Synthesis of C
SCB (C) is synthesized by glycerol derivative and b-keto acid derivative precursors in a reaction catalyzed by ScbA (A).
Contents
Chemical equation
Rate equation
In our model we assume that there is an infinite amount of substrate S for the SCB synthesis and that the rate of the reaction is dependent only on the concentration of the catalyst A. Therefore, the rate of the reaction is:
![r= K_{C}\cdot [A]](/wiki/images/math/d/7/9/d796407593b5d6ed432d122e52d6a2a1.png)
Parameters
The parameter of this reaction is the synthesis rate of SCB (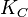 ). The parameter values were chosen with the assumption that GBL production involves a one rate
limiting step involving the Afsa-like protein and then a spontaneous cyclization.
). The parameter values were chosen with the assumption that GBL production involves a one rate
limiting step involving the Afsa-like protein and then a spontaneous cyclization.
| Name | Value | Units | Value in previous GBL models [1] [2] | Remarks-Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
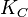
|
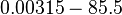 [3] [4] [5] [6] [3] [4] [5] [6]
|
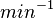
|
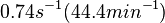
Range tested: ( Bistability range: ( and ( |
Chen et al. calculated a synthesis rate of 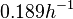 ( (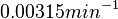 ) for the autoinducer PAI2 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa at stationary phase, by subtracting the ) for the autoinducer PAI2 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa at stationary phase, by subtracting the 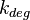 from the net decay constant ( from the net decay constant (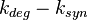 ). ).
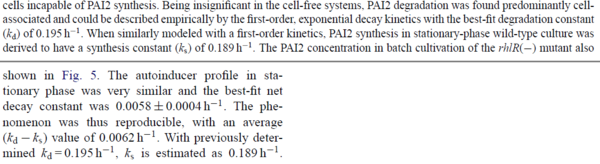 Chen et al. 2005[5] Additionally, Garcia-Ojalvo et al. modelled repressilators coupled by quorum sensing and reported a value for the synthesis rate of Acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) in E. coli of Garcia-Ojalvo et al. 2004[4] Finally, Parsek et al. reported a range of values for the 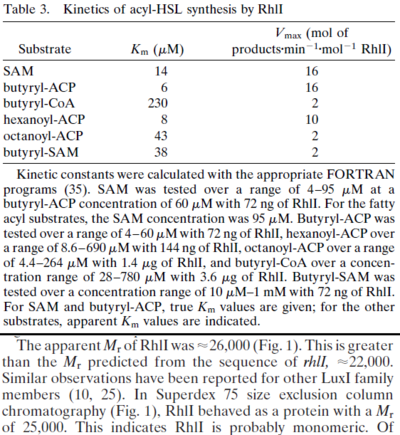 Parsek et al. 1999[6] |
Parameters with uncertainty
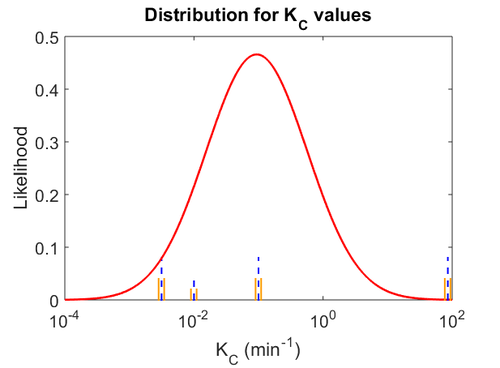
When deciding how to describe the uncertainty for each parameter we must take into consideration that the reported values are either calculated or derived with approximation from experiments. Additionally, they correspond to synthesis rates of autoinducers in other bacteria (E. coli, P. aeruginosa) and not to butyrolactones. This means that there might be a notable difference between actual parameter values and the ones reported in literature. These facts influence the quantification of the parameter uncertainty and therefore the shape of the corresponding distributions. By assigning the appropriate weights to the parameter values and using the method described here, the appropriate probability distribution was designed.
Therefore, the weight of the distribution is kept at 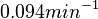 which is set as the mode of the log-normal distribution for
which is set as the mode of the log-normal distribution for 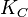 and the Spread is set to
and the Spread is set to 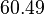 . In this way, the range where 68.27% of the values are found is between
. In this way, the range where 68.27% of the values are found is between 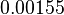 and
and 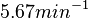 .
.
The probability distribution for the parameter, adjusted accordingly in order to reflect the above values, is the following:
The parameter information of the distribution is:
| Parameter | Mode | Spread | μ | σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
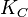
|
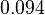
|
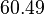
|
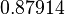
|
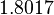
|
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 S. Mehra, S. Charaniya, E. Takano, and W.-S. Hu. A bistable gene switch for antibiotic biosynthesis: The butyrolactone regulon in streptomyces coelicolor. PLoS ONE, 3(7), 2008.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 A. Chatterjee, L. Drews, S. Mehra, E. Takano, Y.N. Kaznessis, and W.-S. Hu. Convergent transcription in the butyrolactone regulon in streptomyces coelicolor confers a bistable genetic switch for antibiotic biosynthesis. PLoS ONE, 6(7), 2011.
- ↑ Schaefer AL, Val DL, Hanzelka BL, Cronan JE, Greenberg EP. Generation of cell-to-cell signals in quorum sensing: acyl homoserine lactone synthase activity of a purified Vibrio fischeri LuxI protein. PNAS 1996;93(18):9505-9509.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 J.Garcia-Ojalvo, M. B. Elowitz, and S. H. Strogatz. Modeling a synthetic multicellular clock: Repressilators coupled by quorum sensing. PNAS 2004;101(30):10955-10960; published ahead of print July 15, 2004.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Chun-Chiang Chen, Lieke Riadi, Sang-Jin Suh, Dennis E. Ohman, and Lu-Kwang Ju. Degradation and synthesis kinetics of quorum-sensing autoinducer in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultivation. J. Biotechnol. 2005; 117:1-10.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Parsek MR, Val DL, Hanzelka BL, Cronan JE, Greenberg EP. Acyl homoserine-lactone quorum-sensing signal generation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1999;96(8):4360-4365.


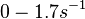
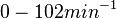 )
)
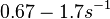
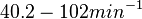 )
)
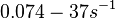
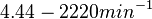 )
)
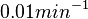 .
.
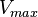 of AHL in E. coli between 2 and 16 (mol of products
of AHL in E. coli between 2 and 16 (mol of products  RhlI). By using the enzyme concentration and
RhlI). By using the enzyme concentration and 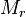 , the
, the 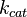 of the AHL synthesis can be calculated (
of the AHL synthesis can be calculated (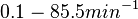 ).
).