Difference between revisions of "Glycogen phosphorylase"
(→Parameter values) |
|||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
<br><br><br> | <br><br><br> | ||
| − | An alternative rate equation without considering the allosteric regulation is given as <ref name="Lambeth_2002> Lambeth M.J. & Kushmerick M.J. (2002). ''A computational model for glycogenolysis in skeletal muscle''. Ann Biomed Eng 30, 808–827</ref> | + | An alternative rate equation without considering the allosteric regulation is given as <ref name="Lambeth_2002"> Lambeth M.J. & Kushmerick M.J. (2002). ''A computational model for glycogenolysis in skeletal muscle''. Ann Biomed Eng 30, 808–827</ref> |
<center><math> \frac{V_{maxf} \frac{Glycogen_{n+1} \times Pi}{K_{iGlyf} \times K_{Pi}} -\frac{V_{maxf} \times K_{Glyb} \times K_{iGlc1P}}{K_{iGlyf} \times K_{Pi} \times Keq} \times \frac{Glycogen_n \times Glc1P}{K_{Glyb} \times K_{iGlc1P}} }{1 + \frac{Glycogen_{n+1}}{K_{iGlyf}} + \frac{Pi}{K_{iPi}} + \frac{Glycogen_n}{K_{iGlyb}} + \frac{Glc1P}{K_{iGlc1P}} \frac{Glycogen_{n+1} \times Pi}{K_{Glyf} \times K_{iPi}} + \frac{Glycogen_n \times Glc1P}{K_{Glyb} \times K_{iGlc1P}} } </math></center> | <center><math> \frac{V_{maxf} \frac{Glycogen_{n+1} \times Pi}{K_{iGlyf} \times K_{Pi}} -\frac{V_{maxf} \times K_{Glyb} \times K_{iGlc1P}}{K_{iGlyf} \times K_{Pi} \times Keq} \times \frac{Glycogen_n \times Glc1P}{K_{Glyb} \times K_{iGlc1P}} }{1 + \frac{Glycogen_{n+1}}{K_{iGlyf}} + \frac{Pi}{K_{iPi}} + \frac{Glycogen_n}{K_{iGlyb}} + \frac{Glc1P}{K_{iGlc1P}} \frac{Glycogen_{n+1} \times Pi}{K_{Glyf} \times K_{iPi}} + \frac{Glycogen_n \times Glc1P}{K_{Glyb} \times K_{iGlc1P}} } </math></center> | ||
| Line 105: | Line 105: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<math>K_{iGlyf}</math> | |<math>K_{iGlyf}</math> | ||
| − | |15<ref name="Lambeth_2002></ref> | + | |15<ref name="Lambeth_2002"></ref> |
|mM | |mM | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<math>K_{Pi}</math> | |<math>K_{Pi}</math> | ||
| − | |4 <ref name="Lambeth_2002></ref> | + | |4 <ref name="Lambeth_2002"></ref> |
|mM | |mM | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<math>K_{Glyb}</math> | |<math>K_{Glyb}</math> | ||
| − | |0.15 <ref name="Lambeth_2002></ref> | + | |0.15 <ref name="Lambeth_2002"></ref> |
|mM | |mM | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<math>K_{iGlc1P}</math> | |<math>K_{iGlc1P}</math> | ||
| − | |10.1 <ref name="Lambeth_2002></ref> | + | |10.1 <ref name="Lambeth_2002"></ref> |
|mM | |mM | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<math>K_{iPi}</math> | |<math>K_{iPi}</math> | ||
| − | |4.6 <ref name="Lambeth_2002></ref> | + | |4.6 <ref name="Lambeth_2002"></ref> |
|mM | |mM | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<math>K_{iGlyb}</math> | |<math>K_{iGlyb}</math> | ||
| − | |4.4 <ref name="Lambeth_2002></ref> | + | |4.4 <ref name="Lambeth_2002"></ref> |
|mM | |mM | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<math>K_{Glyf}</math> | |<math>K_{Glyf}</math> | ||
| − | |1.7 <ref name="Lambeth_2002></ref> | + | |1.7 <ref name="Lambeth_2002"></ref> |
|mM | |mM | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<math>Keq</math> | |<math>Keq</math> | ||
| − | |0.42 <ref name="Lambeth_2002></ref> | + | |0.42 <ref name="Lambeth_2002"></ref> |
|mM | |mM | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 12:12, 1 April 2014
Glycogen phosphorylase (GP) is a dimeric enzyme that catalyses the reaction in which the terminal glucose residue from a glycogen chain is phosphorylated and cleaved from the chain, releasing it as Glc1P.
Chemical equation
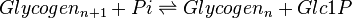
Rate equation
MWC model was used to formualte the rate law. [1]
![\frac{V_{max} \times n \times \frac{[Pi]}{K_{r,Pi}} \left( 1 + \frac{[Pi]}{K_{r,Pi}} + \frac{[Glc1P]}{K_{r,Glc1P}} \right)^{n-1} }{\left( 1 + \frac{[Pi]}{K_{r,Pi}} + \frac{[Glc1P]}{K_{r,Glc1P}} \right)^n + L_u \left( 1 + \frac{[Pi]}{K_{u,Pi}} + \frac{[Glc1P]}{K_{u,Glc1P}} \right)^n \left( \frac{1 + \frac{[Glc6P]}{K_{u,Glc6P}}}{1 + \frac{[AMP]}{K_{r,AMP}} + \frac{[Glc6P]}{K_{r,Glc6P}}} \right)^n } + \frac{V_{max} \times n \times \frac{[Pi]}{K_{r,Pi}} \left( 1 + \frac{[Pi]}{K_{r,Pi}} + \frac{[Glc1P]}{K_{r,Glc1P}} \right)^{n-1} }{\left( 1 + \frac{[Pi]}{K_{r,Pi}} + \frac{[Glc1P]}{K_{r,Glc1P}} \right)^n + L_t \left( 1 + \frac{[Pi]}{K_{t,Pi}} + \frac{[Glc1P]}{K_{t,Glc1P}} \right)^n \left( \frac{1 + \frac{[AMP]}{K_{t,AMP}} \frac{[Glc6P]}{K_{t,Glc6P}}}{1 + \frac{[AMP]}{K_{r,AMP}} + \frac{[Glc6P]}{K_{r,Glc6P}}} \right)^n \left( 1 + \frac{[ATP]}{K_{t,ATP}} \right)^n }](/wiki/images/math/7/e/5/7e599d4304d1f49ee3e3d2d32f556863.png)
An alternative rate equation without considering the allosteric regulation is given as [2]
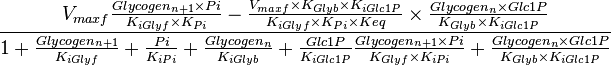
Parameter values
| Parameter | Value | Units | Organism | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
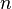
|
2 | Dimensionless | Recombinant, human muscle | |
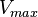
|
50 | 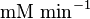
| ||
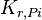
|
2.08 | mM | ||
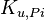
|
4.32 | mM | ||
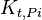
|
41.53 | mM | ||
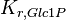
|
0.67 | mM | ||
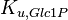
|
82.02 | mM | ||
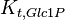
|
27.92 | mM | ||
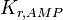
|
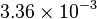
|
mM | ||
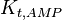
|
0.53 | mM | ||
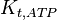
|
3.9 | mM | ||
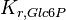
|
7.42 | mM | ||
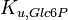
|
0.56 | mM | ||
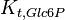
|
0.27 | mM | ||
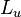
|
5.93 | Dimensionless | ||
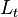
|
34741 | Dimensionless |
The parameter for the alternative equation are
| Parameter | Value | Units | Organism | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
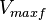
|
50 [1] | 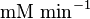
|
Rabbit | |
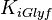
|
15[2] | mM | ||
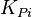
|
4 [2] | mM | ||
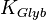
|
0.15 [2] | mM | ||
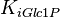
|
10.1 [2] | mM | ||
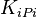
|
4.6 [2] | mM | ||
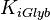
|
4.4 [2] | mM | ||
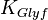
|
1.7 [2] | mM | ||
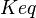
|
0.42 [2] | mM |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Palm, D.C. (2013). The regulatory design of glycogen metabolism in mammalian skeletal muscle (Ph.D.). University of Stellenbosch
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 Lambeth M.J. & Kushmerick M.J. (2002). A computational model for glycogenolysis in skeletal muscle. Ann Biomed Eng 30, 808–827