Difference between revisions of "Enolase"
(→Parameters with uncertainty) |
(→Parameters with uncertainty) |
||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<math>V_{mr}</math> | |<math>V_{mr}</math> | ||
| − | |0. | + | |<math>0.9 \pm 0.5</math> |
|<math> \text{mM min}^{-1} </math> | |<math> \text{mM min}^{-1} </math> | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 16:19, 29 April 2014
Enolase, also known as phosphopyruvate hydratase, catalysis the conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate (2-PG) to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). This is the penultimate step of glycolysis.
Contents
Chemical equation
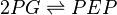
Rate equation
Mono-substrate reversible Michaelis-Menten equation is used. [1]
![\frac{V_{mf}\frac{[2PG]}{K_{2PG}}-V_{mr}\frac{[PEP]}{K_{PEP}}}{1 + \frac{[2PG]}{K_{2PG}} + \frac{[PEP]}{K_{PEP}}}](/wiki/images/math/6/a/9/6a9ca37a2fd76b4eb56a1e6a5cfb67d0.png)
Parameter values
| Parameter | Value | Units | Organism | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
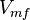
|
0.34 [2] | 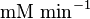
|
HeLa cell line | |
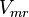
|
0.38[1] | 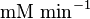
| ||
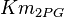
|
0.038[1] | mM | ||
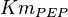
|
0.06[1] | mM |
Parameters with uncertainty
| Parameter | Value | Units | Organism | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
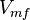
|
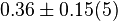 [2] [2]
|
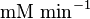
|
HeLa cell line | |
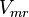
|
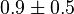
|
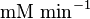
| ||
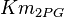
|
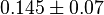
|
mM | ||
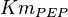
|
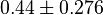
|
mM |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Marín-Hernández A, Gallardo-Pérez JC, Rodríguez-Enríquez S et al (2011) Modeling cancer glycolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1807:755–767 (doi)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Marín-Hernández A , Rodríguez-Enríquez S, Vital-González P A, et al. (2006). Determining and understanding the control of glycolysis in fast-growth tumor cells. Flux control by an over-expressed but strongly product-inhibited hexokinase. FEBS J., 273 , pp. 1975–1988(doi)