modeling of serine and glycine synthesis regulation in Escherichia coli. Proceedings of the fifth international conference on bioinformatics of genome regulation and structure 2:78–83 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Turnaev_2006" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 3.0 3.1 Shetty, V.; Shetty, K.T. (1990), Phosphoserine phosphatase of human brain: partial purification, characterization, regional distribution, and effect of certain modulators including psychoactive drugs, Neurochem. Res. 16, 1203-1210
- ↑ Tribble, G.D.; Mao, S.; James, C.E.; Lamont, R.J. (2006), A Porphyromonas gingivalis haloacid dehalogenase family phosphatase interacts with human phosphoproteins and is important for invasion, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 11027-11032 (2006)