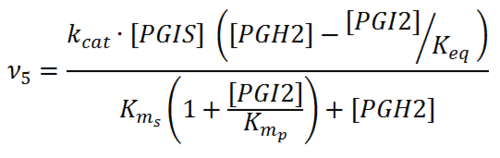Difference between revisions of "Transformation of PGH2 to PGI2"
(→Parameters) |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
==Chemical equation== | ==Chemical equation== | ||
| − | <center><math> | + | <center><math> PGH2 \rightleftharpoons PGI2 </math></center> |
== Rate equation == | == Rate equation == | ||
| + | [[File:R05.PNG|center|500px]] | ||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
Revision as of 15:16, 25 September 2017
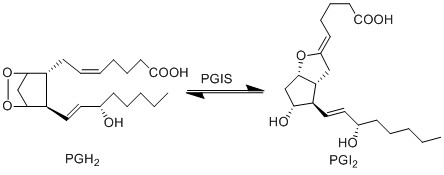
PGH2 is metabolised into the prostacyclin PGI2, by PGIS. This species has been associated with influencing the permeability of vascular compartment (Murata, Ushikubi et al. 1997). Similarly to the TX species, prostacyclins are only found in low concentration and are associated with infiltrating cells from the vascular compartment (Sugimoto, Arai et al. 2006).
Contents
Reaction
Chemical equation
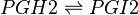
Rate equation
Parameters
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.33E-02 ± 1.40E-03 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Bovine Endothelial and Aorta Cells
Enzyme: Human PGIS pH:7.4 Temperature: 23 |
[1] |
| 9.00E-03 ± 5.00E-03 | 
|
Bovine | Expression Vector: Bovine Endothelial and Aorta Cells
Enzyme: Bovine PGIS pH:7.4 Temperature: 24 |
[2] |
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147 ± 45 | per minute | Cattle | Expression Vector: E. Coli
Enzyme: Bovine PGIS pH:7.4 Temperature: 24 |
[2] |
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 412 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Urinary bladder
Enzyme: PGIS pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
[3] |
| 206 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Lung
Enzyme: PGIS pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
[3] |
| 60.1 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Esophagus
Enzyme: PGIS pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
[3] |
| 9.93 | 
|
Human | Expression Vector: Oral Cavity
Enzyme: PGIS pH: 7.5 Temperature: 37 °C |
[4] |
| Value | Units | Species | Notes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.04 | kcal/mol | Not stated | Estimated
Enzyme: Transacylase Substrate: Product: pH: 7.3 ionic strength: 0.25 |
[5] |
References
- ↑ H. C. Yeh, P. Y. Hsu, Characterization of heme environment and mechanism of peroxide bond cleavage in human prostacyclin synthase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Dec 30;1738(1-3):121-32.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Hara S. , Isolation and molecular cloning of prostacyclin synthase from bovine endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):19897-903. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Hara1994" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 M. Kim A draft map of the human proteome Nature, 2014 509, 575–581
- ↑ M. Wilhelm Mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome Nature, 2014 509, 582–587
- ↑ Caspi et al 2014, "The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of Pathway/Genome Databases," Nucleic Acids Research 42:D459-D471