Monocarboxylate (Lactate) transporter
Monocarboxylate transporters,[1] or MCTs, constitute a family of proton-linked plasma membrane transporters that carry molecules having one carboxylate group (monocarboxylates), such as lactate and pyruvate.
Chemical equation
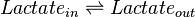
Rate equation
Reversible Michaelis-Menten rate law is used
Parameter values
| Parameter | Value | Units | Organism | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
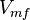
|
2.5 [2] | 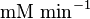
|
Human tumor cells | |
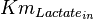
|
4.5 [3] | mM | Rat liver cell | |
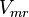
|
2.4 [3] | 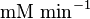
|
Rat liver cells | |
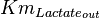
|
4.54 [2] | mM | Human tumor cells |
References
- ↑ Halestrap AP, Meredith D (2004). The SLC16 gene family-from monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs) to aromatic amino acid transporters and beyond. Pflugers Arch. 447 (5): 619–28 (doi)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Manning Fox JE et. al. (2000). Characterisation of human monocarboxylate transporter 4 substantiates its role in lactic acid efflux from skeletal muscle. J Physiol 529(Pt2):285-293
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Jackson VN, Halestrap AP (1996) The kinetics, substrate, and inhibitor specificity of the monocarboxylate (lactate) transporter of rat liver cells determined using the fluorescent intracellular pH indicator, 2’,7’-bis(carboxyethyl)-5(6)-carboxyfluorescein. J Biol Chem 271:861–868