Difference between revisions of "Glycogen synthase"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''Glycogen synthase''' (''' | + | '''Glycogen synthase''' ('''GS''') converts [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucose glucose] to [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycogen glycogen]. It takes short polymers of glucose and converts them into long polymers one by one into a polymeric chain for storage as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycogen glycogen]. |
==Chemical equation== | ==Chemical equation== | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Rate equation== | ==Rate equation== | ||
| − | MWC model (Monod-Wyman-Changeux model) is used to model the reaction mechanism of this enzyme.<ref name="Palm_thesis_2013> Palm, D.C. (2013). ''The regulatory design of glycogen metabolism in mammalian skeletal muscle'' (Ph.D.). University of Stellenbosch</ref> | + | MWC model (Monod-Wyman-Changeux model) is used to model the reaction mechanism of this enzyme.<ref name="Palm_thesis_2013> Palm, D.C. (2013). ''The regulatory design of glycogen metabolism in mammalian skeletal muscle'' (Ph.D.). University of Stellenbosch</ref>. Glc6P activates GS by binding to an allosteric site of this enzyme. |
<center><math>\frac{K_{cat,r}[GS]n\frac{[UDPG]}{K_{UDPG}} \left( 1 + \frac{[UDPG]}{K_{UDPG}} + \frac{[ATP]}{K'_{r,ATP}} \right)^{n-1}}{\left( 1 + \frac{[UDPG]}{K_{UDPG}} + \frac{[ATP]}{K'_{ATP}} \right)^n L_{0} \left( \frac{1 + \frac{[Glc6P]}{K_{t,Glc6P}} + \frac{[ATP]}{K_{t,ATP}} }{1 + \frac{[Glc6P]}{K_{r,Glc6P}} + \frac{[ATP]}{K_{r,ATP}} } \right)^n + \left( 1 + \frac{[UDPG]}{K_{UDPG}} + \frac{[ATP]}{K'_{r,ATP}} \right)^n }</math></center> | <center><math>\frac{K_{cat,r}[GS]n\frac{[UDPG]}{K_{UDPG}} \left( 1 + \frac{[UDPG]}{K_{UDPG}} + \frac{[ATP]}{K'_{r,ATP}} \right)^{n-1}}{\left( 1 + \frac{[UDPG]}{K_{UDPG}} + \frac{[ATP]}{K'_{ATP}} \right)^n L_{0} \left( \frac{1 + \frac{[Glc6P]}{K_{t,Glc6P}} + \frac{[ATP]}{K_{t,ATP}} }{1 + \frac{[Glc6P]}{K_{r,Glc6P}} + \frac{[ATP]}{K_{r,ATP}} } \right)^n + \left( 1 + \frac{[UDPG]}{K_{UDPG}} + \frac{[ATP]}{K'_{r,ATP}} \right)^n }</math></center> | ||
Revision as of 17:39, 28 February 2014
Glycogen synthase (GS) converts glucose to glycogen. It takes short polymers of glucose and converts them into long polymers one by one into a polymeric chain for storage as glycogen.
Chemical equation
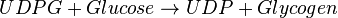
Rate equation
MWC model (Monod-Wyman-Changeux model) is used to model the reaction mechanism of this enzyme.[1]. Glc6P activates GS by binding to an allosteric site of this enzyme.
![\frac{K_{cat,r}[GS]n\frac{[UDPG]}{K_{UDPG}} \left( 1 + \frac{[UDPG]}{K_{UDPG}} + \frac{[ATP]}{K'_{r,ATP}} \right)^{n-1}}{\left( 1 + \frac{[UDPG]}{K_{UDPG}} + \frac{[ATP]}{K'_{ATP}} \right)^n L_{0} \left( \frac{1 + \frac{[Glc6P]}{K_{t,Glc6P}} + \frac{[ATP]}{K_{t,ATP}} }{1 + \frac{[Glc6P]}{K_{r,Glc6P}} + \frac{[ATP]}{K_{r,ATP}} } \right)^n + \left( 1 + \frac{[UDPG]}{K_{UDPG}} + \frac{[ATP]}{K'_{r,ATP}} \right)^n }](/wiki/images/math/9/9/d/99de2ee8cfcb0a5850c32783c00922f0.png)
Parameter values
References
- ↑ Palm, D.C. (2013). The regulatory design of glycogen metabolism in mammalian skeletal muscle (Ph.D.). University of Stellenbosch