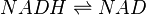Difference between revisions of "Dehydrogenase"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A '''dehydrogenase''' is an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme enzyme] that [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxidize oxidize]s a substrate by a reduction reaction that transfers one or more hydrides (H<sup>−</sup>) to an electron acceptor, usually Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD<sup>+</sup>/NADP. | A '''dehydrogenase''' is an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme enzyme] that [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxidize oxidize]s a substrate by a reduction reaction that transfers one or more hydrides (H<sup>−</sup>) to an electron acceptor, usually Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD<sup>+</sup>/NADP. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Chemical reaction== | ||
| + | <center><math> NADH \rightleftharpoons NAD </math></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Rate equation== | ||
| + | Reversible mass action rate law is used | ||