Difference between revisions of "Transformation of TXA2 to TXB2"
(→Parameters) |
(→Parameters) |
||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
|8 | |8 | ||
|<ref name="Ross1982”>[http://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/ja00370a035 A. Ross "Vinyl epoxide hydrolysis reactions" J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1982, 104 (6), pp 1658–1665]</ref> | |<ref name="Ross1982”>[http://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/ja00370a035 A. Ross "Vinyl epoxide hydrolysis reactions" J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1982, 104 (6), pp 1658–1665]</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2.25 ± 0.12 | ||
| + | | M-1 min-1 | ||
| + | | 25°C, in imidazole buffer and also in phosphate buffers, | ||
| + | | CO2 to H2CO3 | ||
| + | | <ref name="Gibbons1963”>[http://www.jbc.org/content/238/10/3502.full.pdf B. Gibbons "Rate of Hydration of Carbon Dioxide and Dehydration of Carbonic Acid at 25" J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3502-7]</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 09:55, 3 April 2017
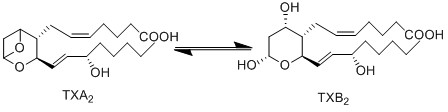
Thromboxane A2 is a bioactive molecule which affects vasoactivity and promotes thrombosis. It is unstable due to the epoxide functional group, and as a consequence has a short half-life of 20- 30 seconds. The hydrolysis reaction results in the generation of biologically inactive TXB2.
Contents
Reaction
Chemical equation
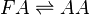
Rate equation
Parameters
| Value | Units | Conditions | Substrate | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.7e3 ± 0.1e3 | M-1 s-1 | NaCl04 (0.1 - 0.2 M)
Temperature: 25°C |
3 | [1] |
| 8.7e3 | M-1 s-1 | KCl (1 M)
Temperature: 25°C |
3 | [1] |
| 1.1e4 ± 0.1e4 | M-1 s-1 | NaCl04 (0.1 - 0.2 M)
Temperature: 25°C |
4 | [1] |
| 2.4 e4 | M-1 s-1 | KCl (1M)
Temperature: 25°C |
4 | [1] |
| 3.7e3 ± 0.1e3 | M-1 s-1 | NaCl04 (0.1 - 0.2 M)
Temperature: 25°C |
5 | [1] |
| 3.6 ± 0.2 | M-1 s-1 | NaCl04 (0.1 - 0.2 M)
Temperature: 25°C |
6 | [1] |
| 1.7 ± 0.1 | M-1 s-1 | NaCl04 (0.1 - 0.2 M)
Temperature: 25°C |
7 | [1] |
| 26.7 ± 0.9 | M-1 s-1 | NaCl04 (0.1 - 0.2 M)
Temperature: 25°C |
8 | [1] |
| 35 | M-1 s-1 | KCl (1M)
Temperature: 25°C |
8 | [1] |
| 2.25 ± 0.12 | M-1 min-1 | 25°C, in imidazole buffer and also in phosphate buffers, | CO2 to H2CO3 | [2] |
| Value | Units | Conditions | Substrate | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Units | Conditions | Substrate | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000038 | mM | Temperature: 35°C
Vector:Mosquito Note: "In solution, it undergoes rapid hydrolysis to form TXB2, a stable but physiologically inactive compound." - therefore they used stable analogues. |
carbocyclic TXA2 (analogue of TXA2) | [3] |
| 0.00000023 | mM | Temperature: 35°C
Vector:Rabbit cultured astrocytes Note: "In solution, it undergoes rapid hydrolysis to form TXB2, a stable but physiologically inactive compound." - therefore they used stable analogues. |
[3H]IONO NT-126, a TXA z antagonist, | [4] |
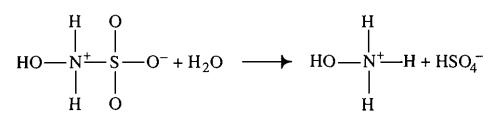
| 1500 ± 500 | mM | Temperature: 25°C
In vitro |
Hydroxysulfamic acid | [5] |
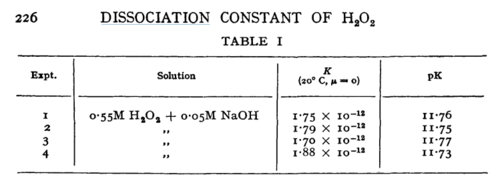
| N/A | Temperature: 20°C
In vitro |
H2O2 | [5] | |
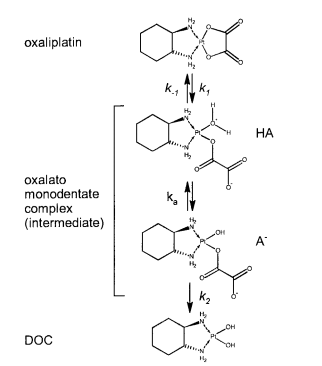
| 5.9 E-8 | N/A | Oxaliplatin | [6] |
Related Reactions
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 A. Ross "Vinyl epoxide hydrolysis reactions" J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1982, 104 (6), pp 1658–1665
- ↑ B. Gibbons "Rate of Hydration of Carbon Dioxide and Dehydration of Carbonic Acid at 25" J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3502-7
- ↑ P. H. Alvarenga "The Function and Three-Dimensional Structure of a Thromboxane A2/Cysteinyl Leukotriene-Binding Protein from the Saliva of a Mosquito Vector of the Malaria Parasite" PLoS Biol. 2010 Nov 30;8(11):e1000547. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000547.
- ↑ N Nakahata et al. "The Presence of Thromboxane A2 Receptors in Cultured Astrocytes From Rabbit Brain" Brain Res 583 (1-2), 100-104. 1992 Jun 26
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 D. LITTLEJOHN "The dissociation constant and acid hydrolysis rate of hydroxysulfamic acid" Can. J. Chem. 67, 1596 (1989). Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Littlejohn1989.E2.80.9D" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Elin Jerremalm "Hydrolysis of Oxaliplatin—Evaluation of the Acid Dissociation Constant for the Oxalato Monodentate Complex" Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Volume 92, Issue 2, February 2003, Pages 436–438