Difference between revisions of "Dephosphorylation"
m |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
<h2> Kinetic equation </h2> | <h2> Kinetic equation </h2> | ||
| − | <center><math>\frac{v_{max} \cdot [\text{phosphorylated-enzyme}] \cdot (1-\frac{[\text{unphosphorylated-enzyme}]}{[\text{phosphorylated-enzyme}] \cdot K_{eq}})}{1 + \frac{[\text{phosphorylated-enzyme}]}{Km_{\text{phosphorylated-enzyme}}} | + | <center><math>v_{dephosphorylation} = \frac{v_{max} \cdot [\text{phosphorylated-enzyme}] \cdot (1-\frac{[\text{unphosphorylated-enzyme}]}{[\text{phosphorylated-enzyme}] \cdot K_{eq}})}{Km_{\text{phosphorylated-enzyme}} \cdot (1 + \frac{[\text{phosphorylated-enzyme}]}{Km_{\text{phosphorylated-enzyme}}} + \frac{[\text{unphosphorylated-enzyme}]}{Km_{\text{unphosphorylated-enzyme}}})}</math></center> |
| + | |||
| + | <h2>General Information</h2> | ||
| + | The most enzymes in the MAP-Kinase signaling pathway are activated by phosphorylation. The inactivation is therefore due to a dephosphorylation step. The amino acids that are phosphorylated are tyrosine, serine, threonine, so the three main dephosphatases address phosphate residues at these side chains. In BRENDA there are several values measured, for the Km and vmax value. In contrast to the reactions in which the enyzme that catalyses the reaction appears also as substrate in the model the concentration of the dephosphatases is assumed to be constant and therefore the v<sub>max</sub> value instead or the k<sub>cat</sub> value is used. Because of the reason that it is not clear which dephoshpatase is mainly responsible for the inactivation an average of all measured dephosphatase values is used in our model as K<sub>m</sub> and as k<sub>cat</sub> the ones used by Xu et al (2010)<ref name="Xu2010"> Tian-Rui Xu et al. (2010) "Inferring signaling pathway topologies from multiple perturbation measurements of specific biochemical species." ''Sci Signal''. 3(134):ra20. ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20234003 pmid:20234003])</ref> are used and the standard deviation is calculated by assuming the same averaged relative error as for the measured values.([[Calculation of the averaged relative error]]). | ||
<h2>final Parameter </h2> | <h2>final Parameter </h2> | ||
| − | <math>v_{max} = | + | <math>v_{max}(BRaf-Inactivation) = 7.59316 \pm 0.78935\ \frac{mol}{s} </math> |
| + | |||
| + | <math>v_{max}(C3G-Inactivation) = 2109.86 \pm 219.33\ \frac{mol}{s} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>v_{max}(Mek-Inactivation) = 632.512 \pm 65.753 \ \frac{mol}{s} </math> | ||
| − | <math>K_{m} = 3.83 \cdot 10^{ | + | <math>v_{max}(Raf1-Inactivation) = 13119.7 \pm 1363.9\ \frac{mol}{s} </math> |
| + | |||
| + | <math>K_{m} = 3.83 \cdot 10^{3} \pm 1.40 \cdot 10^{2}\ \mu M </math> | ||
<h2> Parameter</h2> | <h2> Parameter</h2> | ||
| Line 31: | Line 40: | ||
<th>EC 3.1.3.16 - <br/>phosphoprotein phosphatase</th> | <th>EC 3.1.3.16 - <br/>phosphoprotein phosphatase</th> | ||
<th>EC 3.1.3.48 - <br/>protein-tyrosine phosphatase</th> | <th>EC 3.1.3.48 - <br/>protein-tyrosine phosphatase</th> | ||
| + | <th>average</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 43: | Line 53: | ||
<td align="right">7.43</td> | <td align="right">7.43</td> | ||
<td align="right">3.31</td> | <td align="right">3.31</td> | ||
| + | <td align="right">3.83 mM</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 49: | Line 60: | ||
<td align="right">27.74</td> | <td align="right">27.74</td> | ||
<td align="right">12.90</td> | <td align="right">12.90</td> | ||
| + | <td align="right">1.40 mM</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<!-- <tr> | <!-- <tr> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<td>'''turnover number [1/s]'''</td> | <td>'''turnover number [1/s]'''</td> | ||
<td></td> | <td></td> | ||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
<td align="right">1.09 * 10<sup>2</sup></td> | <td align="right">1.09 * 10<sup>2</sup></td> | ||
<td align="right">67.8</td> | <td align="right">67.8</td> | ||
| + | <td align="right">1.13 * 10<sup>2</sup> 1/s</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 79: | Line 80: | ||
<td align="right">210.26</td> | <td align="right">210.26</td> | ||
<td align="right">256.88</td> | <td align="right">256.88</td> | ||
| − | + | <td align="right">3.09 * 10<sup>2</sup> 1/s</td> | |
| − | + | </tr>--> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | <td align="right"> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | </tr> --> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2>Screenshots of the BRENDA database </h2> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''<u>[http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=3.1.3.3 3.1.3.3-phosphoserine phosphatase]</u>''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery mode="nolines"> | ||
| + | File:L 3.1.3.3-phosphoserine phosphatase.png|3.1.3.3-phosphoserine phosphatase | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''<u>[http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=3.1.3.16 3.1.3.16-phosphoprotein phosphatase] </u>''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery mode="nolines"> | ||
| + | File:L 3.1.3.16-phosphoprotein phosphatase Km.png|3.1.3.16-phosphoprotein phosphatase Km | ||
| + | <!--File:L 3.1.3.16-phosphoprotein phosphatase vmax.png|3.1.3.16-phosphoprotein phosphatase vmax--> | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''<u>[http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=3.1.3.48 3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase] </u>''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''K<sub>m</sub>''' | ||
| + | <gallery mode="nolines"> | ||
| + | File:L 3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase 1.png|3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase Km1 | ||
| + | File:L 3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase 2.png|3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase Km2 | ||
| + | File:L 3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase 3.png|3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase Km3 | ||
| + | File:3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase 4.png|3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase Km4 | ||
| + | File:L 3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase 5.png|3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase Km5 | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | <!-- | ||
| + | '''v<sub>max</sub>''' | ||
| + | <gallery mode="nolines"> | ||
| + | File:L 3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase vmax 1.png|3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase vmax1 | ||
| + | File:L 3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase vmax 2.png|3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase vmax2 | ||
| + | File:L 3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase vmax 3.png|3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase vmax3 | ||
| + | File:L 3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase vmax 4.png|3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase vmax4 | ||
| + | File:L 3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase vmax 5.png|3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase vmax5 | ||
| + | </gallery>--> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2>Km<sub>P</sub> value and equilibrium constant </h2> | ||
| + | The K<sub>m</sub> value for the product is assumed to be similar to but slightly smaller than the the K<sub>m</sub> value of the substrate because of the similarity of the both species. Therefore the K<sub>m</sub> value of the substrate is multiplied by 0.95 to gain the one of the product and the uncertainty is increased by increasing the error on Km<sub>substrate</sub> by 50%. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For information about the equilibrium constant please see [[Equilibrium_constants|here]]. | ||
Latest revision as of 10:04, 12 June 2014
Binding Reaction
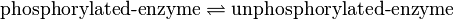
Kinetic equation
![v_{dephosphorylation} = \frac{v_{max} \cdot [\text{phosphorylated-enzyme}] \cdot (1-\frac{[\text{unphosphorylated-enzyme}]}{[\text{phosphorylated-enzyme}] \cdot K_{eq}})}{Km_{\text{phosphorylated-enzyme}} \cdot (1 + \frac{[\text{phosphorylated-enzyme}]}{Km_{\text{phosphorylated-enzyme}}} + \frac{[\text{unphosphorylated-enzyme}]}{Km_{\text{unphosphorylated-enzyme}}})}](/wiki/images/math/7/3/7/73747490b1be1622e749413aeb665ac8.png)
General Information
The most enzymes in the MAP-Kinase signaling pathway are activated by phosphorylation. The inactivation is therefore due to a dephosphorylation step. The amino acids that are phosphorylated are tyrosine, serine, threonine, so the three main dephosphatases address phosphate residues at these side chains. In BRENDA there are several values measured, for the Km and vmax value. In contrast to the reactions in which the enyzme that catalyses the reaction appears also as substrate in the model the concentration of the dephosphatases is assumed to be constant and therefore the vmax value instead or the kcat value is used. Because of the reason that it is not clear which dephoshpatase is mainly responsible for the inactivation an average of all measured dephosphatase values is used in our model as Km and as kcat the ones used by Xu et al (2010)[1] are used and the standard deviation is calculated by assuming the same averaged relative error as for the measured values.(Calculation of the averaged relative error).
final Parameter
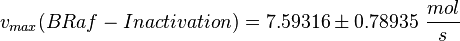
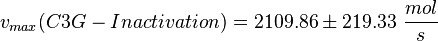
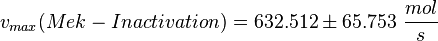
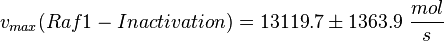
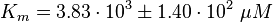
Parameter
| Notes | Data | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| There are three main deophosphatases, phosphoserine phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.3), phosphoprotein phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.16), protein-tyrosine phosphatase (3.1.3.48). The data available in BRENDA is used to calculate the average and standard deviation. |
|
Screenshots of the BRENDA database
3.1.3.3-phosphoserine phosphatase
3.1.3.16-phosphoprotein phosphatase
3.1.3.48 protein-tyrosine-phosphatase
Km
KmP value and equilibrium constant
The Km value for the product is assumed to be similar to but slightly smaller than the the Km value of the substrate because of the similarity of the both species. Therefore the Km value of the substrate is multiplied by 0.95 to gain the one of the product and the uncertainty is increased by increasing the error on Kmsubstrate by 50%.
For information about the equilibrium constant please see here.- ↑ Tian-Rui Xu et al. (2010) "Inferring signaling pathway topologies from multiple perturbation measurements of specific biochemical species." Sci Signal. 3(134):ra20. (pmid:20234003)