Difference between revisions of "Monocarboxylate (Lactate) transporter"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Rate equation== | ==Rate equation== | ||
| − | + | Simple Michaelis-Menten rate law is used | |
| − | <center><math> \frac{V_{ | + | <center><math> \frac{V_{max}[Lactate_{in}]}{Km_{Lactate_{in}} + [Lactate_{in}]} </math></center> |
==Parameter values== | ==Parameter values== | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |<math> | + | |<math>Km_{Lactate_{in}}</math> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|4.5 | |4.5 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
Revision as of 10:56, 5 March 2014
Monocarboxylate transporters,[1] or MCTs, constitute a family of proton-linked plasma membrane transporters that carry molecules having one carboxylate group (monocarboxylates), such as lactate and pyruvate.
Chemical equation
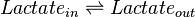
Rate equation
Simple Michaelis-Menten rate law is used
![\frac{V_{max}[Lactate_{in}]}{Km_{Lactate_{in}} + [Lactate_{in}]}](/wiki/images/math/0/6/1/061d22d1d702e36b76b8ef5d7bf1ca3f.png)
Parameter values
| Parameter | Value | Organism | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
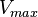
|
2.5 [2] | ||
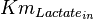
|
4.5 |
References
- ↑ Halestrap AP, Meredith D (2004). The SLC16 gene family-from monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs) to aromatic amino acid transporters and beyond. Pflugers Arch. 447 (5): 619–28 (doi)
- ↑ Manning Fox JE et. al. (2000). Characterisation of human monocarboxylate transporter 4 substantiates its role in lactic acid efflux from skeletal muscle. J Physiol 529(Pt2):285-293